Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
Fujita, Tatsuya; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(2), p.179 - 196, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study newly established a direct coupling code system consisting of the nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 2, and the three-dimensional heterogeneous transport code GENESIS (FRENDY-V2/GENESIS) for easy implementation of the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification considering the implicit effect due to nuclear cross-section (XS) perturbations. The multi-group macroscopic XSs prepared for GENESIS were generated by FRENDY version 2, where the Dancoff factor was calculated by the neutron current method. Then the background XSs were evaluated based on the Carlvik two-term rational approximation. The infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) and the fission reaction rate distribution in UO and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
Nagaya, Yasunobu
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 11, p.1_1 - 1_7, 2025/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing a general-purpose continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP for nuclear reactor core analysis. Recently improvements to MVP have been focused on the development of an advanced neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling code. JAEA has also developed a new Monte Carlo solver Solomon for criticality safety analysis. Solomon aims to calculate the criticality of a damaged reactor core including fuel debris. This paper provides an overview of the capabilities and reviews recent applications of MVP and Solomon.
Kamiya, Tomohiro; Nagatake, Taku; Ono, Ayako; Tada, Kenichi; Kondo, Ryoichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/11
We have developed the JAEA Advances Multi-Physics Analysis platform for Nuclear systems (JAMPAN) to realize high-fidelity neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling simulations. We will perform MVP/JUPITER coupling simulation for a single BWR fuel assembly in order to confirm that the neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling through JAMPAN is feasible. This presentation explains how to send and receive data between MVP and JUPITER through JAMPAN and simulation results.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Kawai, Hiromi*; Wakisaka, Shinji*; Nagase, Sota*; Nakamura, Kento*; Yaguchi, Hiroki*; Ishii, Toshiaki; Nakano, Yumi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-008, 23 Pages, 2024/07
Five people from three universities participated in the 2023 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the analysis of HTTR core, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, the analysis of Iodine deposition behavior in primary cooling system and the feasibility study of energy storage system for HTGRs. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience and some students found it useful for their own research. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Suzuki, Motomu*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.177 - 191, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)With the release of the latest Japanese evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5, the prediction accuracy of JENDL-5 for neutronics parameters of the BEAVRS benchmark for the hot zero power condition was evaluated in this study. The criticality, control rod bank worth (CRW), isothermal temperature coefficient (ITC), and in-core detector signals were calculated and compared with the measured data for evaluation. For the criticality, the calculation-to-experimental (C/E) values varied between 1.0001 and 1.0045. Sensitivity analysis by replacing cross section data from the JENDL-4.0u1 with JENDL-5 revealed that 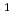 H,
H,  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  O significantly affected the criticality. The individual CRW agreed within 50 pcm, and total CRW also agreed within 100 pcm from the measured values. The ITC results calculated with a temperature deviation of 5.56 K case were negatively overestimated comparing with the measured values; whereas those of with 2.78 K were improved and agree with the measured values within a standard deviation. The axial detector signals indicated a maximum relative error of 4.46% and the root mean squared error (RMSE) of 2.13%. The differences between the previous version of JENDL-4.0u1 and JENDL-5 were also investigated.
