Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
大橋 智典*; 坂巻 竜也*; 舟越 賢一*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; 服部 高典; Yuan, L.*; 鈴木 昭夫*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
0-6GPa, 1000-1300Kのドライおよび含水Na Si
Si O
O 融体の構造と高温高圧から回収したガラスの構造をその場中性子回折及びX線回折により調べた。また、0-10GPa, 3000Kの融体の構造をab-initio分子動力学シミュレーションにより調べた。その場中性子実験から、-O-D-O-架橋種の形成によりD-O距離が圧縮とともに増加することが明らかになり、分子動力学シミュレーションでも再現された。圧力による-O-D-O-形成は、水素がより強固に取り込まれることを反映しており、実験的に観測されたケイ酸塩融体中の水の高い溶解度のメカニズムとして働く。一方、0-10GPa, 3000KにおけるドライNa
融体の構造と高温高圧から回収したガラスの構造をその場中性子回折及びX線回折により調べた。また、0-10GPa, 3000Kの融体の構造をab-initio分子動力学シミュレーションにより調べた。その場中性子実験から、-O-D-O-架橋種の形成によりD-O距離が圧縮とともに増加することが明らかになり、分子動力学シミュレーションでも再現された。圧力による-O-D-O-形成は、水素がより強固に取り込まれることを反映しており、実験的に観測されたケイ酸塩融体中の水の高い溶解度のメカニズムとして働く。一方、0-10GPa, 3000KにおけるドライNa Si
Si O
O の圧縮は、Si-O-Si角の曲げに支配される。さらに、含水Na
の圧縮は、Si-O-Si角の曲げに支配される。さらに、含水Na Si
Si O
O 融体の分子動力学シミュレーションから、圧力上昇とともに、2(
融体の分子動力学シミュレーションから、圧力上昇とともに、2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na およびSi-O
およびSi-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na で示される反応により、ナトリウムイオンがネットワーク修飾の役割を果たさなくなることを示唆している。
で示される反応により、ナトリウムイオンがネットワーク修飾の役割を果たさなくなることを示唆している。
曽根原 正晃; 岡野 靖; 内堀 昭寛; 大木 裕*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.403 - 414, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナトリウム冷却高速炉では、ナトリウム漏えい事故を管理するためにナトリウムの燃焼挙動を理解することが極めて重要である。本研究では、多次元熱流動解析コードAQUA-SFを用いて、サンディア国立研究所(SNL)のT3実験のベンチマーク解析を実施した。この実験は、容器容積100m 、ナトリウム流量1kg/sの密閉空間で実施され、ナトリウム注入直後の局所的な温度上昇がもたらす多次元的な影響を明らかにした。本研究では、AQUA-SFの機能を拡張することを目的として、このような多次元的な温度変動、特に容器底部における高温領域の形成のシミュレーションに焦点を当てた。提案したモデルには、ナトリウム液滴着火の一時停止と床面上のナトリウム飛沫の噴霧燃焼が含まれる。さらに、底部高温域の再現性を高めるためには、床部近傍に熱源を追加することが不可欠であることを示した。そこで、噴霧円錐角の感度解析と床面上の液滴の長時間燃焼を含むケーススタディを実施した。この包括的なアプローチにより、ナトリウム冷却高速炉におけるナトリウム燃焼のダイナミクスと安全対策に関する貴重な知見を得ることができた。
、ナトリウム流量1kg/sの密閉空間で実施され、ナトリウム注入直後の局所的な温度上昇がもたらす多次元的な影響を明らかにした。本研究では、AQUA-SFの機能を拡張することを目的として、このような多次元的な温度変動、特に容器底部における高温領域の形成のシミュレーションに焦点を当てた。提案したモデルには、ナトリウム液滴着火の一時停止と床面上のナトリウム飛沫の噴霧燃焼が含まれる。さらに、底部高温域の再現性を高めるためには、床部近傍に熱源を追加することが不可欠であることを示した。そこで、噴霧円錐角の感度解析と床面上の液滴の長時間燃焼を含むケーススタディを実施した。この包括的なアプローチにより、ナトリウム冷却高速炉におけるナトリウム燃焼のダイナミクスと安全対策に関する貴重な知見を得ることができた。
Hamdani, A.; 相馬 秀; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.53 - 59, 2025/03
This paper presents the experimental study and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis on the effect of thermal radiation in the humid atmosphere inside the containment vessel. The experiment was conducted in the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The numerical analysis was carried out using the open-source CFD code OpenFOAM. The initial gas condition inside the CIGMA containment consists of three gases, helium, air, and water vapor, at room temperature 30  C and a pressure of 1 atm. Initial helium stratification was located 6 m above the bottom vessel, and its molar fraction was 55 %. The initial water vapor molar fraction was set to 0.1% in order to minimize the thermal radiation absorption by the water molecule. Pure helium was injected through a nozzle from the top, leading to increased vessel pressure and a corresponding rise in gas temperature. The numerical validation at low water vapor, i.e., 0.1% H
