Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 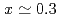
伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 幸田 章宏*; 中村 惇平*; 下村 浩一郎*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
We report on muon spin relaxation ( SR) measurements in a mixed perovskite compound, (LaAlO
SR) measurements in a mixed perovskite compound, (LaAlO )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 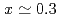 (LSAT), which is widely used as a single-crystalline substrate for thin film deposition. In zero applied field (ZF), muon depolarization due to the distribution of nuclear dipole fields was observed in the temperature range from 4 K to 270 K. Interestingly,
(LSAT), which is widely used as a single-crystalline substrate for thin film deposition. In zero applied field (ZF), muon depolarization due to the distribution of nuclear dipole fields was observed in the temperature range from 4 K to 270 K. Interestingly,  SR time spectra in ZF maintained a Gaussian-like feature over the entire range, while the depolarization rate exhibited a monotonic decrease with increasing temperature. This behavior may be attributed to the thermally activated diffusion of muons between a few adjacent sites within a confined space of the angstrom scale, where the motionally averaged local field that each muon experiences can remain non-zero and result in maintaining the Gaussian-like line shape. The spatial distribution of electrostatic potential at lattice interstices evaluated via density functional theory calculations suggests that such a restriction of muon diffusion paths can be caused by the random distribution of cations with different nominal valences in the mixed perovskite lattice.
SR time spectra in ZF maintained a Gaussian-like feature over the entire range, while the depolarization rate exhibited a monotonic decrease with increasing temperature. This behavior may be attributed to the thermally activated diffusion of muons between a few adjacent sites within a confined space of the angstrom scale, where the motionally averaged local field that each muon experiences can remain non-zero and result in maintaining the Gaussian-like line shape. The spatial distribution of electrostatic potential at lattice interstices evaluated via density functional theory calculations suggests that such a restriction of muon diffusion paths can be caused by the random distribution of cations with different nominal valences in the mixed perovskite lattice.
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
筒井 智嗣; 伊藤 孝; 中村 仁*; 吉田 実生*; 小林 義男*; 依田 芳卓*; 中村 惇平*; 幸田 章宏*; 東中 隆二*; 青木 大*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 Sm SR-based M
Sm SR-based M ssbauer and muon spin relaxation (
ssbauer and muon spin relaxation ( SR) spectroscopies have been applied to Sm
SR) spectroscopies have been applied to Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge . The temperature dependence of the
. The temperature dependence of the  Sm SR-based M
Sm SR-based M ssbauer spectra in the paramagnetic state implies the presence of dynamical nuclear Zeeman and/or quadrupole interactions. The time differential
ssbauer spectra in the paramagnetic state implies the presence of dynamical nuclear Zeeman and/or quadrupole interactions. The time differential  SR spectra also exhibit a marked temperature dependence in the paramagnetic state, indicating the presence of magnetic fluctuation in Sm
SR spectra also exhibit a marked temperature dependence in the paramagnetic state, indicating the presence of magnetic fluctuation in Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge at least. These results in the present work infer that the dynamical hyperfine interactions observed using the mutually complementary spectroscopic methods are connected with the mechanism of the heavy fermion behavior in Sm
at least. These results in the present work infer that the dynamical hyperfine interactions observed using the mutually complementary spectroscopic methods are connected with the mechanism of the heavy fermion behavior in Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge .
.
下村 浩一郎*; 幸田 章宏*; Pant, A. D.*; 砂川 光*; 藤森 寛*; 梅垣 いづみ*; 中村 惇平*; 藤原 理賀; 反保 元伸*; 河村 成肇*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
J-PARC Muon Facility: MUSE (Muon Science Establishment) is responsible for the inter-university user program and the operation, maintenance, and construction of the muon beamlines, namely D-line, S-line, U-line, and H-line, along with the muon source at J-PARC Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF). In this paper, recent developments are briefly presented.
