Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Takumi; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.299 - 304, 2025/05
Currently, much research continues on stable energy sources that do not emit CO in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
Bachmann, A. M.*; Richards, S.*; Feng, B.*; Nishihara, Kenji; Abe, Takumi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
This work demonstrates the value of code verification as an initial step in utilizing fuel cycle simulation. Cyclus and NMB are open-source fuel cycle simulators that provide computational modeling of nuclear fuel cycle alternatives and were chosen by Argonne National Laboratory and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), respectively, for a multi-year collaboration on fuel cycle benchmarks. Both are relatively new and can be improved after conducting a rigorous code-to-code comparison. Initial verification of these simulators was performed using a set of hypothetical scenarios for once-through and multi-recycle fuel cycles. The results of this work identify how differences in scenario definitions and the modeling methodologies of the two simulators lead to differences in results in material inventories, mass flows, and other important metrics for fuel cycle assessments.
 Pu
Pu O
O powder using master sintering curve theory
powder using master sintering curve theoryNakamichi, Shinya; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 595, p.155072_1 - 155072_11, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1331 - 1344, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reactivity was estimated from a time profile of neutron count rate or a simulated data in a quasi-steady state after sudden change of reactivity or external neutron source strength. The estimation was based on the equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state. The purpose of the study is to develop the method of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. The developed method was applied to the data simulating neutron count rate created by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, and Poisson-distributed random noise and to the transient subcritical experiment data measured by using TRACY. The result shows that the difference of the estimated and reference value was within about 5% or less for (
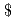
 -1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for
-1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for 
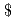
 -1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
-1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
Yoshida, Naoki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2021-011, 12 Pages, 2022/01
In boiling and drying accidents involving high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plants, emphasis is placed on the behavior of ruthenium (Ru). Ru would form volatile species, such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ), and could be released to the environment with coexisting gases, including nitric acid, water, or nitrogen oxides. In this study, to contribute toward safety evaluations of these types of accidents, the migration behavior of gaseous Ru into the liquid phase has been experimentally measured by simulating the condensate during an accident. The gas absorption of RuO
), and could be released to the environment with coexisting gases, including nitric acid, water, or nitrogen oxides. In this study, to contribute toward safety evaluations of these types of accidents, the migration behavior of gaseous Ru into the liquid phase has been experimentally measured by simulating the condensate during an accident. The gas absorption of RuO was enhanced by increasing the nitrous acid (HNO
was enhanced by increasing the nitrous acid (HNO ) concentration in the liquid phase, indicating the occurrence of chemical absorption. In control experiments without HNO
) concentration in the liquid phase, indicating the occurrence of chemical absorption. In control experiments without HNO , the lower the temperature, the greater was the Ru recovery ratio in the liquid phase. Conversely, in experiments with HNO
, the lower the temperature, the greater was the Ru recovery ratio in the liquid phase. Conversely, in experiments with HNO , the higher the temperature, the higher the recovery ratio, suggesting that the reaction involved in chemical absorption was activated at higher temperatures.
, the higher the temperature, the higher the recovery ratio, suggesting that the reaction involved in chemical absorption was activated at higher temperatures.
Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2020-014, 33 Pages, 2020/12
Considering the boiling and drying accident of high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plant, Ruthenium (Ru) is an important element. It is because Ru would form volatile compounds such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric oxides (NOx) such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO
) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric oxides (NOx) such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO ). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the effect of NOx on the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO
). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the effect of NOx on the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO (RuO
(RuO (g)). As a result, the RuO
(g)). As a result, the RuO (g) decomposed over time under the atmospheric gasses with NO or NO
(g) decomposed over time under the atmospheric gasses with NO or NO , however, the decomposition rate was slower than the results of experiments without NOx. These results showed that the NOx stabilized RuO
, however, the decomposition rate was slower than the results of experiments without NOx. These results showed that the NOx stabilized RuO (g).
(g).
