Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 226, p.112198_1 - 112198_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In recent years, the use of radiation-resistant resins of polyimide and polyether ether ketone becomes increasing as vessels for irradiation and unsealed radioisotope experiments. However, in our radiolysis experiments, the possibility of interaction between radiolysis products of water and the resin was found, suggesting concerns that the resin may affect reactions in water in radiation fields. To clarify the interaction, dichromate (Cr O
O
 ) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H
) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) formation in
) formation in  -radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr
-radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr O
O
 reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr
reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr O
O
 reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H
reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H O
O formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 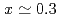
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2024-022, 59 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of effects of nano interfacial phenomena on dissolution aggregation of alpha nanoparticles by using micro nano technologies" conducted in FY2022. To ensure the safety of retrieval and storage management of nuclear fuel debris generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, understanding of dissolution-denaturation behavior of the fuel debris alpha particles is one of the most crucial issues. This research aims to create novel microfluidic real-time measurement device for elucidating dissolution, aggregation, and denaturation processes of metal oxide nanoparticles under various solution environments, and clarify their nano-size and interfacial effects.
 /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2024-019, 102 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to corrosion, which is considered to be an important factor in the aging degradation of confinement functions (PCV, negative pressure maintenance system, etc.) during the fuel debris removal process. If the chemical species (especially H
-rays radiolysis" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to corrosion, which is considered to be an important factor in the aging degradation of confinement functions (PCV, negative pressure maintenance system, etc.) during the fuel debris removal process. If the chemical species (especially H O
O ) generated by radiolysis become locally concentrated in the areas where short-range
) generated by radiolysis become locally concentrated in the areas where short-range  - and
- and  -radiation emitting nuclides come into contact, the corrosion of steels may be greatly accelerated in those areas.
-radiation emitting nuclides come into contact, the corrosion of steels may be greatly accelerated in those areas.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; University of Fukui*
JAEA-Review 2024-014, 112 Pages, 2024/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Clarification of debris formation conditions on the basis of the sampling data and experimental study using simulated fuel debris and reinforcement of the analytical results of severe accident scenario" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to clarify the debris formation mechanism and utilize the results to refine the accident scenario. In the backward analysis of oxide debris formation, we succeeded in the formation of simulated fuel particle by the aerodynamic levitation method and ejection of melted oxides from tungsten pipe with a small hole. And we demonstrated the formation of simulated fuel debris of U1-No.15 obtained by the sampling in 1F.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2024-007, 24 Pages, 2024/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. It has been observed experimentally that volatility of RuO is suppressed by HNO
is suppressed by HNO generated by HNO
generated by HNO radiolysis. The analysis of chemical reactions of NO
radiolysis. The analysis of chemical reactions of NO including HNO
including HNO and HNO
and HNO in the waste tank is essential to simulate of these phenomena. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been attempted to couple dynamically two computer codes SHAWED and SCHERN. The simulation of boiling behavior in the tank is conducted with SHAWED. SCHERN simulates chemical behaviors of HNO
in the waste tank is essential to simulate of these phenomena. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been attempted to couple dynamically two computer codes SHAWED and SCHERN. The simulation of boiling behavior in the tank is conducted with SHAWED. SCHERN simulates chemical behaviors of HNO , HNO
, HNO and NO
and NO in the tank. A programmatic coupling algorithm and a trial simulation of the accident are presented in this report.
in the tank. A programmatic coupling algorithm and a trial simulation of the accident are presented in this report.
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nakajima, Motoki*; Kato, Taichiro*; Nozawa, Takashi*; Ando, Masami*
Materials Today Communications (Internet), 40, p.109659_1 - 109659_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanometric oxide particles play an important role in improving the creep property of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) steels. In our previous research, we examined a microstructural feature known as prior particle boundary (PPB). PPB refers to the surface of mechanically alloyed (MA) powders before consolidation. We revealed that the ODS steel with fine PPBs produced from smaller MA powders, exhibited shorter creep rupture times, compared to that with coarse PPBs produced from larger MA powders. The size of MA powders had an impact on the creep property. In this study, we examined the shape of MA powders, which were non-spherical shapes. Such shapes have the potential to induce anisotropic creep behavior. We conducted small punch creep tests on specimens with two different orientations to study the possible anisotropy. The results revealed that the creep rupture times varied depending on the orientation of specimen, thus indicating anisotropic creep property.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Okajima, Shigeaki*; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.478 - 497, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments was conducted to evaluate the fission and the capture cross- sections of transuranic (TRU) nuclides at the fast critical facility FCA of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The experiments were carried out using seven uranium-fueled assemblies of the FCA. The neutron energy spectra of the core regions were adjusted so as to change from an intermediate neutron spectrum to a fast neutron spectrum on an assembly-by-assembly basis. The integral data measured with these experimental configurations provide some neutron energy characteristics: 1) fission rate ratios (FRRs) of  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am, and
Am, and  Cm relative to
Cm relative to  Pu by using absolutely calibrated fission chambers, 2) small sample reactivity worths (SRWs) of
Pu by using absolutely calibrated fission chambers, 2) small sample reactivity worths (SRWs) of  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am, and
Am, and  Am where oxide powders of around 15 to 20 grams were used, 3) criticalities, and 4) spectral indices such as fission rate ratios of
Am where oxide powders of around 15 to 20 grams were used, 3) criticalities, and 4) spectral indices such as fission rate ratios of  U relative to
U relative to  U. In this paper, details of the SRW measurements are reported, and the latest Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 is tested by using the integral data obtained in systematically varied neutron energy spectra.