二宮 和彦*; 久保 謙哉*; 稲垣 誠*; 吉田 剛*; 竹下 聡史*; 反保 元伸*; 下村 浩一郎*; 河村 成肇*; Strasser, P.*; 三宅 康博*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3445 - 3450, 2024/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:57.00(Chemistry, Analytical)A novel nondestructive light element analysis method for bulk materials using muon beams was demonstrated. This method is based on the lifetime measurement of muons in a material and performed by measuring muon-decay electrons and identifying elements using the atomic number based on muon lifetimes. Muon irradiation on pure iron and two steel samples with known carbon contents was conducted to prepare a calibration curve for the quantitative analysis. We also performed a muon lifetime measurement for a Japanese sword and successfully determined its carbon content as 0.51 wt% using the calibration curve, without sample destruction.
伊藤 孝; 門野 良典*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:68.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose a model to describe the fluctuations in the internal magnetic field due to ion dynamics observed in muon spin relaxation ( SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter
SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter  (where
(where 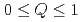 ). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the
). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the  SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI
SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI [with FA referring to HC(NH
[with FA referring to HC(NH )
) ], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI
], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with
lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with 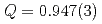 , and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying
, and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying  SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
 CoSi
CoSi山内 宏樹; Sari, D. P.*; 安井 幸夫*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 木村 宏之*; 中尾 朗子*; 大原 高志; 本田 孝志*; 樹神 克明; 井川 直樹; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
 -Mn-type family alloys Mn
-Mn-type family alloys Mn
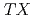 have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn
have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N
RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N el temperature
el temperature  = 190 K. Mn
= 190 K. Mn CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest
CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest  in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15
in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15 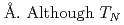 of Mn
of Mn CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn
CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient
CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient  . We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn
. We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn CoSi by using neutron scattering,
CoSi by using neutron scattering,  SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn
SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of
RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of  SR above
SR above  becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature
becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature 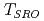 is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn
is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
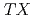 system.
system.
伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 下村 浩一郎*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:58.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In positive muon spin rotation and relaxation ( SR) spectroscopy, positive muons (
SR) spectroscopy, positive muons ( ) implanted into solid oxides are conventionally treated as immobile spin-probes at interstitial sites below room temperature. This is because each
) implanted into solid oxides are conventionally treated as immobile spin-probes at interstitial sites below room temperature. This is because each  is thought to be tightly bound to an oxygen atom in the host lattice to form a muonic analogue of the hydroxy group. On the basis of this concept, anomalies in
is thought to be tightly bound to an oxygen atom in the host lattice to form a muonic analogue of the hydroxy group. On the basis of this concept, anomalies in  SR spectra observed in oxides have been attributed in most cases to the intrinsic properties of host materials. On the other hand, global
SR spectra observed in oxides have been attributed in most cases to the intrinsic properties of host materials. On the other hand, global  diffusion with an activation energy of
diffusion with an activation energy of  0.1~eV has been reported in some chemically-substituted perovskite oxides at cryogenic temperatures, although the reason for the small activation energy despite the formation of the strong O
0.1~eV has been reported in some chemically-substituted perovskite oxides at cryogenic temperatures, although the reason for the small activation energy despite the formation of the strong O bond has not yet been quantitatively understood. In this study, we investigated interstitial
bond has not yet been quantitatively understood. In this study, we investigated interstitial  diffusion in the perovskite oxide lattice using KTaO
diffusion in the perovskite oxide lattice using KTaO cubic perovskite as a model system. We used the
cubic perovskite as a model system. We used the  SR method and density functional theory calculations along with the harmonic transition state theory to study this phenomenon both experimentally and theoretically. Experimental activation energies for global
SR method and density functional theory calculations along with the harmonic transition state theory to study this phenomenon both experimentally and theoretically. Experimental activation energies for global  diffusion obtained below room temperature were less than a quarter of the calculated classical potential barrier height for a bottleneck
diffusion obtained below room temperature were less than a quarter of the calculated classical potential barrier height for a bottleneck  transfer path. The reduction in the effective barrier height could be explained by the harmonic transition state theory with a zero-point energy correction; a significant difference in zero-point energies for
transfer path. The reduction in the effective barrier height could be explained by the harmonic transition state theory with a zero-point energy correction; a significant difference in zero-point energies for  at the positions in the O
at the positions in the O bonding equilibrium state and a bond-breaking transition state was the primary cause of the reduction. This suggests that the assumption of immobile
bonding equilibrium state and a bond-breaking transition state was the primary cause of the reduction. This suggests that the assumption of immobile  in solid oxides is not always satisfied since such a significant decrease in diffusion barrier height can also occur in other oxides.