O significantly affected the criticality. The individual CRW agreed within 50 pcm, and total CRW also agreed within 100 pcm from the measured values. The ITC results calculated with a temperature deviation of 5.56 K case were negatively overestimated comparing with the measured values; whereas those of with 2.78 K were improved and agree with the measured values within a standard deviation. The axial detector signals indicated a maximum relative error of 4.46% and the root mean squared error (RMSE) of 2.13%. The differences between the previous version of JENDL-4.0u1 and JENDL-5 were also investigated.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The benchmark analyses on the TRIGA reactor of the IEU-COMP-THERM-013 (ICT-013) in the ICSBEP handbook using the MVP version 3 code were carried out with the Japanese, US and European nuclear data libraries, including JENDL-5. The analyses on effective neutron multiplication factors (k 's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k
's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k 's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k
's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k 's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k
's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k 's. Most of the errors involved in k
's. Most of the errors involved in k 's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k
's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k 's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ho, H. Q.; Kitagawa, Kanta*; Fukuda, Takahito*; Ito, Ryo*; Nemoto, Masaya*; Kusunoki, Hayato*; Nomura, Takuro*; Nagase, Sota*; Hashimoto, Haruki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-013, 19 Pages, 2023/06
Eight people from five universities participated in the 2022 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the feasibility study for nuclear battery, the burn-up analysis of HTTR core, the feasibility study for  Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Cf production, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, and the thermal-hydraulic analysis near reactor pressure vessel. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience, that some students found it useful for their own research, and that discussion with other university students was a good experience. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai
Proceedings of 20th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM22) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/06
Since the 1990s, the importance of the handbook has changed significantly, as the computational power has improved and continuous energy Monte Carlo codes have become widely used, which enables highly accurate criticality calculations, when necessary, irrespective of the complexity of the system. Because the value of performing a large number of calculations in advance and summarizing the data has decreased, since the second edition was published publicly in 1999, there has been no revision of criticality safety handbooks in Japan for nearly a quarter of a century. In Japan, where the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident occurred in 2011, it became necessary to deal with criticality safety issues in the transport and storage of the fuel debris which contains complex constituent elements, and the summary the criticality safety management for such material is an urgent issue. In the area of burnup credit, the transport and storage of fuel assemblies with low achieved burnups due to the consequences of accidents might be the problem. In addition, nuclear data, which is the input for the continuous energy Monte Carlo code, has been improved several times, now JENDL-5 is available from the end of 2021, and its incorporation becomes a need in the field. This report provides an overview of the latest criticality safety research in Japan and the planned revision of the Criticality Safety Handbook, which could be applied to the transport and storage sectors.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Isogawa, Hiroki*; Naoi, Motomasa*; Yamasaki, Seiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Katayama, Kazunari*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2022-015, 18 Pages, 2022/07
As a summer holiday practical training 2021, the impact of 10 years long-term shutdown on critical control rod position of the HTTR and the delayed neutron fraction (
 ) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0
) of the VHTRC-1 core were investigated using Monte-Carlo MVP code. As a result, a long-term shutdown of 10 years caused the critical control rods of the HTTR to withdraw about 4.0 0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as
0.8 cm compared to 3.9 cm in the experiment. The change in critical control rods position of the HTTR is due to the change of some fission products such as  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am, 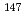 Pm,
Pm, 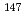 Sm,
Sm,  Gd. Regarding the
Gd. Regarding the 
 calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the
calculation of the VHTRC-1 core, the 
 value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
value is underestimate of about 10% in comparison with the experiment value.
 Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response function
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response functionSato, Shunsuke*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*; Suyama, Kenya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.615 - 623, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new non-destructive method for evaluating  Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.  Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which
Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which  Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of
Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.
Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.  Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified
Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified  Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-023, 190 Pages, 2021/11
Computational analyses on nuclear criticality characteristics were carried out for heterogeneous lattice systems composed of water moderator and fuel rods utilized in low-power research and test reactors, in which the depletion of fuel due to burnup is relatively small, by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP Version 2 with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. In the analyses, the minimum critical number of fuel rods was evaluated using calculated neutron multiplication factors for the heterogeneous systems of the uranium dioxide fuel rod in the Static Experiments Critical Facility (STACY) and the Tank-type Critical Assembly (TCA), and the uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rod in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). In addition, six sorts of the ratio of reaction rates, which are components of neutron multiplication factors, were calculated in the analyses to explain the variation of neutron multiplication factors with the ratio of water moderator to fuel volume in a unit fuel rod cell. Those results of analyses are considered to be useful for the confirmation of reasonableness and validity of criticality safety measures as data showing criticality characteristics for water-moderated heterogeneous lattice systems composed of the existing fuel rods in research and test reactors, of which criticality data are not sufficiently provided by the Criticality Safety Handbook.
Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Mitsui, Wataru*; Yamamoto, Yudai*; Nakagawa, Kyoichi*; Ho, H. Q.; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nagasumi, Satoru; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Kenzhina, I.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-016, 16 Pages, 2021/09
As a summer holiday practical training 2020, the feasibility study for nuclear design of a nuclear battery using HTTR core was carried out, and the downsizing of reactor core were studied by the MVP-BURN. As a result, it is clear that a 1.6 m radius reactor core, containing 54 (18 3 layers) fuel blocks with 20% enrichment of
3 layers) fuel blocks with 20% enrichment of  U, and BeO neutron reflector, could operate continuously for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW. Number of fuel blocks of this compact core is 36% of the HTTR core. As a next step, the further downsizing of core by changing materials of the fuel block will be studied.