C and a pressure of 1 atm. Initial helium stratification was located 6 m above the bottom vessel, and its molar fraction was 55 %. The initial water vapor molar fraction was set to 0.1% in order to minimize the thermal radiation absorption by the water molecule. Pure helium was injected through a nozzle from the top, leading to increased vessel pressure and a corresponding rise in gas temperature. The numerical validation at low water vapor, i.e., 0.1% H O, was performed by comparing the transient profile of pressure, gas molar fraction, and temperature with the experimental data. A Weighted Sum of Gray Gases (WSGG) model was implemented in the OpenFOAM solver. The numerical results showed a reasonable agreement compared to the experimental data. In addition, the numerical simulation with various water vapor mass fractions, i.e., 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and 60%, was performed to analyze the effect of humidity on the radiative heat transfer. The predicted temperature was overestimated when the numerical model neglected thermal radiation. Therefore, it indicated that thermal radiation should be considered when modeling the containment thermohydraulic.
O, was performed by comparing the transient profile of pressure, gas molar fraction, and temperature with the experimental data. A Weighted Sum of Gray Gases (WSGG) model was implemented in the OpenFOAM solver. The numerical results showed a reasonable agreement compared to the experimental data. In addition, the numerical simulation with various water vapor mass fractions, i.e., 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and 60%, was performed to analyze the effect of humidity on the radiative heat transfer. The predicted temperature was overestimated when the numerical model neglected thermal radiation. Therefore, it indicated that thermal radiation should be considered when modeling the containment thermohydraulic.
福田 航大
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 208(1), p.110748_1 - 110748_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Windscale Works criticality accident in 1970 resulted from mixing an aqueous solution with an organic solvent with different plutonium concentrations and densities. Although this accident has been studied using improved computer capabilities in recent years, a precise criticality scenario has not yet been identified. This study aims to clarify a possible criticality scenario of the accident-the time variation of reactivity and its mechanism. The accident was simulated by combining the multiphase computational fluid dynamics solver of OpenFOAM and the delta-tracking-based Monte Carlo neutron transport code Serpent2. Consequently, the periodic uneven arrangement of fluids might have caused oscillations in neutron leakage and absorption, resulting in periodic wavy reactivity changes. Furthermore, the emulsion, which was thought to be the primary cause, might not be the dominant mechanism for reactivity change, although it contributed to the criticality of the accident.
 = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
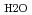 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and 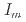 = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; 安楽 総太郎; 笹本 広; 三原 守弘
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)水和した単量体シリカ(Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 及びSiO
及びSiO (OH)
(OH)
 )及び脱水状態を想定した単量体シリカ(SiO
)及び脱水状態を想定した単量体シリカ(SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 及びSiO
及びSiO
 )化学種の状態パラメータに関わる修正Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers式(r-H-K-F EoS)と熱力学特性は、シリカを含む全ての構成物の生成及び分解反応におけるpH、組成、温度及び圧力依存性を表すために幅広く用いられている。そのため、水和及び脱水状態の単量体シリカ化学種の生成反応に関わる平衡定数の実験値を文献から収集し、イオン相互作用理論に基づきイオン強度0へ外挿し、熱力学特性及びr-H-K-F EoSパラメータを導出した。同一の研究で全ての生成反応を考慮することで、単量体シリカ化学種の熱力学特性及びr-H-K-F EoSパラメータが見直され、これにより、温度=0.01-100
)化学種の状態パラメータに関わる修正Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers式(r-H-K-F EoS)と熱力学特性は、シリカを含む全ての構成物の生成及び分解反応におけるpH、組成、温度及び圧力依存性を表すために幅広く用いられている。そのため、水和及び脱水状態の単量体シリカ化学種の生成反応に関わる平衡定数の実験値を文献から収集し、イオン相互作用理論に基づきイオン強度0へ外挿し、熱力学特性及びr-H-K-F EoSパラメータを導出した。同一の研究で全ての生成反応を考慮することで、単量体シリカ化学種の熱力学特性及びr-H-K-F EoSパラメータが見直され、これにより、温度=0.01-100 C、圧力=1-3000 bars,水の密度=0.35-1.1 g cm
C、圧力=1-3000 bars,水の密度=0.35-1.1 g cm の条件において、十分に合致するようになった。これらの温度・圧力は、放射性廃棄物の地層処分が想定される深さ1km程度までの温度(0.01-100
の条件において、十分に合致するようになった。これらの温度・圧力は、放射性廃棄物の地層処分が想定される深さ1km程度までの温度(0.01-100 C)及び圧力(1-270 bars)を包括している。
C)及び圧力(1-270 bars)を包括している。
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 柴本 泰照; 丸山 結
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
, 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
原子力安全の継続的な改善のためにはリスク情報と不確かさ情報を活用した合理的な意思決定が重要であり、近年ではこれを効率的に実施するために人工知能/機械学習(AI/ML)を活用することが期待されている。本報では、原子力分野におけるAI/MLの活用例を調査し、日本原子力研究開発機構が行うAI/MLを活用した動的確率論的リスク評価(PRA)と不確かさ評価・感度解析の研究状況を紹介する。具体的には、決定論的解析コードと機械学習による代替評価モデルを柔軟に共用できる多忠実シミュレーション手法を構築することで、ランダムサンプリングを用いた動的PRAとソースターム不確かさ評価・グローバル感度解析の効率的な実施を可能とした。
杉浦 佑樹; 石寺 孝充; 青柳 登; Mei, H.; 斉藤 拓巳*; 舘 幸男
Applied Clay Science, 258, p.107476_1 - 107476_10, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:69.91(Chemistry, Physical)This study performed batch sorption experiments using Eu and Sm as chemical analogs of trivalent actinides to evaluate their sorption behavior onto illite in the presence of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC). The results were analyzed using a thermodynamic sorption model (TSM), which predicted that Eu/Sm forms ternary-surface complexes with carbonate ions. Time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) measurements were performed to gather information on the chemical forms of sorbed Eu on illite. Parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) of the TRLFS data indicated the presence of two Eu chemical species. The pH dependence of the chemical species was consistent with that of the surface species predicted by TSM. The dominant chemical species in the presence of carbonate was inferred to be coordinating carbonate ions based on the fluorescence lifetime, supporting the validity of the TSM.
