Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Hydrometallurgy, 199, p.105539_1 - 105539_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.21(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The synergistic solvent extraction of lanthanide(III) with mixtures of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA, A) and monoisodecyl phosphoric acid (MIDPA, B) in phosphonium-based ionic liquid was investigated. In the case of D2EHPA or MIDPA single extractant system, Ln(III) (Ln = Pr and Nd) was extracted as [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (
HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (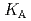 ,
, 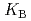 and
and 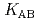 ) and the formation constants (
) and the formation constants (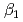 ,
, 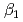 and
and 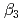 ), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA
), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA B
B or [DyHA
or [DyHA B
B ] was more stable than [LnA
] was more stable than [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
Kurata, Masaki; Shirasu, Noriko; Kawakami, Kazuto*
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on Reactor Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2015) (Internet), p.139 - 156, 2015/09
Thermodynamic database is a useful tool for evaluating preliminary chemical reactions during molten core concrete interaction and phase relations in fuel debris. Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Nippon Steel Sumitomo Metal Corporation are collaborating to develop an open thermodynamic database by combining their own nuclear- and steel/slag-databases. The phase diagrams of Al O
O -UO
-UO , Al
, Al O
O -ZrO
-ZrO , SiO
, SiO -UO
-UO , and UO
, and UO -ZrO
-ZrO sub-systems and those of Al
sub-systems and those of Al O
O -UO
-UO , SiO
, SiO -UO
-UO , and Al
, and Al O
O -ZrO
-ZrO sub-systems were able to be drawn properly using the cell model parameters and the sub-lattice model parameters assessed in the present study, respectively. The concerns for improving accuracy on the assessment were extracted in several sub-systems.
sub-systems were able to be drawn properly using the cell model parameters and the sub-lattice model parameters assessed in the present study, respectively. The concerns for improving accuracy on the assessment were extracted in several sub-systems.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Minase, Naofumi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.150 - 155, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-031, 131 Pages, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Savage, D.*; Lemke, K.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Shibata, Masahiro; Arthur, R. C,*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 2000-004, 30 Pages, 2000/01
Modeling approaches that have been proposed for cement-water system are reviewed in this report, and relevant supporting thsrmodynamic data are compiled. The thermodynamic data include standard molal thermodynamic properties of minerals and related compounds comprising cements, and equilibrium constants for associated hydrolysis reactions. Similar data for minerals that are stable in hyperalkaline geologic environments (e.g., zeolites) are also included because these minerals could be formed as hyperalkaline fluids emanating from cementitious matelials in a repository for radioactive wastes interact with the surrounding host rock. Standard molal properties (i.e., standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation and standard molal entropies), and/or equilibrium constants for associated hydrolysis reactions, are included for. (1)cement minerals and related compounds (Reardon, 1992; Glasser et al., 1999) (2)calcium-silicate hydrate minerals (Sarkar et al., 1982), and (3)zeolites (calorimetric and estimated values from various sources) All these data are accepted at face value, and it is therefore cautioned that the data, considered as a whole, may not be internally consistent. It is also important to note that the accuracy of these data have not been evaluated in the present study. Several models appropriate for cement-water systems have been proposed in recent years. Most are similar in the sense that they represent empirical fits to laboratory data for the CSH gel-water system, and therefore not thermodynamically defensible. An alternative modeling approach based on thermodynamic principles of solid-solution behavior appropriate for CSH gel has recently been proposed, however. It is reviewed in the present study, and evaluated in relation to experimental results obtained by JNC on cement-water interactions. The solid-solution model is based upon a thermodynamically- and structually-justifiable description of CSH gel in terms of a non-ideal ...
Yui, Mikazu; ; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-070, 106 Pages, 1999/11
This report is a summary of status, frozen datasets, and future tasks of the JNC thermodynamic database (JNC-TDB) for assessing performance of high-level radioactive waste in geological environments. The JNC-TDB development was carried out after the first progress report on geological disposal research in Japan (H3). In the development, thermodynamic data (equilibrium constants at 25  C, I=0) for important radioactive elements were selected/determined based on original experimental data using different models (e.g., SIT, Pitzer). As a result, the reliability and traceability of the data for most of the important elements were improved over those of the PNC-TDB used in H-3 report. For detailed information of data analysis and selections for each element, see the JNC technical reports listed in this document.
C, I=0) for important radioactive elements were selected/determined based on original experimental data using different models (e.g., SIT, Pitzer). As a result, the reliability and traceability of the data for most of the important elements were improved over those of the PNC-TDB used in H-3 report. For detailed information of data analysis and selections for each element, see the JNC technical reports listed in this document.
