Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yuki, Kohei*; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Yuki, Kazuhisa*
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Fuel debris in the Fukushima Nuclear Power Station is cooled under immersion condition. However, in the event of an unexpected decrease in water level, coolant contacts high-temperature fuel debris having porous structure. In this event, although fuel debris needs to be cooled rapidly, thermal behavior at liquid-solid contact, such as capillary phenomenon, remains unclear. In this paper, as basic research, we evaluate droplet evaporation characteristics after contact with metal porous media with small pores less than 1 mm. In experiment, to obtain life time curve of a droplet, bronze or stainless steel porous media having 1, 40, or 100  m pore diameter are utilized. Experimental results show that Leidenfrost phenomenon is suppressed on the porous surfaces because generated vapor can be discharged from the pores. Further, for bronze porous media, capillary phenomenon is observed as the temperature of the porous media increase because of generation of oxide film having fine structure. On the other hand, due to low wettability of stainless steel porous media, capillary phenomenon does not occur, and the droplet was not sucked and spread into pore. This indicates that rapid cooling by the capillary phenomenon can not be expected if fuel debris has the same characteristics as the stainless steel porous media.
m pore diameter are utilized. Experimental results show that Leidenfrost phenomenon is suppressed on the porous surfaces because generated vapor can be discharged from the pores. Further, for bronze porous media, capillary phenomenon is observed as the temperature of the porous media increase because of generation of oxide film having fine structure. On the other hand, due to low wettability of stainless steel porous media, capillary phenomenon does not occur, and the droplet was not sucked and spread into pore. This indicates that rapid cooling by the capillary phenomenon can not be expected if fuel debris has the same characteristics as the stainless steel porous media.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wells, S. R.*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In this study, triple and double resonance ionization schemes of atomic Ca were developed, aiming for the separation of odd isotopes by (i) laser polarization-dependent selection rules, and (ii) large isotope shifts of odd Ca isotopes in the Rydberg levels. Separation of odd isotopes was confirmed under the orthogonal condition. Suppression of non-resonant ionization of  Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of
Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of  Ca.
Ca.
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2024-031, 75 Pages, 2024/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research on radioactive aerosol control and decontamination at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station decommissioning" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop a safe laser decontamination system that can control aerosol diffusion during laser decontamination while simultaneously allowing advanced particle measurement and evaluation, in cooperation with a research group in the United Kingdom.
Riyana, E. S.; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Kanno, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.269 - 276, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 41(1), p.119 - 126, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:42.60(Optics)Calcium Rydberg levels are of significant interest for efficient and isotope-selective resonance ionization of trace radionuclides such as calcium-41 ( Ca). In this study, we report novel measurement data on the energy level shifts of calcium-43 (
Ca). In this study, we report novel measurement data on the energy level shifts of calcium-43 (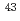 Ca) for 4sns
Ca) for 4sns  S
S and 4s(n-1)d
and 4s(n-1)d  D
D (n=40, 45, 50, 55, 60) Rydberg levels due to hyperfine-induced singlet-triplet mixing specific to isotopes with an odd mass number.
(n=40, 45, 50, 55, 60) Rydberg levels due to hyperfine-induced singlet-triplet mixing specific to isotopes with an odd mass number.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kawashima, Shigeto*; Kajino, Mizuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.743 - 758, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)An accurate estimation of radionuclides released during the Fukushima accident is essential. Therefore, authors investigated Te release using the Unit emission-regression estimation method, in which the deposition distribution is weighted based on the hourly deposition obtained from mesoscale meteorological model calculations assuming Unit emissions. The previous study focused on confirming the applicability of this method. Subsequent examination revealed that if any part of the time when a release have occurred is missing from the estimated release period, the entire source term calculation will be distorted. Therefore, this study performed the recalculation by extending the estimation period to cover all major releases. Consequently, unspecified release events were clarified, and their correspondence to in-core events was confirmed. The 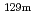 Te release caused by Zr cladding complete oxidation can explain the regional dependence of the
Te release caused by Zr cladding complete oxidation can explain the regional dependence of the 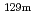 Te/
Te/ Cs ratio in the soil contamination map.
