Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
河口 宗道*; 池田 明日香; 斉藤 淳一
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 226, p.111880_1 - 111880_9, 2026/02
被引用回数:0This study performed sodium experiments and developed a new kinetic model to investigate the oxide dissolution and precipitation behavior on the stainless-steel (SS) surface in stagnant liquid sodium. The experiment revealed that the oxygen of Na FeO
FeO on the SS surface was dissolved into the liquid sodium with v
on the SS surface was dissolved into the liquid sodium with v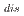
 9.3
9.3  10
10  wt.ratio/h in less than 20 h, and the oxide precipitation occurred on the SS surface with v
wt.ratio/h in less than 20 h, and the oxide precipitation occurred on the SS surface with v
 1.4
1.4  10
10 wt.ratio/h after the dissolution. Furthermore, the phase-field (PF) calculation code was developed to investigate the dependence of six parameters (T, c
wt.ratio/h after the dissolution. Furthermore, the phase-field (PF) calculation code was developed to investigate the dependence of six parameters (T, c ,
, 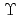 , D
, D 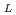 , k, and
, k, and  t) of the oxide precipitation velocity in the liquid sodium. As a result, the precipitation velocity increased linearly as the oxygen concentration (c
t) of the oxide precipitation velocity in the liquid sodium. As a result, the precipitation velocity increased linearly as the oxygen concentration (c ) and the oxygen diffusion coefficient (D
) and the oxygen diffusion coefficient (D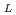 ) in liquid sodium increased. In contrast, its velocity decreased exponentially as the sodium temperature (T) and the interfacial energy of oxide (
) in liquid sodium increased. In contrast, its velocity decreased exponentially as the sodium temperature (T) and the interfacial energy of oxide (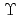 ) increased. The quasi-partial coefficient (k) and the time step (
) increased. The quasi-partial coefficient (k) and the time step ( t) did not affect the calculation results at all. In these sensitivity analyses, the oxide precipitation velocity obtained by the PF calculation shows consistency with the laboratory-scale experimental findings of Latge et al.
t) did not affect the calculation results at all. In these sensitivity analyses, the oxide precipitation velocity obtained by the PF calculation shows consistency with the laboratory-scale experimental findings of Latge et al.
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 北海道大学*
JAEA-Review 2025-028, 66 Pages, 2025/11