寺田 敦彦; 永石 隆二
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(8), p.1135 - 1154, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)天井と側面に換気口を設けた部屋の床面から漏洩した水素の挙動について、CFD解析を用いて実験結果との照合を行うことで、部屋周囲の風況による影響を明らかにした。室内の水素濃度の経時変化は、天井と床面付近の間で成層化がみられ、計算結果については局所的な流れ場の特性変化を反映できる乱流モデルと比較的大きな乱流シュミット数(1.0)を組み合わせた場合に実験結果の再現性が向上した。風況によって、室内に水素が滞留したケースについて、天井開口部にシンプルな板を設置することで換気の改善が図れることを示した。
Li, C.-Y.; 渡部 晃*; 内堀 昭寛; 岡野 靖
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.935 - 957, 2024/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)For all the nuclear reactor systems, quantitative assessment of the accident management (AM) effects against long-term external hazards became one of the essential issues after the lesson learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. However, the influence from the safety systems' stochastic and dynamic shifting between multiple working states, which is related to the interaction with the adjacent components/systems in general, has not been accounted for yet. Therefore, this research aims to develop a dynamic probability risk assessment tool considering repairable multi-component interdependency for investigating the AM influences on the multi-state safety systems under long-term external hazards. Based on the newly proposed methodology in this research via integrating the Petri Net (PN) model with the continuous Markov chain Monte Carlo (CMMC) method, a framework applying PN-CMMC methodology to a severe accident analysis code, SPECTRA, had been originally constructed. Different AM influences on the multi-state decay heat removal systems against long-term volcanic ashfall were also quantitatively confirmed, indicating that halving the repairing time is more influential in suppressing the core damage frequency than doubling the number of adjacent electricity support systems. Therefore, the PN-CMMC-SPECTRA framework can further assess the uncharted dynamic multi-state concerns, leading to a safer AM strategy.
Li, L.*; 宮本 吾郎*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; 諸岡 聡; 及川 勝成*; 友田 陽*; 古原 忠*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation (DT) of austenite ( ) to ferrite (
) to ferrite ( ) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with
) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with  +
+ duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in
duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in  +
+ two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.
two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.  to
to  DT during isothermal compression and
DT during isothermal compression and  to
to  reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between
reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between  and
and  was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft
was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft  phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the
phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the  to
to  transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
伊藤 孝; 門野 良典*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose a model to describe the fluctuations in the internal magnetic field due to ion dynamics observed in muon spin relaxation ( SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter
SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter  (where
(where 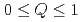 ). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the
). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the  SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI
SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI [with FA referring to HC(NH
[with FA referring to HC(NH )
) ], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI
], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with
lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with 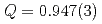 , and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying
, and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying  SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
広田 憲亮; 中野 寛子; 藤田 善貴; 武内 伴照; 土谷 邦彦; 出村 雅彦*; 小林 能直*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
沸騰水型原子炉を模擬した高温高圧水中環境下では、溶存酸素量(DO)の変化により動的ひずみ時効(DSA)と粒界型応力腐食割れ(粒界SCC)がそれぞれ発生する。これらの現象の違いを明確に理解するために、その発生メカニズムを整理した。その結果、SUS304ステンレス鋼では、DOが1ppb未満の低濃度では粒内割れによるDSAが発生し、DOが100 8500ppbでは表面の酸化膜形成によりDSAは抑制されることがわかった。一方、DOが20000ppbまで上昇すると、皮膜が母材から剥離し、母材の結晶粒界に酸素元素が拡散し、粒界SCCが発生した。これらの結果から、DSAや粒界SCCによるクラック発生を抑制するためには、最適なDO濃度を調整する必要があることが示唆された。
8500ppbでは表面の酸化膜形成によりDSAは抑制されることがわかった。一方、DOが20000ppbまで上昇すると、皮膜が母材から剥離し、母材の結晶粒界に酸素元素が拡散し、粒界SCCが発生した。これらの結果から、DSAや粒界SCCによるクラック発生を抑制するためには、最適なDO濃度を調整する必要があることが示唆された。
沖田 将一朗; 後藤 実
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The recently released JENDL-5 and ENDF/B-VIII.0 have adopted porosity-dependent thermal neutron scattering law (TSL) data for reactor graphite, and they improve neutronic calculation accuracy of criticality for graphite-moderated cores. Currently, we can only handle neutronic calculations for three graphite porosities of 0%, 10%, and 30%. The uncertainties associated with the difference between the porosity of actual reactor graphite ( 20%) and the porosity remains. Toward the future update of JENDL-5, we are planning to preparing new TSL data of reactor graphite. As a first step, it is essential to evalute phonon density state distribution of reactor graphite. In this study, in order to evalute it, molecular dynamic (MD) analysis is performed for three MD models: ideal crystalline graphite (Ideal model), 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore (Monoatomic random model), and 20%-porous reactor graphite with atomic cluster random pore (Cluster random model). The ideal crystalline graphite is modeled without any pores for reference. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore is modeled by randomly removing atoms from the ideal crystalline graphite. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with cluster random pore is modeled by randomly removing atomic clusters of approximately 2 nm in diameter from the ideal crystalline graphite. Their interatomic interactions are on the basis of Reactive Empirical Bond Order (REBO) potential. Velocity autocorrelation functions and phonon density of states distributions are calculated for these models. For validation, specific heat for each model is evaluated, and they are compred with experimental values.