in solid oxides is not always satisfied since such a significant decrease in diffusion barrier height can also occur in other oxides.
美崎 慧*; 三輪 寛子*; 伊藤 孝; 吉田 健文*; 長谷川 慎吾*; 中村 由紀奈*; 徳竹 駿太*; 高畠 萌*; 下村 浩一郎*; Chun, W.-J.*; et al.
ACS Catalysis, 13(18), p.12281 - 12287, 2023/09
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:48.53(Chemistry, Physical)The direct alkylation of benzenes with simple alkanes is one of the ideal processes for the production of alkylbenzenes. We demonstrated that Pd nanoparticles on the outer surface of H-ZSM-5 are efficient catalysts for direct alkylation. The reaction proceeds through the activation of an alkane on the acid sites present inside the zeolite pores. This process is followed by the nucleophilic addition of an arene to the activated alkane. The spillover of the abstracted hydrogen atoms from the acid sites to the Pd nanoparticles on the outer surface accelerates recombination to H . A maximum toluene conversion of 58.5% and selectivity of 95.6% for the alkylated products are achieved when toluene is reacted with
. A maximum toluene conversion of 58.5% and selectivity of 95.6% for the alkylated products are achieved when toluene is reacted with  -heptane.
-heptane. 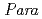 -selective alkylation is achieved, due to the effect of the pore size of H-ZSM-5. The
-selective alkylation is achieved, due to the effect of the pore size of H-ZSM-5. The  SR study of muonium, a pseudo-isotope of hydrogen, in aluminosilicates suggested that the formation of atomic hydrogen is possible and its lifetime is in the sub-microsecond range or longer, which is long enough for chemical reactions.
SR study of muonium, a pseudo-isotope of hydrogen, in aluminosilicates suggested that the formation of atomic hydrogen is possible and its lifetime is in the sub-microsecond range or longer, which is long enough for chemical reactions.
 inferred from muon study
inferred from muon study門野 良典*; 平石 雅俊*; 岡部 博孝*; 幸田 章宏*; 伊藤 孝
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285503_1 - 285503_13, 2023/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.20(Physics, Condensed Matter)Magnesium hydride has great potential as a solid hydrogen (H) storage material because of its high H storage capacity of 7.6 wt%. However, its slow hydrogenation and dehydrogenation kinetics and the high temperature of 300  C required for decomposition are major obstacles to small-scale applications such as automobiles. The local electronic structure of interstitial H in MgH
C required for decomposition are major obstacles to small-scale applications such as automobiles. The local electronic structure of interstitial H in MgH is an important fundamental knowledge in solving this problem, which has been studied mainly based on density functional theory (DFT). However, few experimental studies have been performed to assess the results of DFT calculations. We have therefore introduced muon (Mu) as pseudo-H into MgH
is an important fundamental knowledge in solving this problem, which has been studied mainly based on density functional theory (DFT). However, few experimental studies have been performed to assess the results of DFT calculations. We have therefore introduced muon (Mu) as pseudo-H into MgH and investigated the corresponding interstitial H states by analyzing their electronic and dynamical properties in detail. As a result, we observed multiple Mu states similar to those observed in wide-gap oxides, and found that their electronic states can be attributed to relaxed-excited states associated with donor/acceptor levels predicted by the recently proposed ambipolarity model. This provides an indirect support for the DFT calculations on which the model is based via the donor/acceptor levels. An important implication of the muon results for improved hydrogen kinetics is that dehydrogenation, serving as a reduction for hydrides, stabilises the interstitial H
and investigated the corresponding interstitial H states by analyzing their electronic and dynamical properties in detail. As a result, we observed multiple Mu states similar to those observed in wide-gap oxides, and found that their electronic states can be attributed to relaxed-excited states associated with donor/acceptor levels predicted by the recently proposed ambipolarity model. This provides an indirect support for the DFT calculations on which the model is based via the donor/acceptor levels. An important implication of the muon results for improved hydrogen kinetics is that dehydrogenation, serving as a reduction for hydrides, stabilises the interstitial H state.