U, and BeO neutron reflector, could operate continuously for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW. Number of fuel blocks of this compact core is 36% of the HTTR core. As a next step, the further downsizing of core by changing materials of the fuel block will be studied.
Ikeda, Reiji*; Ho, H. Q.; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nakano, Yumi*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Fujimoto, Nozomu*
JAEA-Technology 2021-015, 32 Pages, 2021/09
Burnup calculation of the HTTR considering temperature distribution and detailed burning regions was carried out using MVP-BURN code. The results show that the difference in k , as well as the difference in average density of some main isotopes, is insignificant between the cases of uniform temperature and detailed temperature distribution. However, the difference in local density is noticeable, being 6% and 8% for
, as well as the difference in average density of some main isotopes, is insignificant between the cases of uniform temperature and detailed temperature distribution. However, the difference in local density is noticeable, being 6% and 8% for  U and
U and  Pu, respectively, and even 30% for the burnable poison
Pu, respectively, and even 30% for the burnable poison  B. Regarding the division of burning regions to more detail, the change of k
B. Regarding the division of burning regions to more detail, the change of k is also small of 0.6%
is also small of 0.6% k/k or less. The small burning region gives a detailed distribution of isotopes such as
k/k or less. The small burning region gives a detailed distribution of isotopes such as  U,
U,  Pu, and
Pu, and  B. As a result, the effect of graphite reflector and the burnup behavior could be evaluated more clearly compared with the previous study.
B. As a result, the effect of graphite reflector and the burnup behavior could be evaluated more clearly compared with the previous study.
Ho, H. Q.; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nagasumi, Satoru; Goto, Minoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 377, p.111161_1 - 111161_9, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Nakashima, Koki*; Nakagawa, Naoki*; Ho, H. Q.; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Kenzhina, I.*; Chikhray, Y.*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-008, 16 Pages, 2020/08
As a summer holiday practical training 2019, the feasibility study for nuclear design of a nuclear battery using HTTR core was carried out, and the  U enrichment and burnable poison of the fuel, which enables continuous operation for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW, were studied by the MVP-BURN. As a result, it is clear that a fuel with
U enrichment and burnable poison of the fuel, which enables continuous operation for 30 years with thermal power of 5 MW, were studied by the MVP-BURN. As a result, it is clear that a fuel with  U enrichment of 12%, radius of burnable poison and natural boron concentration of 1.5 cm and 2wt% are required. As a next step, the downsizing of core will be studied.
U enrichment of 12%, radius of burnable poison and natural boron concentration of 1.5 cm and 2wt% are required. As a next step, the downsizing of core will be studied.
Nagasumi, Satoru; Matsunaka, Kazuaki*; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishii, Toshiaki; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2020-003, 13 Pages, 2020/05
The influence of the control rod model on the nuclear characteristics of the HTTR has been evaluated, by creating detailed control rod model, in which geometric shape was close to that of the actual control rod structure, in MVP code. According to refinement of the control rod model, the critical control rod position was 11 mm lower than that of the conventional model, and this was close to the measured value of 1775 mm. The reactivity absorbed by the shock absorber located at the tip of the control rod was 0.2% k/k, and this was 14 mm difference at the critical control rod position. Considering the effect of refinement of the control rod and the effect of the shock absorber, the correction amount for the analysis value in SRAC code due to the shape effect of the control rod, is -0.05%
k/k, and this was 14 mm difference at the critical control rod position. Considering the effect of refinement of the control rod and the effect of the shock absorber, the correction amount for the analysis value in SRAC code due to the shape effect of the control rod, is -0.05% k/k in reactivity, and -3 mm in the critical control rod position at low temperature criticality.
k/k in reactivity, and -3 mm in the critical control rod position at low temperature criticality.
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Ishii, Toshiaki; Takada, Shoji; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 6(2), p.021902_1 - 021902_6, 2020/04
Komeda, Masao; Toh, Yosuke
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 135, p.106993_1 - 106993_6, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents a conceptual study of a novel active method using a neutron source. The main feature of this new method is the fast rotation of a neutron source in order to derive the fission neutron counts and applying the counts to detect the nuclear material. Irradiating neutrons to a container that involves nuclear material, the measurement data include both neutrons from the neutron source and fission neutrons. However, if the neutron source is rotated quite fast, the components of the irradiation neutrons and fission neutrons are separated. Since this novel method does not require an expensive D-T tube, this new system is expected to be affordable and easy to assemble.