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和5年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和5年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「遮蔽不要な耐放射線性ダイヤモンド中性子計測システムのプロトタイプ開発」の令和5年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、1F廃炉事業で強いニーズのある遮蔽不要な中性子計測システムのプロトタイプを開発する。本システムは、ダイヤモンド中性子検出素子と耐放射線性シリコン集積回路から構成され、部品レベルでは積算線量でそれぞれ10MGy以上、4MGy以上の耐放射線性を有し、1.5kGy/hの 線線量率環境下で安定動作した実績を持つ。将来的な用途として、デブリ調査用中性子検出器、臨界近接監視モニタ、圧力容器内ドライチューブ調査用中性子検出器等への適用が想定される。本開発では、5mm角相当のダイヤモンド検出素子100枚規模からなるプロトタイプを開発し、システム構築技術の獲得とシステム性能を評価する。併せて未臨界度評価手法の開発も進める。これによりシステム開発までを完了し、メーカーとの連携による実機開発、1F廃炉事業への投入につなげる。令和5年度は、合成装置の電源改修や2cm角以上の合成範囲での検出器グレードのダイヤモンド単結晶合成条件を探索し、中性子・荷電粒子コンバータの合成条件を探索した。積層型ダイヤモンド検出素子の開発では、メタン濃度(CH
線線量率環境下で安定動作した実績を持つ。将来的な用途として、デブリ調査用中性子検出器、臨界近接監視モニタ、圧力容器内ドライチューブ調査用中性子検出器等への適用が想定される。本開発では、5mm角相当のダイヤモンド検出素子100枚規模からなるプロトタイプを開発し、システム構築技術の獲得とシステム性能を評価する。併せて未臨界度評価手法の開発も進める。これによりシステム開発までを完了し、メーカーとの連携による実機開発、1F廃炉事業への投入につなげる。令和5年度は、合成装置の電源改修や2cm角以上の合成範囲での検出器グレードのダイヤモンド単結晶合成条件を探索し、中性子・荷電粒子コンバータの合成条件を探索した。積層型ダイヤモンド検出素子の開発では、メタン濃度(CH /H
/H )、酸素濃度(O/C)が積層型構造のp-層中の不純物濃度や表面形態に与える影響を調べ、さらに中性子検出素子用信号処理集積回路では、特性ばらつきを評価し、キャリブレーション手法を検討した。また、臨界近接監視法の開発では、1Fにおける燃料デブリ取り出し作業時の臨界近接監視を行うための方法論の検討を進め、
)、酸素濃度(O/C)が積層型構造のp-層中の不純物濃度や表面形態に与える影響を調べ、さらに中性子検出素子用信号処理集積回路では、特性ばらつきを評価し、キャリブレーション手法を検討した。また、臨界近接監視法の開発では、1Fにおける燃料デブリ取り出し作業時の臨界近接監視を行うための方法論の検討を進め、 線照射試験では、照射場の整備を進めた。中性子感度測定試験では、必要な照射設備や照射方法等について参画機関と協議し、試験環境の整備を進めた。
線照射試験では、照射場の整備を進めた。中性子感度測定試験では、必要な照射設備や照射方法等について参画機関と協議し、試験環境の整備を進めた。
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 東京科学大学*
JAEA-Review 2025-026, 72 Pages, 2025/11
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和5年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和4年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「マイクロ・ナノテクノロジーを利用したアルファ微粒子の溶解・凝集分散に及ぼすナノ界面現象の探求」の令和5年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。安全で合理的な燃料デブリ取出しを進めるためには、デブリ加工時に発生するアルファ微粒子の溶解や変性挙動の把握は不可欠である。本研究は、金属酸化物ナノ粒子の凝集、溶解、変性挙動を熱力学的・速度論的に解明しうるマイクロ・ナノデバイスを創出すると共に、数理科学と組み合わせることで、アルファ微粒子の溶解・凝集・変性プロセスのメカニズム解明と反応モデル化を実現することを目的としている。具体的には、(1)ナノ粒子溶解特性評価、(2)溶解ダイナミクス分析、(3)凝集ダイナミクス分析、(4)表面微構造解析、(5)数理科学的モデリングの5項目を日本側・英国側で分担し、互いに有機的に連携しながら推し進める。令和5年度には、模擬燃料デブリ微粒子(UO メカニカル微粒子、UO
メカニカル微粒子、UO ケミカル微粒子及び(U,Zr)O
ケミカル微粒子及び(U,Zr)O 微粒子)のバルク及びマイクロ溶解試験を実施し、これらナノ粒子の溶解挙動に与える粒子サイズ、反応時間、H
微粒子)のバルク及びマイクロ溶解試験を実施し、これらナノ粒子の溶解挙動に与える粒子サイズ、反応時間、H O
O 濃度の効果について解析することに成功した。特に、(U,Zr)O
濃度の効果について解析することに成功した。特に、(U,Zr)O デブリ微粒子では、H
デブリ微粒子では、H O
O 濃度に応じてZrの触媒反応の進行度合いが異なり、H
濃度に応じてZrの触媒反応の進行度合いが異なり、H O
O 濃度に依存してガス発生量とU溶解量が変化することを明らかにした。また、ナノ粒子分散液と反応溶液とを瞬時に反応させ、動的な凝集・溶解挙動の評価及び溶出したUを定量することができるマイクロ流体デバイスを構築し、マイクロ流路内でのH
濃度に依存してガス発生量とU溶解量が変化することを明らかにした。また、ナノ粒子分散液と反応溶液とを瞬時に反応させ、動的な凝集・溶解挙動の評価及び溶出したUを定量することができるマイクロ流体デバイスを構築し、マイクロ流路内でのH O
O 処理によるUの凝集・溶解速度を算出した。英国側研究者と連携を密にして研究を進め、所期の目標を達成した。
処理によるUの凝集・溶解速度を算出した。英国側研究者と連携を密にして研究を進め、所期の目標を達成した。
柳澤 宏司; 求 惟子
JAEA-Research 2025-010, 197 Pages, 2025/11