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.926 - 931, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)An equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state has been derived based on one-point kinetics equations for the purpose of utilizing it for the development of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. It linearly relates power,  , to a new variable
, to a new variable  , which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (
, which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (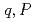 ) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (
) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (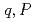 ) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Review 2018-022, 201 Pages, 2019/01
Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC), Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is conducting technical support to nuclear safety regulation and safety research based on the Mid-Long Term Target determined by Japanese government. This report summarizes the research structure of NSRC and the cooperative research activities with domestic and international organizations as well as the nuclear safety research activities and results in the period from JFY 2015 to 2017 on the nine research fields in NSRC; (1) severe accident analysis, (2) radiation risk analysis, (3) safety of nuclear fuels in light water reactors (LWRs), (4) thermohydraulic behavior under severe accident in LWRs, (5) materials degradation and structural integrity, (6) safety of nuclear fuel cycle facilities, (7) safety management on criticality, (8) safety of radioactive waste management, and (9) nuclear safeguards.
Amano, Yuki; Watanabe, Koji; Masaki, Tomoo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Technology 2016-012, 21 Pages, 2016/06
To contribute to safety evaluation of fire accident in fuel reprocessing plants, solvent extraction behavior of ruthenium, which could form volatile species, was investigated. Distribution ratios of ruthenium at fire accident conditions were obtained by extraction experiments with several solvent composition at different temperature as parameters. In order to investigate release behavior of ruthenium and europium at fire accident, release ratios of ruthenium and europium were also obtained by solvent combustion experiments.
Abe, Hitoshi; Masaki, Tomoo; Amano, Yuki; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Research 2014-022, 12 Pages, 2014/11
To contribute safety evaluation of boiling and drying accident of high active liquid waste (HALW) in fuel reprocessing plant, release behavior of Ru, which was considered as an important nuclide for evaluating public dose from the volatile viewpoint, has been investigated. It has been reported that release of Ru becomes conspicuously after HALW is dried up. In this work, to grasp the release behavior of Ru, release ratio of Ru with thermal decomposition of Ru nitrate, which would be in the dried HALW, was measured and release rate constant of Ru from the nitrate was estimated. It was found that the calculation result of release rate of Ru from the nitrate with rise of temperature by using the constant could well simulate the result acquired from the beaker-scale experiment.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2005/10
For a basis of the future nuclear cycle, it is very important to understand and control the behavior of TRU (Np, Pu, Am, Cm) in the nuclear fuel cycle. Experimental study of pyrochemical process of fuels containing TRU requires the facility having not only shielding for  -ray and neutron but also ability to keep a high purity inert gas atmosphere; because minor actinide chlorides can easily react with oxygen or water vapor in an atmosphere. The module for TRU high temperature chemistry (TRU-HITEC) had been installed to study the basic properties of TRU in the pyrochemical processes. In the present work, the behavior of
-ray and neutron but also ability to keep a high purity inert gas atmosphere; because minor actinide chlorides can easily react with oxygen or water vapor in an atmosphere. The module for TRU high temperature chemistry (TRU-HITEC) had been installed to study the basic properties of TRU in the pyrochemical processes. In the present work, the behavior of  Am in pyrochemical process was investigated by electrochemical methods.
Am in pyrochemical process was investigated by electrochemical methods.
Otaki, Kiyoshi*; Tanaka, Yoji*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Aoki, Kazuo*
JAERI-Review 2005-035, 79 Pages, 2005/09
In order to collect technical information for the assessment on future nuclear power reactors and fuel cycle systems in Japan, investigation has been made on the characteristics and performance of future reactor options including reduced moderation water reactors (RMWRs) and their fuel cycle systems since the fiscal year 1998. The subjects of investigation are divided into three categories; breeder reactors and their fuel cycle, alternative to sodium-cooled FBR systems,plutonium recycling, spent fuel reprocessing and waste disposal. This report is a summary of the investigation carried out so far.
Editorial Committee on Nuclear Safety Research Results
JAERI-Review 2005-009, 151 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Tahara, Yoshihisa*; Fukahori, Tokio
JAERI-Conf 2005-003, 254 Pages, 2005/03
The 2004 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Tokai Research Establishment, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), on 11th and 12th of November 2004. Japanese Nuclear Data Committee and Nuclear Data Center, JAERI organized this symposium. In the oral sessions, presented were 19 papers on topics of nuclear data for LWR and nuclear fuel cycle, nuclear data for ADS development, experiences from use of JENDL-3.3 and requests to JENDL-4, recent cross section measurements, nuclear data for life and material sciences, and nuclear data needs and activities in the World. In the poster session, presented were 21 papers concerning experiments, evaluations, benchmark tests, applications and so on. Those presented papers are compiled in the proceedings.