Cs ratio in the soil contamination map.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 28, 5 Pages, 2023/05
We implemented and investigated the data assimilation (DA) of two-dimensional isotropic turbulence using the lattice Boltzmann method and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LBM-LETKF). We carried out the numerical experiment with 256 grids, 256
grids, 256 or less observation points, 10% root mean square (RMS) observation noise in the velocity observation, and 4, 16, or 64 ensemble members. The numerical experiment showed that the accuracy of the LETKF was better than the nudging DA with both dense and sparse observation. The lack of observation points caused the numerical instability in the LETKF, but such a numerical instability can be suppressed by increasing the number of ensemble members. In the sparse observation case (8
or less observation points, 10% root mean square (RMS) observation noise in the velocity observation, and 4, 16, or 64 ensemble members. The numerical experiment showed that the accuracy of the LETKF was better than the nudging DA with both dense and sparse observation. The lack of observation points caused the numerical instability in the LETKF, but such a numerical instability can be suppressed by increasing the number of ensemble members. In the sparse observation case (8 8 observation points) with 64 ensemble members, the root means squared error (RMSE) of the velocity in the LBM-LETKF was smaller than the RMS of the observation noise, while the nudging DA required 32
8 observation points) with 64 ensemble members, the root means squared error (RMSE) of the velocity in the LBM-LETKF was smaller than the RMS of the observation noise, while the nudging DA required 32 32 observation points to obtain the same accuracy. Overall, the LETKF with sufficiently large number of ensemble members was highly accurate and robust, thus, the LETKF was a good choice for the DA of turbulent flows using the LBM.
32 observation points to obtain the same accuracy. Overall, the LETKF with sufficiently large number of ensemble members was highly accurate and robust, thus, the LETKF was a good choice for the DA of turbulent flows using the LBM.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-061, 59 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research on radioactive aerosol control and decontamination at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station decommissioning" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop a safe laser decontamination system that simultaneously incorporates an advanced particle detection and characterization system together with aerosol dispersion control in collaboration with the UK researchers. By using the UK partner's fundamental studies related to aerosol and water interface interactions, various methods such as electro-chemical processing of water-mist particles and spray droplets will be applied for effective control of ultra-fine aerosol particle dispersions in a large containment volume.
Porcheron, E.*; Leblois, Y.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Molina, D.*; Suteau, C.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Roulet, D.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
One of the important challenges for the decommissioning of the damaged reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is the fuel debris retrieval. The URASOL project, which is undertaken by a French consortium consisting of ONET Technologies, CEA, and IRSN for JAEA/CLADS, is dedicated to acquiring basic scientific data on the generation and characteristics of radioactive aerosols from the thermal or mechanical processing of fuel debris simulant. Heating process undertaken in the VITAE facility simulates some representative conditions of thermal cutting by LASER. For mechanical cutting, the core boring technique is implemented in the FUJISAN facility. Fuel debris simulants have been developed for inactive and active trials. The aerosols are characterized in terms of mass concentration, real time number concentration, mass size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties. The chemical characterization aims at identifying potential radioactive particles released and the associated size distribution, both of which are important information for assessing possible safety and radioprotection measures during the fuel debris retrieval operations at 1F.
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 223, p.108503_1 - 108503_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:81.06(Engineering, Industrial)Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We developed GPU implementation of ensemble data assimilation (DA) using the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). The performance test was carried out upto 32 ensembles of two-dimensional isotropic turbulence simulations using the D2Q9 LBM. The computational cost of the LETKF was less than or nearly equal to that of the LBM upto eight ensembles, while the former exceeded the latter at larger ensembles. At 32 ensembles, their computational costs per cycle were respectively 28.3 msec and 5.39 msec. These results suggested that further speedup of the LETKF is needed for practical 3D LBM simulations.
Riyana, E. S.; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.424 - 430, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ogawa, Hiroki; Hama, Yuki*; Asamori, Koichi; Ueda, Takumi*
Butsuri Tansa, 75, p.38 - 55, 2022/00
In the magnetotelluric (MT) method, so as to identify the subsurface resistivity structure, the apparent resistivity and phase profiles are calculated by transforming time-series data into spectral data. The continuous wavelet transform (CWT) is well known as a new method of time-frequency analysis instead of the short-time Fourier transform. The CWT is superior in processing non-stationary wideband signals like the MT signal by adjusting the size of the wavelet according to the value of frequency. However, the calculation settings of the CWT, such as the type of basis function and the wavelet parameter, are often determined empirically because of the arbitrariness of the shape of the wavelet. Although there might be differences between the calculated MT responses and the true responses due to improper settings of the CWT, there are no detailed studies considering the effect of numerical errors derived from spectral transforms on MT data. In this study, focusing on the frequency band between 0.001 Hz and 1 Hz, we examined the optimum calculation settings of the CWT in processing MT data in terms of suppressing the numerical errors caused by the spectral transform of time-series data. We also show the validity of the proposed calculation settings by applying the CWT to MT survey data of different types. Superiority of the CWT with proposed settings is suggested especially when the signal-to-noise ratio of observed data is low. Consequently, the proposed calculation settings were confirmed to strike a balance between the resolutions of the time and frequency domains well and will therefore be effective in obtaining reliable MT responses.