TRIGA燃料棒の臨界リスクの把握とその取扱いの安全対策の検討のため、NSRR燃料棒からなる無限及び有限非均質格子体系の臨界特性を、燃料棒の詳細な計算モデルを用いて再評価した。再評価には、最新バージョンのJENDL-5を含むJENDLライブラリとMVPバージョン3コードが使用された。臨界特性として、無限及び水反射有限体系の中性子増倍率の変化を、格子ピッチと減速材水の密度をパラメータとして詳細に調べた。再評価された臨界特性の結果から、JENDL-5ライブラリを用いて、水反射の六角格子体系の最小臨界燃料棒本数は46.8 0.2本と得られた。さらに、TRIGA燃料棒には水素化ジルコニウム減速材と黒鉛反射材が備わっているため、減速材及び反射材としての水が存在しない場合の臨界到達可能性を検討した。その結果、水が存在しない場合でも、NSRR標準炉心に装荷されている燃料棒の本数よりも少ない115.7
0.2本と得られた。さらに、TRIGA燃料棒には水素化ジルコニウム減速材と黒鉛反射材が備わっているため、減速材及び反射材としての水が存在しない場合の臨界到達可能性を検討した。その結果、水が存在しない場合でも、NSRR標準炉心に装荷されている燃料棒の本数よりも少ない115.7 0.6本の燃料棒で臨界に到達することが可能であることが分かった。
0.6本の燃料棒で臨界に到達することが可能であることが分かった。
篠原 佑也*; 岩下 拓哉*; 中西 真大*; Liu, Y.*; Cooper, V. R.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 楡井 真実; Dmowski, W.*; Hickner, M. A.*; 江上 毅*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 129(47), p.12330 - 12337, 2025/11
Enhancing proton transport in polymer electrolytes is crucial for advancing next-generation solid-state batteries, yet our understanding of proton conductivity in nonaqueous environments remains limited due to a lack of atomic-scale insights. In this study, we investigated the atomic-scale dynamics of 1,2,3-triazole, a small molecule capable of dynamic hydrogen bonding, as a model system for proton hopping in nonaqueous environments. Using the real-space correlation function determined by the double Fourier transformation of inelastic neutron scattering spectra, we identified that the self-motion of protons and intermolecular dynamics occur on comparable time scales. Furthermore, we observed that the activation energy associated with the intermolecular dynamics matches the energy barrier for molecular rotations determined through Density Functional Theory calculations. These findings underscore the importance of controlling molecular dynamics at the atomic scale to control proton transport. Additionally, we demonstrated that intermolecular dynamics in systems involving protons can be studied using inelastic neutron scattering even without deuteration, thereby providing a broader avenue for studying atomic-scale dynamics in soft matter systems.
木村 祥紀; 山口 知輝
Radioisotopes, 74(3), p.251 - 264, 2025/11
ガンマ線スペクトル分析による放射性核種判定(RIID)は幅広い分野で利用されており、正確な放射性同位元素の同定は様々な分野で重要な課題となっている。ラボラトリ外の現場におけるRIIDにはハンドヘルド機器が一般的に使用されているが、その性能が限定的であることに課題がある。本稿では、現場使用を想定したハンドヘルド機器によるRIIDのための、教師なしニューラルネットワークモデルを用いたスペクトルデコンボリューション手法を提案する。本手法では、測定されたスペクトルとエネルギーゆらぎ行列(energy-broadening matrix)に基づいたデコンボリューションのためのニューラルネットワークの最適化が可能であり、大規模な訓練データセットや検出器・測定条件の正確なモデリングを必要としない。CsI(Tl)スペクトロメータを用いた放射性同位元素の測定を想定し、シミュレーションと実測スペクトルの両方で提案手法の性能を調べた。その結果として、教師なしニューラルネットワークモデルは従来のデコンボリューションアルゴリズムと比較してもピーク分解能を大幅に向上させることができ、本手法が低エネルギー分解能スペクトルにおけるRIID性能に寄与することを実証した。
 Cu and
Cu and  Cu with accelerator neutrons by deuterons and their separation from zinc
Cu with accelerator neutrons by deuterons and their separation from zinc永井 泰樹*; 川端 方子*; 佐伯 秀也*; 本石 章司*; 橋本 和幸; 塚田 和明; 本村 新*; 太田 朗生*; 高島 直貴*; 橋本 慎太郎; et al.