Tatematsu, Kenji; Sato, Osamu
JAERI-Research 2004-024, 35 Pages, 2005/01
Many scenarios were defined for future development of nuclear power generation and fuel cycle systems in Japan. These scenarios were quantitatively analyzed from the viewpoint of plutonium recycling, natural uranium consumption, stock of spent fuel, etc. Following findings were obtained from the analysis. RMWRs will contribute to control the uranium consumption at certain finite levels if net conversion ratio (CR) is kept higher than 1.0. However, since RMWRs do not have an excellent breeding performance in comparison with FBRs, their effect is very sensitive to the conditions on fuel recycling processes. Judging from the results of analysis using a RMWR design with gross CR 1.06, it would be necessary for RMWRs to have net CR 1.04 in order to replace enriched uranium fuelled LWRs by around the year 2200, and thereby to keep ultimate natural uranium consumption at rather low levels. This can be achieved by controlling fuel duration time outside reactors to shorter than 4 years or 6 years, when total loss of plutonium during the processes of recycling is 1.0% or 0.2%, respectively.
Editorial Committee on Nuclear Safety Research Results
JAERI-Review 2004-010, 155 Pages, 2004/03
JAERl is conducting nuclear safety research primarily at the Nuclear Safety Research Center in close cooperation with the related departments in accordance with the Long Term Plan for Development and Utilization of Nuclear Energy and Annual Plan for Safety Research issued by the Japanese government. The fields of conducting safety research at JAERl are the engineering safety of nuclear power plants and nuclear fuel cycle facilities, and radioactive waste management as well as advanced technology for safety improvement or assessment. Also, JAERI has conducted international collaboration to share the information on common global issues of nuclear safety and to supplement own research. This report summarizes the nuclear safety research activities of JAERI from April 2001 through March 2003 and utilized facilities.
Nuclear Safety Research Center Planning and Analysis Division
JAERI-Review 2003-040, 298 Pages, 2004/01
JAERl is conducting nuclear safety research primarily at the Nuclear Safety Research Center in close cooperation with the related departments in accordance with the Annual Plan for Nuclear Safety Research issued by the Nuclear Safety Commission. The fields of conducting safety research at JAERl are the engineering safety of nuclear power plants and nuclear fuel cycle facilities, and radioactive waste management as well as advanced technology for safety improvement or assessment. This report summarizes the nuclear safety research activities of JAERI from April 2001 through March 2003.
Committee for the Joint Research Project on Backend Chemistry; Committee for the Collaborative Research on the Advanced Radiation Technology
JAERI-Review 2003-001, 97 Pages, 2003/02
no abstracts in English
Editorial Committee on Nuclear Safety Research Results
JAERI-Review 2002-030, 143 Pages, 2002/11
JAERl is conducting nuclear safety research primarily at the Nuclear Safety Research Center in close cooperation with the related departments in accordance with the Long Term Plan for Development and Utilization of Nuclear Energy or the Safety Research Annual Plan issued by the Japanese government. The safety research at JAERl concerns the engineering safety of nuclear power plants and nuclear fuel cycle facilities, and radioactive waste management as well as advanced technology for safety improvement or assessment. Also, JAERI has conducted international collaboration to share the information on common global issues of nuclear safety. This report summarizes the nuclear safety research activities of JAERI from April 2000 through April 2002.
NUCEF 2001 Symposium Working Group
JAERI-Conf 2002-004, 714 Pages, 2002/03
This volume contains 94 papers presented at the 3rd NUCEF International Symposium NUCEF 2001 held on October 31 - November 2, 2001, in Tokai, Japan, following the 1st symposium NUCEF'95 (Proceedings: JAERI-Conf 96-003) and the 2nd symposium NUCEF'98 (Proceedings: JAERI-Conf 99-004). The theme of this symposium was " Scientific Basis for Criticality Safety, Separation Process and Waste Disposal". The papers were presented in oral and poster sessions on following research fields: (1) Separation Process, (2) TRU Chemistry, (3) Radioactive Waste Disposal, (4) Criticality Safety.