Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Polytechnic University*
JAEA-Review 2022-011, 80 Pages, 2022/07
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of semantic survey map building system using semi-autonomous mobile robots for surveying of disaster area and gathering of information in nuclear power station" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to research and develop semi-autonomous mobile robot systems (multi-sensor fusion system, semantic simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), system for traversable-route learning and safe traversable-route presentation, etc.) that simply, safely, and rapidly make semantic survey maps …
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.121 - 125, 2022/04
The effect of solution layer thickness on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel was investigated using novel devices fabricated by a 3D printer. These novel devices allowed us to control the solution layer thickness precisely. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed under thickness-controlled solution layer, and oxygen diffusion limiting current density ( ) and anodic current density (
) and anodic current density ( ) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,
) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,  increased and
increased and  decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20
decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20 10
10 cm
cm s
s from the relationship between
from the relationship between  and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 342, p.117580_1 - 117580_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.04(Chemistry, Physical)Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) and pulsed-field-gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFGNMR) analyses of a nanofluid composed of silicon dioxide (SiO ) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO
) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO
particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO nanofluids.
nanofluids.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Polytechnic University*
JAEA-Review 2020-062, 47 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Semantic Survey Map Building System using Semi-autonomous Mobile Robots for Surveying of Disaster Area and Gathering of Information in Nuclear Power Station" conducted in FY2019.
Cantarel, V.; Lambertin, D.*; Labed, V.*; Yamagishi, Isao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.62 - 71, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)The gas production of wasteforms is a major safety concern for encapsulating active nuclear wastes. For geopolymers and cements, the H produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the gas composition evolution around geopolymers was monitored on line under
produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the gas composition evolution around geopolymers was monitored on line under  Co gamma irradiation. Transient evolution of the hydrogen production yield was measured for samples with different formulations. The rate of its evolution and the final values are consistent with the presence of a chemical reaction of the pseudo-first order consuming hydrogen in the samples. The results show this phenomenon can significantly reduce the hydrogen source term of geopolymer wasteform provided their diffusion constant remains low. Lower hydrogen production rates and faster kinetics were observed with geopolymers formulations in which pore water pH was higher. Besides hydrogen production, a steady oxygen consumption was observed for all geopolymers samples. The oxygen consumption rates are proportional to the diffusion constants estimated in the modelization of hydrogen recombination by a pseudo first order reaction.
Co gamma irradiation. Transient evolution of the hydrogen production yield was measured for samples with different formulations. The rate of its evolution and the final values are consistent with the presence of a chemical reaction of the pseudo-first order consuming hydrogen in the samples. The results show this phenomenon can significantly reduce the hydrogen source term of geopolymer wasteform provided their diffusion constant remains low. Lower hydrogen production rates and faster kinetics were observed with geopolymers formulations in which pore water pH was higher. Besides hydrogen production, a steady oxygen consumption was observed for all geopolymers samples. The oxygen consumption rates are proportional to the diffusion constants estimated in the modelization of hydrogen recombination by a pseudo first order reaction.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Polytechnic University*
JAEA-Review 2019-022, 35 Pages, 2020/01
CLADS, JAEA, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the Development of Semantic Survey Map Building System Using Semi-autonomous Mobile Robots for Surveying of Disaster Area and Gathering of Information in Nuclear Power Station. The objective of the present study is to research and develop semi-autonomous mobile robot systems (multi-sensor fusion system, semantic simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), system for traversable-route learning and safe traversable-route presentation, etc.) that simply, safely, and rapidly make semantic survey maps including multiple information (air dose rate, temperature, obstacles, etc.). The system will be applied to the investigation of the situation inside the building of the nuclear power station where people cannot access at the time of disaster.