state.

中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 岡部 博孝*; Li, B.*; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 175, p.111199_1 - 111199_8, 2023/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:14.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Muon spin rotation ( SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe
SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe . The detailed investigation of the
. The detailed investigation of the  SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
奥村 拓馬*; 橋本 直; 他40名*
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.173001_1 - 173001_7, 2023/04
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:80.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To test bound-state quantum electrodynamics (BSQED) in the strong-field regime, we have performed high-precision X-ray spectroscopy of the 5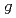 -4
-4 and 5
and 5 -4
-4 transitions (BSQED contribution of 2.4 eV and 5.2 eV, respectively) of muonic neon atoms in the low-pressure gas phase without bound electrons. Muonic atoms have been recently proposed as an alternative to few-electron high-Z ions for BSQED tests by focusing on circular Rydberg states where nuclear contributions are negligibly small. We determined the
transitions (BSQED contribution of 2.4 eV and 5.2 eV, respectively) of muonic neon atoms in the low-pressure gas phase without bound electrons. Muonic atoms have been recently proposed as an alternative to few-electron high-Z ions for BSQED tests by focusing on circular Rydberg states where nuclear contributions are negligibly small. We determined the 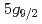 -
-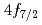 transition energy to be 6297.08
transition energy to be 6297.08  0.04 (stat.)
0.04 (stat.)  0.13 (syst.) eV using superconducting transition-edge sensor microcalorimeters (5.2-5.5 eV FWHM resolution), which agrees well with the most advanced BSQED theoretical prediction of 6297.26 eV.
0.13 (syst.) eV using superconducting transition-edge sensor microcalorimeters (5.2-5.5 eV FWHM resolution), which agrees well with the most advanced BSQED theoretical prediction of 6297.26 eV.
 SR) methods
SR) methods伊藤 孝; 下村 浩一郎*
Hydrogenomics; The Science of Fully Utilizing Hydrogen (Internet), p.43 - 49, 2023/03
A brief introduction to the muon spin rotation, relaxation, and resonance ( SR) methods is given for researchers and students involved in hydrogen science research. The text includes several examples of how the
SR) methods is given for researchers and students involved in hydrogen science research. The text includes several examples of how the  SR methods can be used to elucidate the behavior of hydrogen in materials.
SR methods can be used to elucidate the behavior of hydrogen in materials.
下村 浩一郎*; 幸田 章宏*; Pant, A. D.*; 名取 寛顕*; 藤森 寛*; 梅垣 いづみ*; 中村 惇平*; 反保 元伸*; 河村 成肇*; 手島 菜月*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)At J-PARC MUSE, since the  SR2017 conference and up to FY2022, there have been several new developments at the facility, including the completion of a new experimental area S2 at the surface muon beamline S-line and the first muon beam extraction to the H1 area in the H-line, mainly to carry out high-statistics fundamental physics experiments. Several new studies are also underway, such as applying negative muon non-destructive elemental analysis to the analysis of samples returned from the asteroid Ryugu in the D2 area of the D-line. This paper reports on the latest status of MUSE.
SR2017 conference and up to FY2022, there have been several new developments at the facility, including the completion of a new experimental area S2 at the surface muon beamline S-line and the first muon beam extraction to the H1 area in the H-line, mainly to carry out high-statistics fundamental physics experiments. Several new studies are also underway, such as applying negative muon non-destructive elemental analysis to the analysis of samples returned from the asteroid Ryugu in the D2 area of the D-line. This paper reports on the latest status of MUSE.
 ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; 金子 竜也*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
A pyrite system NiS Se
Se exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at
exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at 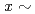 0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at
0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at 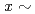 1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se)
1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se) is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
 =
=  quasikagome-lattice compound CeRh
quasikagome-lattice compound CeRh Pd
Pd Sn investigated using muon spin relaxation and neutron scattering
Sn investigated using muon spin relaxation and neutron scatteringTripathi, R.*; Adroja, D. T.*; Ritter, C.*; Sharma, S.*; Yang, C.*; Hillier, A. D.*; Koza, M. M.*; Demmel, F.*; Sundaresan, A.*; Langridge, S.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(6), p.064436_1 - 064436_17, 2022/08
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:59.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present the results of muon spin relaxation ( SR) and neutron scattering measurements on the Ce-based quasikagome lattice CeRh
SR) and neutron scattering measurements on the Ce-based quasikagome lattice CeRh Pd
Pd Sn (
Sn ( = 0.1 to 0.75). Our
= 0.1 to 0.75). Our  SR results reveal the absence of both static long-range magnetic order and spin freezing down to 0.05 K in the
SR results reveal the absence of both static long-range magnetic order and spin freezing down to 0.05 K in the  = 0.1 sample, which is consistent with neutron scattering results. The weak temperature-dependent plateaus of the dynamic spin fluctuations below 0.2 K in zero field together with its longitudinal-field (LF) dependence indicate the presence of dynamic spin fluctuations persisting even at 0.05 K without static magnetic order. We argue that such a behavior for
= 0.1 sample, which is consistent with neutron scattering results. The weak temperature-dependent plateaus of the dynamic spin fluctuations below 0.2 K in zero field together with its longitudinal-field (LF) dependence indicate the presence of dynamic spin fluctuations persisting even at 0.05 K without static magnetic order. We argue that such a behavior for  = 0.1 can be attributed to a metallic spin-liquid-like ground state near the quantum critical point in the frustrated Kondo lattice. The LF-
= 0.1 can be attributed to a metallic spin-liquid-like ground state near the quantum critical point in the frustrated Kondo lattice. The LF- SR study suggests that the out of kagome plane spin fluctuations are responsible for the spin-liquid behavior.
SR study suggests that the out of kagome plane spin fluctuations are responsible for the spin-liquid behavior.
 complex as a possible origin of localized electron behavior in hydrogen-irradiated SrTiO
complex as a possible origin of localized electron behavior in hydrogen-irradiated SrTiO
伊藤 孝
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 20(3), p.128 - 134, 2022/05
A recent muon spin rotation ( SR) study on a paramagnetic defect complex formed upon implantation of
SR) study on a paramagnetic defect complex formed upon implantation of  pseudo-proton into SrTiO
pseudo-proton into SrTiO is reviewed with a specific focus on the relation with experimental signatures of coexisting delocalized and localized electrons in hydrogen-irradiated metallic SrTiO
is reviewed with a specific focus on the relation with experimental signatures of coexisting delocalized and localized electrons in hydrogen-irradiated metallic SrTiO films. The paramagnetic defect complex, composed of interstitial
films. The paramagnetic defect complex, composed of interstitial  and Ti
and Ti small polaron, is characterized by a small dissociation energy of about 30 meV. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations in the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) +
small polaron, is characterized by a small dissociation energy of about 30 meV. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations in the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) + scheme for a corresponding hydrogen defect complex reveal that a thermodynamic donor level associated with electron transfer from an H
scheme for a corresponding hydrogen defect complex reveal that a thermodynamic donor level associated with electron transfer from an H -Ti
-Ti complex to the conduction band can form just below the conduction band minimum for realistic
complex to the conduction band can form just below the conduction band minimum for realistic  values. These findings suggest that the coexistence of delocalized and localized electrons can be realized in hydrogen-irradiated SrTiO
values. These findings suggest that the coexistence of delocalized and localized electrons can be realized in hydrogen-irradiated SrTiO in electron-rich conditions.
in electron-rich conditions.