U. In this paper, details of the SRW measurements are reported, and the latest Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 is tested by using the integral data obtained in systematically varied neutron energy spectra.
 -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Physics, Applied)Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:88.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C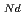 and C
and C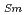 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C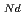 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C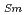 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.

McGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kimuro, Shingo; Ishidera, Takamitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1586 - 1594, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:62.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Bess, J. D.*; Chipman, A. S.*; Pope, C. L.*; Jensen, C. B.*; Ozawa, Takayuki; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 197(8), p.1845 - 1872, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pretransient characterization was performed for the EBR-II MOX fuel pellets from the SPA-2/-2B Operational Reliability Testing collaboration between Japan and US. The continued collaboration will investigate the transient performance of these rods in TREAT at Idaho National Laboratory. The results will fill a gap in existing transient performance data for MOX as these rods have a peak burnup of ~134.4 GWd/t in the EBR-II. Fuel pellet properties were gathered from available resources and their irradiation and decay history evaluated. Further reactor physics calculations were performed to support the experiment design, reactor operations, and safety analyses necessary to enable the programmatic success. Of the three irradiated fuel pins, two will undergo transient testing, and all three will undergo post-irradiation examination.
Watanabe, Nao; Yamashita, Susumu; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Nishihara, Kenji; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.3522 - 3534, 2023/08
Accelerator-driven system (ADS), the coolant of which is lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE), has been designed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Estimating corrosion rate at the wall surface of LBE channel is an important issue in considering safety and the life of the entire structure. The corrosion rate depends on state of oxygen layers forming at the material surface. Therefore, this study aims to develop a method to evaluate the corrosion rate in ADS for the design study by estimation of the oxide layer growth and dissolution (OLGD) rates by means of numerical analysis. The OLGD rates, mass transfer rates of oxygen and iron between the material and LBE and advection-diffusion rates of them in LBE depend on each other. Therefore, in order to estimate OLGD rates, the three numerical analysis models should be coupled. For the advection-diffusion calculation, to use CFD code should be reasonable approach to analyze complex flow in ADS, while for the OLGD and the mass transfer calculation, to use some correlation equations should be reasonable because their scales are much smaller than the advection-diffusion. The present work has developed the analysis method of OLGD rates by using JUPITER code, which is CFD code developed in JAEA. In terms of the correlation equations of OLGD and mass transfer rates, existing models used in a previous study were used with modified.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been developed using computer simulation programs to assess the radioactive source term from those facilities. The proposed approach consists analyses with three computer programs. At first, the simulation of boiling behavior in the HLLW tank is conducted with SHAWED code. Next step, the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code based on the results at the first step simulation such as flowed out mixed steam flow rate, temperature and volatilized Ru from the tank. The final analysis step is carried out for estimating amount of released radioactive materials with SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitric acid, nitrogen oxide and Ru based on the condition also simulated MELCOR. Series of sample simulations of the accident at a hypothetical typical facility are presented with the data transfer between those codes in this report.
Maamoun, I.; Rushdi, M.*; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, R.*; Eljamal, O.*
Separation and Purification Technology, 308, p.122863_1 - 122863_16, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:44.82(Engineering, Chemical)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; University of Fukui*
JAEA-Review 2022-046, 108 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Clarification of debris formation conditions on the basis of the sampling data and experimental study using simulated fuel debris and reinforcement of the analytical results of severe accident scenario" conducted in FY2021. The research on fuel debris so far is based on TMI-2 accident that is typical PWR accident but resent scenario analysis of sever accident progression and sampling data of the in reactor materials predict that fuel debris is diversity and piled up complicatedly depending on the unit and in reactor position. We are necessary to presume the thermodynamic condition of fuel debris during the accident in order to estimate accumulation state of debris.
Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1082324_1 - 1082324_9, 2023/01
Since the oxygen potential and the oxygen coefficient of UO have a significant impact on fuel performance, many experimental data have been obtained. However, experimental data of the oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient in the high temperature region above 1673 K are very limited. In the present study, we aimed to obtain these data and analyze them by defect chemistry. The oxygen potentials and the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient of UO
have a significant impact on fuel performance, many experimental data have been obtained. However, experimental data of the oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient in the high temperature region above 1673 K are very limited. In the present study, we aimed to obtain these data and analyze them by defect chemistry. The oxygen potentials and the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient of UO were measured by the gas equilibrium method in the near stoichiometric region at temperatures ranging from 1673 to 1873 K. A data set of oxygen potentials was made together with literature data and analyzed by defect chemistry. The oxygen potential of UO
were measured by the gas equilibrium method in the near stoichiometric region at temperatures ranging from 1673 to 1873 K. A data set of oxygen potentials was made together with literature data and analyzed by defect chemistry. The oxygen potential of UO was determined as a function of O/U ratio and temperature, and an equation representing the relationship was derived. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient values obtained in this study were reasonably close to the literature values. The oxygen partial pressure dependence of the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients was predicted from the evaluated results of the oxygen potential data, but no clear dependence was observed.
was determined as a function of O/U ratio and temperature, and an equation representing the relationship was derived. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient values obtained in this study were reasonably close to the literature values. The oxygen partial pressure dependence of the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients was predicted from the evaluated results of the oxygen potential data, but no clear dependence was observed.
Idham, M. F.*; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, R.*; Maamoun, I.; Eljamal, O.*
Journal of Water Process Engineering (Internet), 50, p.103289_1 - 103289_16, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:95.24(Engineering, Environmental)