Akagi, Yosuke*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakamoto, Hiroyuki*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.233 - 236, 2018/11
A large amount of radioactive contaminated concrete will be generated from the decommissioning in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP). For developing the plans of decommissioning and waste management including decontamination and disposal, it is important to estimate radionuclides inventory and concentration distribution in the concrete materials. In this study, effective diffusivities (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of HTO, Cs, I and U in OPC mortar were measured by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments. De values derived were in the sequence of HTO, I, Cs, U, implying that cation exclusion effects may be important mechanisms in OPC mortar. Kd values derived by batch tests were higher by more than one order of magnitude than the diffusion-derived Kd values, indicating that crushing of samples had a strong influence on sorption. Diffusion and sorption mechanisms in OPC mortar were evaluated to predict the penetration behavior of these radionuclides.
Higashijima, Satoru; Kamada, Yutaka; Barabaschi, P.*; Shirai, Hiroshi; JT-60SA Team
Fusion Science and Technology, 68(2), p.259 - 266, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/05
Effect of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide on corrosion rate of carbon steel in diluted artificial seawater was investigated by electrochemical methods. Diffusion coefficient and thickness of diffusion layer for oxygen and hydrogen peroxide were measured to estimate the diffusion limiting current density. Corrosion tests of carbon steel were also conducted in diluted artificial seawater containing oxygen and/or hydrogen peroxide at 323K. The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen peroxide was about 0.8 times lower than that of oxygen, and the thickness of diffusion layer was almost equivalent between oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Diffusion limiting current density of hydrogen peroxide was estimated to be 0.4 times lower than that of oxygen in the same concentration at 323K. Plot of corrosion rate with the addition of concentration of oxygen and 0.4 times concentration of hydrogen peroxide showed good correlation.
Nishimura, Arata*; Muroga, Takeo*; Takeuchi, Takao*; Nishitani, Takeo; Morioka, Atsuhiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1675 - 1681, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fusion reactor plant, a neutral beam injector (NBI) will be operated for a long time, and it will allow neutron streaming from NBI ports to outside of the plasma vacuum vessel. It requires the superconducting magnet to develop nuclear technology to produce stable magnetic field and to reduce activation of the magnet components. In this report, the back ground of the necessity and the contents of the nuclear technology of the superconducting magnets for fusion application are discussed and some typical investigation results are presented, which are the neutron irradiation effect on Nb Sn wire, the development of low activation superconducting wire, and the design concept to reduce nuclear heating and nuclear transformation by streaming. In addition, recent activities in high energy particle physics are introduced and potential ripple effect of the technology of the superconducting magnets is described briefly.
Sn wire, the development of low activation superconducting wire, and the design concept to reduce nuclear heating and nuclear transformation by streaming. In addition, recent activities in high energy particle physics are introduced and potential ripple effect of the technology of the superconducting magnets is described briefly.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.957 - 962, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:96.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of blistering on deuterium retention in W was investigated using the newly established plasma generator with controllable incident energies ranging from 100 eV down to around 10 eV and incident flux of 1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5
/s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5  C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850
C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850  C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 347(1-2), p.111 - 117, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:98.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Polycrystalline tungsten samples have been irradiated at room temperature by high flux (1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7
/s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7  98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering
98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering 
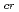 was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies
was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies  20 eV/D,
20 eV/D, 
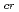 increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of
increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of 
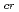 may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2
may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2 m.
m.
Ochiai, Kentaro; Kondo, Keitaro; Murata, Isao*; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Takahashi, Akito*; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 75-79, p.859 - 863, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fusion Neutronics Source (FNS) of JAERI currently carries out the measurements of energetic charged particles emitted from fusion materials irradiated with a well-collimated 14 MeV neutron beam. At the beginning, the double differential cross section beryllium was measured. We have measured proton, triton and a particle emitted from a beryllium sample of 100  m in thickness.The a particle and triton were produced by
m in thickness.The a particle and triton were produced by  Be(n,
Be(n, )
) He,
He,  Be(n,2n)2
Be(n,2n)2 and
and  Be(n,t)
Be(n,t) Li reactions respectively. Measured total reaction rates from the counts of a particles and tritons were 2.7
Li reactions respectively. Measured total reaction rates from the counts of a particles and tritons were 2.7 10
10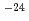 and 6
and 6 10
10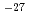 /atom/neutron, respectively, which were consistent with the calculated values from the nuclear data JENDL-3.2.