Frontiers in Nuclear Medicine (Internet), 5, p.1657125_1 - 1657125_11, 2025/10
近年、 Cuと
Cuと CuのRIペアは、理想的な治療診断一体型放射性核種として注目を集めている。我々は、加速器施設において重陽子ビームを用いて生成した中性子源を利用する、新しい製造手法を提案しており、濃縮
CuのRIペアは、理想的な治療診断一体型放射性核種として注目を集めている。我々は、加速器施設において重陽子ビームを用いて生成した中性子源を利用する、新しい製造手法を提案しており、濃縮 Zn試料にこの中性子源を照射し、生成された
Zn試料にこの中性子源を照射し、生成された Cuの放射化量の絶対値および核種純度を測定した。その結果、測定値は評価済み核データライブラリJENDL-5を用いたPHITSの計算結果と一致すること、また測定困難な微量放射性核種の生成量を見積もることが可能であることがわかった。さらに、我々が開発した昇華およびカラム分離法により、照射後のZn試料から
Cuの放射化量の絶対値および核種純度を測定した。その結果、測定値は評価済み核データライブラリJENDL-5を用いたPHITSの計算結果と一致すること、また測定困難な微量放射性核種の生成量を見積もることが可能であることがわかった。さらに、我々が開発した昇華およびカラム分離法により、照射後のZn試料から Cuを適切に分離できることも確認した。これらの成果により、
Cuを適切に分離できることも確認した。これらの成果により、 Cuおよび
Cuおよび Cuの製造を、複数の拠点で経済的かつ持続可能な方法で実施できる可能性が示された。
Cuの製造を、複数の拠点で経済的かつ持続可能な方法で実施できる可能性が示された。
 Cs released by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant to the coastal area
Cs released by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant to the coastal area佐藤 俊; 脇山 義史*; 高橋 史明; 高田 兵衛*
Science of the Total Environment, 1000, p.180380_1 - 180380_14, 2025/10
福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPP)の事故から10年が経過したが、福島沿岸域の海水中 Csの濃度は事故前に比べて高く、継続的に
Csの濃度は事故前に比べて高く、継続的に Csが流入していることが考えられる。本研究では2012年以降において、FDNPPからの
Csが流入していることが考えられる。本研究では2012年以降において、FDNPPからの Csの直接流入量と、河川経由での
Csの直接流入量と、河川経由での Csの流入量を比較した。直接流入は、FDNPPが実施した海側遮水壁の設置などの流出対策により、2012-2014年の17.5TBqから2019-2021年の0.6TBqへと明らかに減少した。それに対し、河川からの流入は、2012-2014年の2.2TBqから2019-2021年の2.0TBqへとわずかに減少した。また、FDNPP周辺の沿岸水への全
Csの流入量を比較した。直接流入は、FDNPPが実施した海側遮水壁の設置などの流出対策により、2012-2014年の17.5TBqから2019-2021年の0.6TBqへと明らかに減少した。それに対し、河川からの流入は、2012-2014年の2.2TBqから2019-2021年の2.0TBqへとわずかに減少した。また、FDNPP周辺の沿岸水への全 Csフラックスに対する直接流入の割合は、2012-2014年の89%から2019-2021年の23%に減少した。事故初期に比べ、福島沿岸域の海水中
Csフラックスに対する直接流入の割合は、2012-2014年の89%から2019-2021年の23%に減少した。事故初期に比べ、福島沿岸域の海水中 Cs濃度変動に対する河川経由での流入の寄与が大きくなっており、特に大量出水時にはより顕著な影響が生じることが示唆された。福島沿岸域における
Cs濃度変動に対する河川経由での流入の寄与が大きくなっており、特に大量出水時にはより顕著な影響が生じることが示唆された。福島沿岸域における Csの長期的な動態を正確に予測するには、さまざまな環境要因と人為的要因を併せて考慮する必要がある。
Csの長期的な動態を正確に予測するには、さまざまな環境要因と人為的要因を併せて考慮する必要がある。
坂本 雅洋; 奥村 啓介; 神野 郁夫; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; Riyana, E. S.; 金子 純一*; 溝上 暢人*; 溝上 伸也*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(8), p.756 - 765, 2025/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this paper, we propose a new nuclide inventory estimation method based on computational methods, called a "theoretical scaling factor method" for difficult-to-measure (DTM) nuclides in fuel debris and radioactive wastes. The theoretical scaling factor method provides a method similar to a conventional scaling factor method. The theoretical scaling factor method, however, does not require performing many measurements to obtain correlations between a key nuclide which is easy-to-measure and a DTM nuclide. Instead of actual analytical measurements, the results of theoretical calculations are used. A correlation equation between the key nuclide and the DTM nuclide is created based on the results of theoretical calculations, and the DTM nuclide is deterministically estimated using the measurement value of the key nuclide only. In this paper, we selected Cs-135 as the DTM nuclide and Cs-137 as the key nuclide. Cs-135 has a long half-life of 2.3 10
10 years and is one of the important fission products in the safety evaluation for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, because it dissolves and migrates in groundwater easily. We confirmed the validity of the proposed method using measured data of Cs-137 and Cs-135 on radioactive wastes from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) accident obtained by many researchers. It can be used as a rational and efficient technology to reduce the analysis costs of various types of fuel debris and radioactive waste present at 1F.
years and is one of the important fission products in the safety evaluation for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, because it dissolves and migrates in groundwater easily. We confirmed the validity of the proposed method using measured data of Cs-137 and Cs-135 on radioactive wastes from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) accident obtained by many researchers. It can be used as a rational and efficient technology to reduce the analysis costs of various types of fuel debris and radioactive waste present at 1F.
