Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
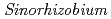 with
with 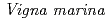 under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding
under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding丸山 雄大*; 武田 喜代子*; 友岡 憲彦*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 99, 2016/02
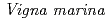 is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants.
is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants. 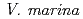 can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on
can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on 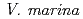 have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus
have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus 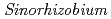 having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45
having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45  C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however,
C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however, 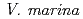 cannot develop root nodules with
cannot develop root nodules with 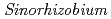 at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of
at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of 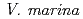 with
with 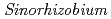 under high salt conditions,
under high salt conditions, 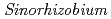 bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 120, 2015/03
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a viability loss of beneficial microorganisms in biofertilizers by high temperature stress during both storage and transportation. Therefore, we have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42
USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42  C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
佐藤 喬*; 久米 民和; 平田 熙*
日本土壌肥料学雑誌, 69(1), p.62 - 72, 1998/00
VA菌根菌(Vesicular-Arbuscular Mycorshizal Fungi,VAMF)の感染によるダイズの生育と根粒活性の反応を、 線殺菌処理(15kGy)した黒ボク土の施肥リンレベルを変えて検討した。生育、リン・窒素吸収、根粒活性(アセチレン還元活性)及び固定窒素に対するVAMF感染効果は、低リンレベルほどかつ生育初期ほど高かった。結実期の生育とくに根粒重の増加や、莢実・根粒へのリン・窒素の集積が、VAMFの感染により高まった。遮光処理下でのVAMF感染効果について、播種後25日目(開花前)から約50%遮光下で検討した結果、結実期の生育とリン吸収、固定窒素などが顕著に高まり、特に莢実と根粒内リン濃度の増大にVAMF感染が効果的であった。
線殺菌処理(15kGy)した黒ボク土の施肥リンレベルを変えて検討した。生育、リン・窒素吸収、根粒活性(アセチレン還元活性)及び固定窒素に対するVAMF感染効果は、低リンレベルほどかつ生育初期ほど高かった。結実期の生育とくに根粒重の増加や、莢実・根粒へのリン・窒素の集積が、VAMFの感染により高まった。遮光処理下でのVAMF感染効果について、播種後25日目(開花前)から約50%遮光下で検討した結果、結実期の生育とリン吸収、固定窒素などが顕著に高まり、特に莢実と根粒内リン濃度の増大にVAMF感染が効果的であった。
武田 喜代子*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
現在、化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では根粒菌を用いたバイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。これまで我々は、ダイズ根粒菌の優良接種菌株である USDA110株を対象とした、イオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42
USDA110株を対象とした、イオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42 CのYM液体培地内で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を保つことができる高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によって高温耐性変異株において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。
CのYM液体培地内で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を保つことができる高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によって高温耐性変異株において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。
佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子*; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
根粒菌はマメ科植物と共生し、窒素栄養をマメ科植物に供給する。現在、化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では、この共生関係を生かした根粒菌バイオ肥料の利用が奨励されている。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、バイオ肥料は、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。これまで我々は、ダイズ根粒菌の温帯優良接種菌株である USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42
USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42 Cの液体培地中で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を維持することが可能な高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によってDNA変異部位を同定した。ゲノムDNA塩基配列の比較解析の結果、高温耐性変異株M14において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異がM14株の高温耐性に関与している可能性が考えられた。
Cの液体培地中で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を維持することが可能な高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によってDNA変異部位を同定した。ゲノムDNA塩基配列の比較解析の結果、高温耐性変異株M14において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異がM14株の高温耐性に関与している可能性が考えられた。