 C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditions
C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditionsHidaka, Akihide
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.341 - 356, 2021/10
Soba, A.*; Prudil, A.*; Zhang, J.*; Dethioux, A.*; Han, Z.*; Dostal, M.*; Matocha, V.*; Marelle, V.*; Lasnel-Payan, J.*; Kulacsy, K.*; et al.
Proceedings of TopFuel 2021 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/10
Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Junichi*; Ito, Masahiro*; Ishitani, Ikuo*; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Otsuka, Satoshi
Nuclear Technology, 207(8), p.1280 - 1289, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Computer codes for irradiation behavior analysis of a fuel pin and a fuel pin bundle and for coolant thermal hydraulics analysis were coupled into an integrated code system. In the system, each code provides data required by other codes and the analyzed results are shared among them. The system allows for the synthesizing of analyses of thermal, chemical and mechanical behaviors in a fuel subassembly under irradiation. A test analysis was made for a fuel subassembly containing a mixed oxide fuel pin bundle irradiated in a fast reactor. The results of the analysis were presented with transverse cross-sectional images of the fuel subassembly and three-dimensional images of a fuel pin and fuel pin bundle models. For detailed evaluation, various irradiation behaviors of all fuel pins in the subassembly were analyzed and correlated with irradiation conditions.
Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Amaya, Masaki
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 155, p.108171_1 - 108171_11, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yokoyama, Kenji; Jin, Tomoyuki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-001, 47 Pages, 2021/03
A new burnup/depletion calculation code, CRAMO, was developed by combining an ORIGEN2 cross-section library set, ORLIB, based on Japanese evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL, and a burnup/depletion solver based on Chebyshev rational approximation method. CRAMO uses the ORIGEN2 cross-section library set ORLIBJ40 based on JENDL-4.0, and the burnup/depletion solver implemented in the versatile reactor analysis code system, MARBLE. It was confirmed that results of CRAMO agreed well with those of ORIGEN2 for burnup/depletion and radioactivity calculation cases. The development of CRAMO made it possible to use ORLIB without using ORIGEN2. It will be possible to provide an easy-to-use processed JENDL data set for burnup/depletion and radioactivity calculations in combination with a burnup/depletion based on Chebyshev rational approximation method. The present version of CRAMO is a subset of ORIGEN2 and can compute only compositions and radioactivities after irradiation. However, since various kinds of outputs of ORIGEN2 can be evaluated by using the composition, it is possible to reproduce many functions of ORIGEN2 by adding post-processing modules.
Miake, Yasuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011114_1 - 011114_8, 2021/03
Having the QGP formation confirmed at RHIC and LHC, the next step of the research is to look for the critical end point and the first order phase boundary. For this purpose, new heavy ion acceleration schema to obtain  10 AGeV heavy ion beam has been proposed in Germany, Russia, China and Japan. Unlike at the RHIC 200 GeV and LHC, the heavy ion collisions of
10 AGeV heavy ion beam has been proposed in Germany, Russia, China and Japan. Unlike at the RHIC 200 GeV and LHC, the heavy ion collisions of 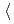
 10 AGeV region, the matter should have larger
10 AGeV region, the matter should have larger 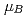 , and we may reach the region of the interest. J-PARC is the high intensity proton accelerator at the energy of 30 GeV. With an additional heavy ion injector, high intensity heavy ion beams can be obtained. Superior performance of the J-PARC-HI scheme and proposed experiments are discussed.
, and we may reach the region of the interest. J-PARC is the high intensity proton accelerator at the energy of 30 GeV. With an additional heavy ion injector, high intensity heavy ion beams can be obtained. Superior performance of the J-PARC-HI scheme and proposed experiments are discussed.