Oda, Chie; Arthur, R. C,*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Shibata, Masahiro; Yui, Mikazu; Neyama, Atsushi*
JNC TN8400 99-079, 287 Pages, 1999/09
Two thermodynamic databases for geochemical calculations supporting research and development on geological disposal concepts for high level radioactive waste are described in this report. One, SPRONS.JNC, is compatible with thermodynamic relations comprising the SUPCRT model and software, which permits calculation of the standard molal and partial molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species and reactions from 1 to 5000 bars and 0 to 1000 C. This database includes standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard molal entropies and volumes, and Maier-Kelly heat capacity coefficients at the reference pressure (1 bar) and temperature (25
C. This database includes standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard molal entropies and volumes, and Maier-Kelly heat capacity coefficients at the reference pressure (1 bar) and temperature (25 C) for 195 minerals and 16 gases. It also includes standard partial molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard partial molal entropies, and Helgeson, Kirkham and Flowers (HKF) equation-of-state coefficients at the reference pressure and temperature for 1147 inorganic and organic aqueous ions and complexes. SPRONS.JNC extends similar databases described elsewhere by incorporating new and revised data published in the peer-reviewed literature since 1991. The other database, PHREEQE.JNC, is compatible with the PHREEQE series of geochemical modeling codes. It includes equilibrium constants at 25
C) for 195 minerals and 16 gases. It also includes standard partial molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard partial molal entropies, and Helgeson, Kirkham and Flowers (HKF) equation-of-state coefficients at the reference pressure and temperature for 1147 inorganic and organic aqueous ions and complexes. SPRONS.JNC extends similar databases described elsewhere by incorporating new and revised data published in the peer-reviewed literature since 1991. The other database, PHREEQE.JNC, is compatible with the PHREEQE series of geochemical modeling codes. It includes equilibrium constants at 25 C and 1 bar for mineral-dissolution, gas-solubility, aqueous-association and oxidation-reduction reactions. Reaction enthalpies, or coefficients in an empirical log K(T) function, are also included in this database, which permits calculation of equilibrium constants between 0 and 100
C and 1 bar for mineral-dissolution, gas-solubility, aqueous-association and oxidation-reduction reactions. Reaction enthalpies, or coefficients in an empirical log K(T) function, are also included in this database, which permits calculation of equilibrium constants between 0 and 100 C at 1 bar. All equilibrium constants, reaction enthalpies, and logK(T) coefficients in PHREEQE.JNC are calculated usig SUPCRT and SPRONS.JNC, which ensures that these two databases are mutually consistent. They are also internally consistent insofar as all the data are compatible with basic thermodynamic definitions and functional relations in the SUPCRT ...
C at 1 bar. All equilibrium constants, reaction enthalpies, and logK(T) coefficients in PHREEQE.JNC are calculated usig SUPCRT and SPRONS.JNC, which ensures that these two databases are mutually consistent. They are also internally consistent insofar as all the data are compatible with basic thermodynamic definitions and functional relations in the SUPCRT ...
Takeda, Seiji
JAERI-Research 99-047, 71 Pages, 1999/08
no abstracts in English

 and AnO
and AnO
 Species in Geologic Environments
Species in Geologic EnvironmentsChoppin, G. R.*; Bronikowski, M.*; Chen, J.*; Byegard, J.*; Rai, D.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-012, 155 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of pentavalent and hexavalent actinide species (AnO and AnO
and AnO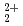 ) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO
) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO and AnO
and AnO
 , redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
, redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
Lothenbach, B.*; Ochs, M.*; Wanner, H.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-011, 340 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of palladium Pd, lead Pb, tin Sn, antimony Sb, niobium Nb and bismuth Bi in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system of high-level radioactive wastes. Besides treating hydrolysis in detail, this report focuses on the formation of complexes or compounds with chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate. Other important inorganic ligands (sulfide for lead and antimony, ammonia for palladium) are also included. In this study, the specific ion interaction theory (SIT) approach is used to extrapolate thermodynamic constants to zero ionic strength at 25 C.
C.
Rai, D.*; Rao, L.*; Weger, H. T.*; GREGORY R.CHOPPI*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-010, 95 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of Pu(III), Am(III), and Cm(III) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. Where data for specific actinide(III) species are lacking, the data were selected based on chemical analogy to other trivalent actinides. In this study, the Pitzer ion-interaction model is mainly used to extrapolate thermodynamic constants to zero ionic strength at 25 C.
C.
Rai, D.*; Rao, L.*; Weger, H. T.*; Felmy, A. R.*; Choppin, G. R.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-009, 115 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of Th(IV), U(IV), Np(IV), and Pu(IV) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. Where data for specific actinide(IV) species was lacking, the data were selected based on chemical analogy to other tetravalent actinides. ln this study, the Pitzer ion-interaction model is used to extrapolate thermodynamic constants to zero ionic strength at 25 C.
C.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Takeda, Seiji
JAERI-Data/Code 99-001, 74 Pages, 1999/01
no abstracts in English
Oda, Chie;
JNC TN8400 98-001, 14 Pages, 1998/11
Solubilities of amorphous stannic oxide, SnO (am) in Na-ClO
(am) in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH
aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH , Cl
, Cl and SO
and SO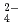 on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl
on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl , SO
, SO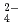 concentrations were observed in Na-ClO
concentrations were observed in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO
aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO (am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
(am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
Nakayama, Shinichi
KURRI-KR-17, p.1 - 14, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji;
Hoshasei Haikibutsu Kenkyu, 3(1), p.49 - 61, 1996/08
no abstracts in English
Kurata, Masaki; Nakamura, Kinya*; Tanaka, Masahiro*; Koyama, Toshiyuki*; Takaki, Tomohiro*; Tokunaga, Tatsuya*; Nanko, Makoto*
no journal, ,
The outline and the present status of METI project entitled Advanced Multi-scale Modeling and Experimental Tests on Fuel Degradation in Severe Accident Condition are overviewed.