茂木 孝介; 松本 俊慶; 塩津 弘之
Proceedings of 21st International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-21) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2025/08
Since the hydrogen explosion at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants accident in March 2011, hydrogen management during severe accidents at nuclear power plants has attracted attention as an important issue. In order to improve hydrogen management under severe accident conditions, the propagation of flames and the resulting loads on structures need to be predicted accurately. For this reason, the use of computational fluid dynamics methods is expected. Various benchmark experiments have been carried out and turbulence models, turbulent combustion models and chemical reaction models have been discussed, but the uncertainties of each model have not been treated independently. Analysis including uncertainty assessment is necessary to promote efficient research activities through uncertainty-based prioritisation and to reflect the latest findings in best practice guidelines. The aim of this study is to establish a methodology for quantifying the chemical reaction uncertainty in turbulent premixed flame CFD and to perform CFD and uncertainty analyses on existing benchmark experiments.
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 福島大学*
JAEA-Review 2025-002, 108 Pages, 2025/07
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和5年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和元年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「化学計測技術とインフォマティックスを融合したデブリ性状把握手法の開発とタイアップ型人材育成」の令和元年度から令和5年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、新しい化学分析法の構築によるインフォマティックスとの融合技術の実現を目指し、少ない情報量で全体像を推定するシステムの開発を実施することを目的とする。JAEA研究者とのタイアップ方式による研究を実施することで、博士前期課程 ポスドクまでの研究者の地域実践型の深化する横断的な人材育成を行うとともに、国際感覚豊かな人材の育成を目指し、実施した。
ポスドクまでの研究者の地域実践型の深化する横断的な人材育成を行うとともに、国際感覚豊かな人材の育成を目指し、実施した。
竹田 武司
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEAでは、加圧水型軽水炉(PWR)解析のためのRELAP5/MOD3.3コードの入力データを、主に大型非定常実験装置(LSTF)の参照4ループPWRである敦賀発電所2号機の設計情報を基に作成してきた。PWR解析に関する代表的なOECD/NEAの活動として、BEMUSEプログラムの枠組みにおける低温側配管大破断冷却材喪失事故(LBLOCA)の計算が挙げられる。また、わが国の新規制基準に係るPWRの炉心損傷防止対策の有効性評価事象には、低温側配管LBLOCA時の非常用炉心冷却系(ECCS)の再循環機能喪失事象が含まれる。本検討において、PWRの安全設計上想定すべき設計基準事故の一つであるLBLOCAを解析するための入力データを整備した。本報告書では、PWRLBLOCA解析の入力データの主な特徴を示す。PWRの原子炉容器、加圧器(PZR)、高温側配管、蒸気発生器(SG)、SG二次系、クロスオーバーレグ、低温側配管、ECCSなどをモデル化し、参照4ループPWRを2ループで模擬した。その際、PZRは3ループ分を模擬するループAに接続し、破断口は1ループ分を模擬するループBに設置した。PWRのコンポーネントのノード分割は、LSTFのコンポーネントのノード分割を参照した。また、PWRLBLOCA解析の主な入力データに対して、解釈を加えるとともに、設定根拠などの付加情報を提供した。さらに、整備した入力データを用いて、ECCS再循環機能喪失事象を対象とした過渡解析を実施した。RELAP5/MOD3.3コードによる既往研究の計算と比較することにより、過渡解析は概ね妥当であることを確認した。加えて、RELAP5/MOD3.3コードを用いて感度解析を実施し、破断口の流出係数や代替再循環注水流量が燃料棒被覆管表面温度に及ぼす影響を明らかにした。本報告書では、設定した条件の範囲内での感度解析結果について示し、ECCS再循環機能喪失事象に対する既往研究の計算内容の一部を補完する。
大橋 智典*; 坂巻 竜也*; 舟越 賢一*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; 服部 高典; Yuan, L.*; 鈴木 昭夫*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:72.19(Mineralogy)0-6GPa, 1000-1300Kのドライおよび含水Na Si
Si O
O 融体の構造と高温高圧から回収したガラスの構造をその場中性子回折及びX線回折により調べた。また、0-10GPa, 3000Kの融体の構造をab-initio分子動力学シミュレーションにより調べた。その場中性子実験から、-O-D-O-架橋種の形成によりD-O距離が圧縮とともに増加することが明らかになり、分子動力学シミュレーションでも再現された。圧力による-O-D-O-形成は、水素がより強固に取り込まれることを反映しており、実験的に観測されたケイ酸塩融体中の水の高い溶解度のメカニズムとして働く。一方、0-10GPa, 3000KにおけるドライNa
融体の構造と高温高圧から回収したガラスの構造をその場中性子回折及びX線回折により調べた。また、0-10GPa, 3000Kの融体の構造をab-initio分子動力学シミュレーションにより調べた。その場中性子実験から、-O-D-O-架橋種の形成によりD-O距離が圧縮とともに増加することが明らかになり、分子動力学シミュレーションでも再現された。圧力による-O-D-O-形成は、水素がより強固に取り込まれることを反映しており、実験的に観測されたケイ酸塩融体中の水の高い溶解度のメカニズムとして働く。一方、0-10GPa, 3000KにおけるドライNa Si
