Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takei, Hayanori; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Meigo, Shinichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(5), p.588 - 603, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has designed a Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) as an experimental facility in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The TEF-P is a critical assembly driven by a low-power proton beam, a maximum of 10 W, which is extracted from a high-power beam source, such as 250 kW of 400 MeV proton beam of the J-PARC Linac. To extract such a low-power proton beam from the high-power proton beam, we developed a laser charge exchange (LCE) device and employed its technique, which is one of the non-contact beam extraction techniques. For the proof of performance of the LCE device to the TEF-P, a low-power proton beam was extracted using a negative-hydrogen (H ) Linac having an energy of 3 MeV, and a bright continuous laser. Proton beam with the power of 0.57 mW was successfully extracted with a laser stripping efficiency of
) Linac having an energy of 3 MeV, and a bright continuous laser. Proton beam with the power of 0.57 mW was successfully extracted with a laser stripping efficiency of 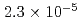 . These experimental values are in good agreement with the estimated ones.
. These experimental values are in good agreement with the estimated ones.
Koyanagi, Yoshihiko*; Ueta, Shigeki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Cho, K.*; Yasuda, Hiroyuki*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 773, p.138822_1 - 138822_11, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.45(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Tamakuma, Yuki*; Yamada, Ryohei; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Kuroki, Tomohiro*; Mizuno, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Koji*; Furukawa, Masahide*; Tokonami, Shinji*
Perspectives in Science (Internet), 12, p.100414_1 - 100414_4, 2019/09
In this study, a portable radioactive plume monitor using a silicon photodiode was developed for the detection of a radioactive plume (e.g.  I,
I,  Cs and
Cs and  Cs) in an emergency situation. It was found that the background count rate was proportional to ambient dose equivalent rate and the detection limit for the monitor at 20
Cs) in an emergency situation. It was found that the background count rate was proportional to ambient dose equivalent rate and the detection limit for the monitor at 20  Sv h
Sv h as an ambient dose equivalent rate was evaluated to be 187 Bq m
as an ambient dose equivalent rate was evaluated to be 187 Bq m using the ISO11929 method. These results suggest that the detection limit for the system can be decreased effectively by lead shielding with optimized thickness.
using the ISO11929 method. These results suggest that the detection limit for the system can be decreased effectively by lead shielding with optimized thickness.
Matsukawa, Shun*; Itakura, Kenichi*; Hayano, Akira; Suzuki, Yukinori*
Journal of MMIJ, 133(11), p.256 - 263, 2017/11
LIDAR detects a rock mass surface configurations as a point cloud. DiAna (Discontinuity Analysis) is a Matlab tool which was developed for geo-structural analysis of rock mass discontinuities. DiAna segments a point cloud into bounding boxes to estimate the surface of a rock mass. However, an expert's skills necessary to determine the appropriate size of the bounding boxes for DiAna. We developed the VBS (Variable-Box Segmentation) algorithm to determine the appropriate box size depending on the location of the point cloud and to estimate the surface of a rock mass. The performance of the VBS algorithms was evaluated by comparison with the DiAna algorithm. The results of comparison showed that the VBS algorithm estimated planes more accurately for the reference planes than the DiAna algorithm. Therefore, the VBS algorithm determines appropriate box sizes automatically depending on the location of the point cloud and estimates the surface appropriately.
Kuwagaki, Kazuki*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-007, 27 Pages, 2017/03
The integral benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 for U-233 systems using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP was conducted. The previous benchmark test was performed only for U-233 thermal solution and fast metallic systems in the ICSBEP handbook. In this study, MVP input files were prepared for uninvestigated benchmark problems in the handbook including compound thermal systems (mainly lattice systems) and integral benchmark test was performed. The prediction accuracy of JENDL-4.0 was evaluated for effective multiplication factors (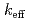 's) of the U-233 systems. As a result, a trend of underestimation was observed for all the categories of U-233 systems. In the benchmark test of ENDF/B-VII.1 for U-233 systems with the ICSBEP handbook, it is reported that a decreasing trend of calculated
's) of the U-233 systems. As a result, a trend of underestimation was observed for all the categories of U-233 systems. In the benchmark test of ENDF/B-VII.1 for U-233 systems with the ICSBEP handbook, it is reported that a decreasing trend of calculated 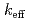 values in association with a parameter ATFF (Above-Thermal Fission Fraction) is observed. The ATFF values were also calculated in this benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 and the same trend as ENDF/B-VII.1 was observed.
values in association with a parameter ATFF (Above-Thermal Fission Fraction) is observed. The ATFF values were also calculated in this benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 and the same trend as ENDF/B-VII.1 was observed.
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakurai, Takeshi; Mori, Takamasa
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-019, 450 Pages, 2017/03
In order to realize fast and accurate Monte Carlo simulation of neutron and photon transport problems, two Monte Carlo codes MVP (continuous-energy method) and GMVP (multigroup method) have been developed at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The codes have adopted a vectorized algorithm and have been developed for vector-type supercomputers. They also support parallel processing with a standard parallelization library MPI and thus a speed-up of Monte Carlo calculations can be achieved on general computing platforms. The first and second versions of the codes were released in 1994 and 2005, respectively. They have been extensively improved and new capabilities have been implemented. The major improvements and new capabilities are as follows: (1) perturbation calculation for effective multiplication factor, (2) exact resonant elastic scattering model, (3) calculation of reactor kinetics parameters, (4) photo-nuclear model, (5) simulation of delayed neutrons, (6) generation of group constants, etc. This report describes the physical model, geometry description method used in the codes, new capabilities and input instructions.