勅使河原 誠; 中村 充孝; 金正 倫計; 曽山 和彦
JAEA-Technology 2021-022, 208 Pages, 2022/02
J-PARCの定格出力1MWの物質・生命科学実験施設において、今後の具体的かつ現実的な高度化戦略を展開するため、線源性能に大きく影響する加速器技術(リニアックおよびRCS)、線源技術、中性子・ミュオン輸送技術、検出技術、そしてそれらが結実する中性子・ミュオン ビーム利用装置等の現状(所期設計値に対する到達度)について整理した。さらに、現状分析に基づき出力増強に向けた改良点等について報告する。
二宮 和彦*; 伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 河村 成肇*; Strasser, P.*; 長友 傑*; 下村 浩一郎*; 三宅 康博*; 喜多 真琴*; 篠原 厚*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 319(3), p.767 - 773, 2019/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:73.30(Chemistry, Analytical)Per-atom muon capture ratios are precisely determined from characteristic muonic X-ray measurements of three nitrogen oxide samples (NO, N O, and NO
O, and NO ) at pressures below 100 kPa. A higher density of covalent electrons at the N atoms relative to the O atoms is required if we explain the experimental results using the proposed muon capture models. From molecular orbit calculations, we found that the electron distributions of only the highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO) are dominant at the N atoms, and the electrons in the HOMO significantly contribute to the muon capture phenomena in the nitrogen oxide molecules.
) at pressures below 100 kPa. A higher density of covalent electrons at the N atoms relative to the O atoms is required if we explain the experimental results using the proposed muon capture models. From molecular orbit calculations, we found that the electron distributions of only the highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO) are dominant at the N atoms, and the electrons in the HOMO significantly contribute to the muon capture phenomena in the nitrogen oxide molecules.
Strasser, P.*; 阿部 充志*; 青木 正治*; Choi, S.*; 深尾 祥紀*; 東 芳隆*; 樋口 嵩*; 飯沼 裕美*; 池戸 豊*; 石田 勝彦*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology)High precision measurements of the ground state hyperfine structure (HFS) of muonium is a stringent tool for testing bound-state quantum electrodynamics (QED) theory, determining fundamental constants of the muon magnetic moment and mass, and searches for new physics. Muonium is the most suitable system to test QED because both theoretical and experimental values can be precisely determined. Previous measurements were performed decades ago at LAMPF with uncertainties mostly dominated by statistical errors. At the J-PARC Muon Science Facility (MUSE), the MuSEUM collaboration is planning complementary measurements of muonium HFS both at zero and high magnetic field. The new high-intensity muon beam that will soon be available at H-Line will provide an opportunity to improve the precision of these measurements by one order of magnitude. An overview of the different aspects of these new muonium HFS measurements, the current status of the preparation for high-field measurements, and the latest results at zero field are presented.
下村 浩一郎*; 伊藤 孝
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 85(9), p.091013_1 - 091013_5, 2016/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen in semiconductors and insulators plays a crucial role in their electric conductivity. Substantial experimental and theoretical efforts have been made to establish this hypothesis in the last decade, and the muon spin rotation technique has played a pioneering role. Positive muons implanted into such low-carrier systems often form a muonium (a hydrogen analogue). Although its dynamical aspect may be different from the heavier hydrogen, the electronic structure of the muonium is expected to be identical to that of hydrogen after a small correction of the reduced mass. Since the discovery of a shallow muonium in CdS, its properties have been intensively studied in many semiconductors and insulators, and then it was interpreted as a possible origin of  -type conductivity under the context of a classical shallow donor model. In this article, we will describe the principle of muonium experiments and survey recent achievements in this field.
-type conductivity under the context of a classical shallow donor model. In this article, we will describe the principle of muonium experiments and survey recent achievements in this field.