Si O
O の圧縮は、Si-O-Si角の曲げに支配される。さらに、含水Na
の圧縮は、Si-O-Si角の曲げに支配される。さらに、含水Na Si
Si O
O 融体の分子動力学シミュレーションから、圧力上昇とともに、2(
融体の分子動力学シミュレーションから、圧力上昇とともに、2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na およびSi-O
およびSi-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na で示される反応により、ナトリウムイオンがネットワーク修飾の役割を果たさなくなることを示唆している。
で示される反応により、ナトリウムイオンがネットワーク修飾の役割を果たさなくなることを示唆している。
曽根原 正晃; 岡野 靖; 内堀 昭寛; 大木 裕*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.403 - 414, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナトリウム冷却高速炉では、ナトリウム漏えい事故を管理するためにナトリウムの燃焼挙動を理解することが極めて重要である。本研究では、多次元熱流動解析コードAQUA-SFを用いて、サンディア国立研究所(SNL)のT3実験のベンチマーク解析を実施した。この実験は、容器容積100m 、ナトリウム流量1kg/sの密閉空間で実施され、ナトリウム注入直後の局所的な温度上昇がもたらす多次元的な影響を明らかにした。本研究では、AQUA-SFの機能を拡張することを目的として、このような多次元的な温度変動、特に容器底部における高温領域の形成のシミュレーションに焦点を当てた。提案したモデルには、ナトリウム液滴着火の一時停止と床面上のナトリウム飛沫の噴霧燃焼が含まれる。さらに、底部高温域の再現性を高めるためには、床部近傍に熱源を追加することが不可欠であることを示した。そこで、噴霧円錐角の感度解析と床面上の液滴の長時間燃焼を含むケーススタディを実施した。この包括的なアプローチにより、ナトリウム冷却高速炉におけるナトリウム燃焼のダイナミクスと安全対策に関する貴重な知見を得ることができた。
、ナトリウム流量1kg/sの密閉空間で実施され、ナトリウム注入直後の局所的な温度上昇がもたらす多次元的な影響を明らかにした。本研究では、AQUA-SFの機能を拡張することを目的として、このような多次元的な温度変動、特に容器底部における高温領域の形成のシミュレーションに焦点を当てた。提案したモデルには、ナトリウム液滴着火の一時停止と床面上のナトリウム飛沫の噴霧燃焼が含まれる。さらに、底部高温域の再現性を高めるためには、床部近傍に熱源を追加することが不可欠であることを示した。そこで、噴霧円錐角の感度解析と床面上の液滴の長時間燃焼を含むケーススタディを実施した。この包括的なアプローチにより、ナトリウム冷却高速炉におけるナトリウム燃焼のダイナミクスと安全対策に関する貴重な知見を得ることができた。
上澤 伸一郎; 小野 綾子; 永武 拓; 山下 晋; 吉田 啓之
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.432 - 456, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ワイヤメッシュセンサ(WMS)の精度を明らかにするため、単一の球形気泡と気泡流に対してWMSの静電場シミュレーションを実施した。単一気泡の静電場シミュレーションでは、様々な気泡位置における電流密度分布と、送信ワイヤから受信ワイヤまでの電流経路を示した。その結果、WMS周囲の不均一な電流密度分布に基づく系統的誤差があることを明らかにした。また、数値流体解析コードJAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER)で得られた気泡流結果に対して静電場シミュレーションを実施したところ、線形近似やMaxwellの式などの、WMS信号からボイド率への既存の変換方法では0と1の間の瞬間ボイド率の中間値を定量的に推定できなかった。また、WMS信号に対してボイド率 0.2という大きなばらつきがあり、瞬間ボイド率を定量的に計測することが困難であることがわかった。一方で、時間平均ボイド率においては、流路の中心付近のボイド率は線形近似を使用して推定でき、流路壁面近くのボイド率はMaxwellの式を使用して推定できることがわかった。
0.2という大きなばらつきがあり、瞬間ボイド率を定量的に計測することが困難であることがわかった。一方で、時間平均ボイド率においては、流路の中心付近のボイド率は線形近似を使用して推定でき、流路壁面近くのボイド率はMaxwellの式を使用して推定できることがわかった。
福田 航大; 小原 徹*; 須山 賢也
Nuclear Technology, 211(5), p.963 - 973, 2025/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:35.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)An application of the boiling water reactor (BWR) to an offshore floating nuclear power plant (OFNP) is discussed in Japan. The BWR-type OFNP has some challenges for practical use, although it has high economic efficiency because of downsizing and simplification. One challenge is understanding reactor kinetics under conditions specific to the marine environment. This study quantitatively clarifies the total and spatial changes in power when the BWR is inclined during regular operation. Therefore, the TRAC/RELAP Advanced Computational Engine (TRACE) and Purdue Advanced Reactor Core Simulator (PARCS) codes were used to perform a three-dimensional neutronics-thermal-hydraulics-coupled transient analysis. The calculation model is based on Peach Bottom II. This study clarifies the changing trend in total and local BWR power by inclination with simplified modeling and conditions. Reasons for such changes are discussed based on changes in several thermal-hydraulic parameters. The difference in BWR power against the inclinations is small. Thus, it was implied that the BWR-type OFNP is expected to have a stable power supply capability during natural disasters. Finally, requires further studies to support the obtained conclusions are discussed.