/atom/neutron, respectively, which were consistent with the calculated values from the nuclear data JENDL-3.2.
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Nagai, Yasuki
JAERI-Review 2005-004, 208 Pages, 2005/03
The Working Group on Energy (WG) was organized under International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP). The WG has been considering problems on future energy supply and role of physics to solve the subjects. As one of activities of the WG, a Workshop on Energy was held on May 13, 2004 at Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) in Tokyo hosted by IUPAP and co-hosted by JAERI and High Energy Accelerator Research Organization. The objectives of this workshop are to suggest active contributions of pure and applied physics field to the solution of the energy problem and to advance research and development (R&D) of future energy through the discussions about present status, problem and prospect of different energy development in the world and in Japan. This report records the summary of the Workshop and, abstracts and materials of 12 presentations. After the invited presentations about overview of energy problems in the world, in China and in Japan, R&D activities on the following four fields were presented; "Research and Development of New Energy", "Research and Development of Fusion Energy", "Prospect of Accelerator Driven System (ADS)", and "Hydrogen Production, Storage and Transportation".
Inoue, Takashi; Sakamoto, Keishi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 47(2), p.120 - 127, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Ueda, Yoshio*; Inoue, Takashi; Kurihara, Kenichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 46(12), p.845 - 852, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Nishitani, Takeo; Ochiai, Kentaro; Maekawa, Fujio; Shibata, Keiichi; Wada, Masayuki*; Murata, Isao*
IAEA-CN-116/FT/P1-22 (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Aiba, Nobuyuki*; Tokuda, Shinji; Ishizawa, Tomoko*; Okamoto, Masao*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(11), p.1699 - 1721, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.72(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The theory of the Newcomb equation has been applied to low-n external modes in a tokamak and a method has been developed to compute the stability matrix that gives the change of plasma potential energy due to external modes in terms of the surface values of the perturbations. By using this method, the spectral properties of the ideal external modes has been elucidated, such as coupling between external modes and internal modes, and the difference of the stability properties between a normal shear tokamak and a reversed shear tokamak. These results will be also useful in the stability analysis of resistive wall modes.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Ohira, Shigeru; Nishi, Masataka
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(11), p.4374 - 4378, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:85.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)The ion species ratios in low energy high flux deuterium plasma beams formed in a linear plasma generator were measured by a quadrupole mass spectrometer. And the species control in the plasma generator was evaluated by changing the operational parameters like neutral pressure, arc current, and axial magnetic confinement to the plasma column. The measurements reveal that the lower pressures prefer to form more D ions, and the medium magnetic confinement at the higher pressures results in production of more D
ions, and the medium magnetic confinement at the higher pressures results in production of more D
 , while the stronger confinement and /or larger arc current are helpful to D
, while the stronger confinement and /or larger arc current are helpful to D
 conversion into D
conversion into D
 . Therefore, the ion species can be controlled by adjusting the operational parameters of the plasma generator. With suitable adjustment, we can easily achieve plasma beams highly enriched with a single species of D
. Therefore, the ion species can be controlled by adjusting the operational parameters of the plasma generator. With suitable adjustment, we can easily achieve plasma beams highly enriched with a single species of D , D
, D
 , or D
, or D
 , to a ratio over 80%. It has been found that the axial magnetic configuration played a significant role in the formation of D
, to a ratio over 80%. It has been found that the axial magnetic configuration played a significant role in the formation of D
 within the experimental pressure range.
within the experimental pressure range.
Furuya, Kazuyuki
JAERI-Research 2004-013, 165 Pages, 2004/09
no abstracts in English