20%) and the porosity remains. Toward the future update of JENDL-5, we are planning to preparing new TSL data of reactor graphite. As a first step, it is essential to evalute phonon density state distribution of reactor graphite. In this study, in order to evalute it, molecular dynamic (MD) analysis is performed for three MD models: ideal crystalline graphite (Ideal model), 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore (Monoatomic random model), and 20%-porous reactor graphite with atomic cluster random pore (Cluster random model). The ideal crystalline graphite is modeled without any pores for reference. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore is modeled by randomly removing atoms from the ideal crystalline graphite. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with cluster random pore is modeled by randomly removing atomic clusters of approximately 2 nm in diameter from the ideal crystalline graphite. Their interatomic interactions are on the basis of Reactive Empirical Bond Order (REBO) potential. Velocity autocorrelation functions and phonon density of states distributions are calculated for these models. For validation, specific heat for each model is evaluated, and they are compred with experimental values.
久保 光太郎; Zheng, X.; 田中 洋一; 玉置 等史; 杉山 智之; Jang, S.*; 高田 孝*; 山口 彰*
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 237(5), p.947 - 957, 2023/10
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:53.83(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)確率論的リスク評価(Probabilistic Risk Assessment: PRA)は、大規模かつ複雑なシステムのリスクを評価するために用いられる手法である。しかし、従来のイベントツリーやフォールトツリーを用いたPRAでは、原子力発電所の構造物、系統及び機器が損傷するタイミングを考慮することは困難である。そこで、この課題を解決するために、RAPID(Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics)を用いて、熱水力解析と外部事象のシミュレーションを組み合わせた手法を提案した。加圧水型原子炉のタービン建屋内での内部溢水を表現するために、ベルヌーイの定理に基づいた溢水伝播モデルを適用した。加えて、溢水源の流量や緩和システムの故障基準などの不確実さを考慮した。シミュレーションでは、運転員がいくつか簡略化を行うことにより、運転員による溢水源の隔離操作と排水ポンプを用いた回復操作をモデル化した。その結果、隔離と排水を組み合わせることで、溢水発生時の条件付炉心損傷確率を約90%低減できることが示された。
 (cr) at 318 K in the presence of iron
(cr) at 318 K in the presence of iron吉田 泰*; 北村 暁; 澁谷 早苗*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.900 - 910, 2023/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concentration of Se equilibrated with FeSe (cr) was determined by solubility experiments under reducing conditions and 318
(cr) was determined by solubility experiments under reducing conditions and 318  1 K. Agreement between the solubility data obtained from the over and under saturation directions suggested the attainment of equilibrium. FeSe
1 K. Agreement between the solubility data obtained from the over and under saturation directions suggested the attainment of equilibrium. FeSe (cr) phase only formed. The log
(cr) phase only formed. The log
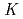
 values of -5.0
values of -5.0  1.4 and -14.9
1.4 and -14.9  1.5 for the FeSe
1.5 for the FeSe (cr) solubility reactions respectively were determined. Moreover, the selenium solubility was discussed. At the experimental conditions corresponding to the typical pH and Eh of anoxic groundwater and the equilibrium with stable FeSe
(cr) solubility reactions respectively were determined. Moreover, the selenium solubility was discussed. At the experimental conditions corresponding to the typical pH and Eh of anoxic groundwater and the equilibrium with stable FeSe (cr), the Se solubilities were remained as constant in spite of the linear relationship between iron concentrations with pH. This indicated that Se was consumed before the formation of FeSe
(cr), the Se solubilities were remained as constant in spite of the linear relationship between iron concentrations with pH. This indicated that Se was consumed before the formation of FeSe (cr). This behavior indicated that consideration of reaction paths to equilibrium with FeSe
(cr). This behavior indicated that consideration of reaction paths to equilibrium with FeSe (cr) is necessary for an estimation of Se solubility for performance assessment in geological disposal system.