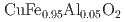
玉造 博夢; 内原 猛*; 満田 節生*; 石井 祐太*; 中尾 裕則*; 竹端 寛治*; 今中 康貴*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:64.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In multiferroic CuFe Al
Al O
O , applying uniaxial pressure
, applying uniaxial pressure  generates a magnetoferroelectric phase distinct from the well-studied spin-driven ferroelectric phase associated with helical magnetic ordering in this system. Using a four-circle neutron diffractometer, the magnetic structure of the
generates a magnetoferroelectric phase distinct from the well-studied spin-driven ferroelectric phase associated with helical magnetic ordering in this system. Using a four-circle neutron diffractometer, the magnetic structure of the  -induced magnetoferroelectric phase is determined as the collinear sinusoidal type, which itself does not break the inversion symmetry in this system. Additionally, synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction experiments are conducted to investigate how the triangular lattice in CuFe
-induced magnetoferroelectric phase is determined as the collinear sinusoidal type, which itself does not break the inversion symmetry in this system. Additionally, synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction experiments are conducted to investigate how the triangular lattice in CuFe Al
Al O
O is distorted by applied
is distorted by applied  . Although lattice distortion during the magnetic phase transition in CuFe
. Although lattice distortion during the magnetic phase transition in CuFe Al
Al O
O is mitigated by the substitution of nonmagnetic Al
is mitigated by the substitution of nonmagnetic Al , the application of
, the application of  along the conjugate direction revives the "latent" spin-lattice coupling, causing the triangular lattice to distort during magnetic phase transition. The application of a magnetic filed considerably reduces
along the conjugate direction revives the "latent" spin-lattice coupling, causing the triangular lattice to distort during magnetic phase transition. The application of a magnetic filed considerably reduces  -induced ferroelectric polarization, but does not affect lattice distortion. These results indicate that
-induced ferroelectric polarization, but does not affect lattice distortion. These results indicate that  -induced ferroelectric polarization is not a consequence of the piezoelectric effect. Instead, the sinusoidal magnetic structure would contribute to the emergence of
-induced ferroelectric polarization is not a consequence of the piezoelectric effect. Instead, the sinusoidal magnetic structure would contribute to the emergence of  -induced ferroelectric polarization through spin-lattice coupling.
-induced ferroelectric polarization through spin-lattice coupling.
冠城 雅晃; 宮本 勇太; 森 教匡; 岩井 紘基; 手塚 将志; 黒澤 俊介*; 田川 明広; 高崎 浩司
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.308 - 316, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear decommissioning has recently accelerated, particularly following the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Holdings.  -ray/X-ray (radiation photon) spectroscopy provides information on the types of radionuclides with radiation photon emissions. Radiation photon spectroscopy in a control rod guide tube positioned at the center of Fugen was conducted. Fugen is a prototype advanced thermal reactor with 165 MWe electric power generation that is being decommissioned. The dose rates measured in a control rod guide tube positioned at the center of the reactor were 4.1 - 9.1 Gy/h. The dose rate considerably increased at a position close to a tank that contained
-ray/X-ray (radiation photon) spectroscopy provides information on the types of radionuclides with radiation photon emissions. Radiation photon spectroscopy in a control rod guide tube positioned at the center of Fugen was conducted. Fugen is a prototype advanced thermal reactor with 165 MWe electric power generation that is being decommissioned. The dose rates measured in a control rod guide tube positioned at the center of the reactor were 4.1 - 9.1 Gy/h. The dose rate considerably increased at a position close to a tank that contained  Co caused by the radioactivation of stainless steel. Radiation photon spectroscopy was performed without radiation shielding, identifying
Co caused by the radioactivation of stainless steel. Radiation photon spectroscopy was performed without radiation shielding, identifying  Co with an energy resolution better than 5.4% at 1333 keV and
Co with an energy resolution better than 5.4% at 1333 keV and  Nb with an energy resolution better than 5.9% at 871 keV.