 -ray irradiated amino acids
-ray irradiated amino acidsNagata, Natsuki*; Komoda, Seiichi*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Nakamura, Hideo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ukai, Mitsuko*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 103, 2016/02
no abstracts in English
Kanda, Nobuhiro; Daiten, Masaki; Endo, Yuji; Yoshida, Hideaki; Mita, Yutaka; Naganawa, Hirochika; Nagano, Tetsushi; Yanase, Nobuyuki
JAEA-Technology 2015-007, 43 Pages, 2015/03
The centrifuge which has the subtlety information concerning the nuclear nonproliferation used for uranium enrichment technical development exists in the uranium enrichment facilities of Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This centrifugal is performing separation processing of the radioactive material adhering to the surface of parts by wet decontamination of ultrasonic cleaning by dilute sulfuric acid and water, etc. By removing the uranium contained in waste fluid, generated sludge reduces activity concentration. And the possibility of reduction of sludge processing is examined. For this reason, from the 2007 fiscal year, Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate and cooperation are aimed at, and development of the extraction separation technology of the "uranium" by the emulsion flow method is furthered. The test equipment using the developed emulsion flow method was tested. And dilute sulfuric acid and water were used for the examination as actual waste fluid. The result checked whether the various performances in Basic test carried out in Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate would be obtained.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.92(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 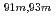 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
 /He mixed gas under room temperature
/He mixed gas under room temperatureTanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya
Shinku, 46(3), p.154 - 157, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Uehara, Kazuya; Maeda, Mitsuru; Tsushima, Akira*; Amemiya, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72(1), p.94 - 100, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.09(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yoshikawa, Masahito; Sato, Mirei; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
Materials Science Forum, 389-393, p.1009 - 1012, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
 H
H +Cl
+Cl reaction in water; Ab initio molecular orbital study using a cluster model
reaction in water; Ab initio molecular orbital study using a cluster modelKurosaki, Yuzuru
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 105(49), p.11080 - 11087, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:11.96(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 41(10), p.1311 - 1325, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:89.16(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 /He mixture gas
/He mixture gasTanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya; Inohara, Takashi*
Shinku, 44(7), p.667 - 670, 2001/07
no abstracts in English
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Gu, W.*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Arai, Taketoshi; Nakamura, Hitoshi*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 206(1), p.1 - 12, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takenaga, Hidenobu; JT-60 Team
Physics of Plasmas, 8(5), p.2217 - 2223, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:76.48(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ito, Yasuhisa; Noda, Kimio; ;
JNC TN8410 2001-018, 67 Pages, 2001/04
There are waste storage pits where non-radioactive wastes generated from plutonium fuel facilities were stored in JNC Tokai Works. But radioactive wastes were found in one of the pit during wastes arrangement works. Therefore we set the pit temporary controlled area and recovered wastes from it. This report describes the radiation control technique of recovery work in detail.
Izaki, Kenji; Noda, Kimio; ; Kashimuta, Yoshio*
JNC TN8410 2001-005, 30 Pages, 2001/01
Stack monitoring is the most important work in radiation control works. Exhaust monitors used for stack monitoring have the background (which is the counts by natural radio-nuclides) on normal condition, and the values of the background vary with the facilities. Therefore, if the value of background is high, it is difficult to estimate rapidly the radioactive concentration in the exhaust. In order to estimate rapidly the radioactive concentration in exhaust, we analyzed the behavior of natural radioactivity in the facilities and examine the technique fo reducing the value of the background. As a result of the examination, we found that it is possible to estimate rapidly if we change over the monitoring point to immediately after the HEPA filters on the exhaust duct. In this reports, the analyzed results of behavior of natural radio-nuclides in the facilities and the technique for reducing the values of the background are described. To reduce the value of the background has a major effect on not only rapidly estimating the radioactive density in the exhaust but also finding the unusual things on stack monitoring.
Okumura, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Masayuki; Kaneko, Kunio*;
JAERI-Conf 2000-018, p.31 - 41, 2001/01
Burnup calculation codes based on the conventional deterministic approach often encounter difficult problems because of the constraints on the geometry description, limit of approximation on the effective resonance cross-sections, failing of the diffusion approximation due to extremely strong anisotropic or heterogenity. They are, for example, the prediction of burn characteristics of plutonium spot, core design of ultra-small reactors, analysis of the sample material in an irradiation capsule of the research rector. To deal with these problems any time, a burn-up calculation code (MVP-BURN) was developed by using a continuous energy Monte Carlo code MVP. MVP-BURN was validated by comparison with the results of deterministic codes in the international benchmark problems, and by comparison with the measured values of the spent fuel composition irradiated in a commercial reactor.