(cr) is necessary for an estimation of Se solubility for performance assessment in geological disposal system.
久保 光太郎
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2023, p.7402217_1 - 7402217_12, 2023/06
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is an effective methodology that could be used to improve the safety of nuclear power plants in a reasonable manner. Dynamic PRA, as an advanced PRA allows for more realistic and detailed analyses by handling time-dependent information. However, the applications of this method to practical problems are limited because it remains in the research and development stage. This study aimed to investigate the possibility of utilizing dynamic PRA in risk-informed decision-making. Specifically, the author performed an accident sequence precursor (ASP) analysis on the failure of emergency diesel generators that occurred at Unit 1 of the Tomari Nuclear Power Plant in Japan using dynamic PRA. The results were evaluated by comparison with the results of simplified classical PRA. The findings indicated that dynamic PRA may estimate lower risks compared with those obtained from classical PRA by reasonable modeling of alternating current power recovery. The author also showed that dynamic PRA can provide detailed information that cannot be obtained with classical PRA, such as uncertainty distribution of core damage timing and importance measure considering the system failure timing.
Li, C.-Y.; 渡部 晃*; 内堀 昭寛; 岡野 靖
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Quantitative assessment of the effect of accident management on the various external hazards is essential in the nuclear safety analysis. This study aims to establish the dynamic probabilistic risk assessment methodology for sodium-cooled fast reactors that can consider the transient plant status under continuous external hazards with corresponding countermeasures operating stochastically. Specifically, the Continuous Markov chain Monte Carlo (CMMC) and Deterministic and Stochastic Petri Nets (DSPN) methods are newly applied to the severe accident analysis code, SPECTRA, which can conduct dynamic plant evaluation in the different severe accident conditions of nuclear reactors, to develop an evaluation methodology for typical external hazards. In the DSPN-CMMC-SPECTRA coupled frame, the latest safety functions of the plant components/systems can be stochastically determined by the DSPN-CMMC grounded on the current plant states under continuous hazard and the interaction between the multi-state components/systems; then, SPECTRA can evaluate the following plant state determined by the latest safety function of the components/systems. Therefore, the advantage of this newly developed DSPN-CMMC-SPECTRA frame is having the capability to quantitatively and stochastically evaluate the transient accident progressions that potentially lead to the core damage under the continuous external hazard scenario. As for the preliminary exam on the DSPN-CMMC-SPECTRA frame, one of the typical external hazards of continuous volcanic ashfall is selected in this research. In addition, the numerical investigation of alternative accident management' effects has also been carried out and quantitatively confirmed in this research.