Nb with an energy resolution better than 5.9% at 871 keV.
Hamdani, A.; 相馬 秀; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.53 - 59, 2025/03
This paper presents the experimental study and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis on the effect of thermal radiation in the humid atmosphere inside the containment vessel. The experiment was conducted in the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The numerical analysis was carried out using the open-source CFD code OpenFOAM. The initial gas condition inside the CIGMA containment consists of three gases, helium, air, and water vapor, at room temperature 30  C and a pressure of 1 atm. Initial helium stratification was located 6 m above the bottom vessel, and its molar fraction was 55 %. The initial water vapor molar fraction was set to 0.1% in order to minimize the thermal radiation absorption by the water molecule. Pure helium was injected through a nozzle from the top, leading to increased vessel pressure and a corresponding rise in gas temperature. The numerical validation at low water vapor, i.e., 0.1% H
C and a pressure of 1 atm. Initial helium stratification was located 6 m above the bottom vessel, and its molar fraction was 55 %. The initial water vapor molar fraction was set to 0.1% in order to minimize the thermal radiation absorption by the water molecule. Pure helium was injected through a nozzle from the top, leading to increased vessel pressure and a corresponding rise in gas temperature. The numerical validation at low water vapor, i.e., 0.1% H O, was performed by comparing the transient profile of pressure, gas molar fraction, and temperature with the experimental data. A Weighted Sum of Gray Gases (WSGG) model was implemented in the OpenFOAM solver. The numerical results showed a reasonable agreement compared to the experimental data. In addition, the numerical simulation with various water vapor mass fractions, i.e., 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and 60%, was performed to analyze the effect of humidity on the radiative heat transfer. The predicted temperature was overestimated when the numerical model neglected thermal radiation. Therefore, it indicated that thermal radiation should be considered when modeling the containment thermohydraulic.
O, was performed by comparing the transient profile of pressure, gas molar fraction, and temperature with the experimental data. A Weighted Sum of Gray Gases (WSGG) model was implemented in the OpenFOAM solver. The numerical results showed a reasonable agreement compared to the experimental data. In addition, the numerical simulation with various water vapor mass fractions, i.e., 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and 60%, was performed to analyze the effect of humidity on the radiative heat transfer. The predicted temperature was overestimated when the numerical model neglected thermal radiation. Therefore, it indicated that thermal radiation should be considered when modeling the containment thermohydraulic.
吉越 章隆; 津田 泰孝; 小畠 雅明; 岡根 哲夫; 佐藤 志彦; 大河内 拓雄*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 23(1), p.16 - 21, 2025/02
Synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy (SR-PEEM) combining with hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) was utilized to obtain detailed structural and chemical insights into radioactive cesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs) smaller than 10  m. HAXPES data revealed the presence of several elements such as C, O, Mg, Al, Si, Sr and Cs, while the chemical mapping images obtained by SR-PEEM clearly demonstrated that Cs atoms almost exclusively cover the particle surface. Owing to the surface-sensitive nature of SR-PEEM, the results notably indicate inhomogeneous distributions of elements, suggesting an eggshell-like structure with a Cs shell, with a thickness greater than the escape depth of the photoelectrons (a few nanometers). These novel findings strongly suggest that the aggregation of Cs atoms likely occurs at the microparticle surface and are expected to have applications in the remediation of nuclear power plant accidents.
m. HAXPES data revealed the presence of several elements such as C, O, Mg, Al, Si, Sr and Cs, while the chemical mapping images obtained by SR-PEEM clearly demonstrated that Cs atoms almost exclusively cover the particle surface. Owing to the surface-sensitive nature of SR-PEEM, the results notably indicate inhomogeneous distributions of elements, suggesting an eggshell-like structure with a Cs shell, with a thickness greater than the escape depth of the photoelectrons (a few nanometers). These novel findings strongly suggest that the aggregation of Cs atoms likely occurs at the microparticle surface and are expected to have applications in the remediation of nuclear power plant accidents.