久保 光太郎; Jang, S.*; 高田 孝*; 山口 彰*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.359 - 373, 2023/04
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:81.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)確率論的リスク評価(PRA)は、原子力発電所の安全性を向上させるための重要なアプローチである。しかし、この手法では、複合ハザードのモデル化は困難である。地震に起因した溢水シナリオでは、地震による炉心損傷、溢水による炉心損傷、地震と溢水が組み合わさった炉心損傷といった複数の炉心損傷シーケンスを含んでいる。溢水に係るフラジリティは、溢水がタンクなどの水源から区画に伝播するため、時間依存性を有している。そのため、現実的なリスク評価及び定量化を行うためには、動的リスク評価を用いる必要がある。本研究では、地震,溢水,熱水力シミュレーションを連成させ、複数ハザード間の依存関係を明示的に考慮し、地震起因溢水のリスク評価を行った。特に、福島第一原子力発電所事故を踏まえた安全性向上対策に注目し、システムの耐力に関する感度解析と可搬型ポンプを用いた蒸気発生器代替注水の効果を評価した。我々は、シミュレーションに基づく動的PRA手法の複合ハザード起因のリスクの評価への使用を実証した。
奥村 拓馬*; 橋本 直; 他40名*
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.173001_1 - 173001_7, 2023/04
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:84.12(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To test bound-state quantum electrodynamics (BSQED) in the strong-field regime, we have performed high-precision X-ray spectroscopy of the 5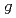 -4
-4 and 5
and 5 -4
-4 transitions (BSQED contribution of 2.4 eV and 5.2 eV, respectively) of muonic neon atoms in the low-pressure gas phase without bound electrons. Muonic atoms have been recently proposed as an alternative to few-electron high-Z ions for BSQED tests by focusing on circular Rydberg states where nuclear contributions are negligibly small. We determined the
transitions (BSQED contribution of 2.4 eV and 5.2 eV, respectively) of muonic neon atoms in the low-pressure gas phase without bound electrons. Muonic atoms have been recently proposed as an alternative to few-electron high-Z ions for BSQED tests by focusing on circular Rydberg states where nuclear contributions are negligibly small. We determined the 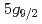 -
-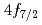 transition energy to be 6297.08
transition energy to be 6297.08  0.04 (stat.)
0.04 (stat.)  0.13 (syst.) eV using superconducting transition-edge sensor microcalorimeters (5.2-5.5 eV FWHM resolution), which agrees well with the most advanced BSQED theoretical prediction of 6297.26 eV.
0.13 (syst.) eV using superconducting transition-edge sensor microcalorimeters (5.2-5.5 eV FWHM resolution), which agrees well with the most advanced BSQED theoretical prediction of 6297.26 eV.
山本 智彦; 加藤 篤志; 早川 雅人; 下山 一仁; 荒 邦章; 畠山 望*; 山内 和*; 江田 優平*; 由井 正弘*
Proceedings of 2023 International Congress on Advanced in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/04
In the secondary cooling system of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), a rapid detection of hydrogen explosion due to sodium-water reaction by water leakage from heat exchanger tube is steam generator (SG) is important in terms of safety and property protection. For the hydrogen detection, Ni-membrane hydrogen detectors using atomic transmission phenomenon were used in Japanese proto-type sodium-cooled fast reactor "Monju". However, during the plant operation, many alarms of water leakage were occurred without sodium-water reaction in relation to temperature up and down. The authors focus on the difference in composition of hydrogen and the difference between the background hydrogen under normal operation and the hydrogen generated by the sodium-water reaction and theoretically estimate the hydrogen behavior in liquid sodium by using ultra-accelerated quantum chemical molecular dynamics (UA-QCMD). As the results of theoretical estimation, dissolved H or NaH, rather than H , is the predominant form of the background hydrogen in liquid sodium, and hydrogen produced in large amounts by sodium-water reaction can exist stably as fine bubbles with a NaH layer on their surface. Currently, the authors study the new hydrogen detector system focusing on the difference between the background hydrogen (dissolved H) and the hydrogen by sodium-water reaction (fine bubbles H
, is the predominant form of the background hydrogen in liquid sodium, and hydrogen produced in large amounts by sodium-water reaction can exist stably as fine bubbles with a NaH layer on their surface. Currently, the authors study the new hydrogen detector system focusing on the difference between the background hydrogen (dissolved H) and the hydrogen by sodium-water reaction (fine bubbles H ). This paper describes the comparison between the theoretical estimation and experimental results based on hydrogen form in sodium.
). This paper describes the comparison between the theoretical estimation and experimental results based on hydrogen form in sodium.