Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aoyama, Takahito; Choudhary, S.*; Pandaleon, A.*; Burns, J. T.*; Kokaly, M.*; Restis, J.*; Ross, J.*; Kelly, R. G.*
Corrosion, 81(6), p.609 - 621, 2025/06
Aoyama, Takahito; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Otani, Kyohei; Igarashi, Takahiro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111229_1 - 111229_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Li, X.; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Sato, Ikken*; Yamashita, Takuya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111217_1 - 111217_13, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sonehara, Masateru; Okano, Yasushi; Uchibori, Akihiro; Oki, Hiroshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.403 - 414, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For sodium-cooled fast reactors, understanding sodium combustion behaviour is crucial for managing sodium leakage accidents. In this study, we perform benchmark analyses of the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL) T3 experiment using the multi-dimensional thermal hydraulic code AQUA-SF. Conducted in an enclosed space with a large vessel volume of 100 m and a sodium mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the experiment highlighted the multi-dimensional effects of local temperature increase shortly after sodium injection. This study aims to extend the capabilities of AQUA-SF by focusing on the simulation of these multi-dimensional temperature variations, in particular the formation of high temperature regions at the bottom of the vessel. The proposed models include the temporary stopping of sodium droplet ignition and spray combustion of sodium splash on the floor. Furthermore, it has been shown that additional heat source near the floor is essential to enhance the reproduction of the high temperature region at the bottom. Therefore, case studies including sensitivity analyses of spray cone angle and prolonged combustion of droplets on the floor are conducted. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the dynamics of sodium combustion and safety measures in sodium-cooled fast reactors.
and a sodium mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the experiment highlighted the multi-dimensional effects of local temperature increase shortly after sodium injection. This study aims to extend the capabilities of AQUA-SF by focusing on the simulation of these multi-dimensional temperature variations, in particular the formation of high temperature regions at the bottom of the vessel. The proposed models include the temporary stopping of sodium droplet ignition and spray combustion of sodium splash on the floor. Furthermore, it has been shown that additional heat source near the floor is essential to enhance the reproduction of the high temperature region at the bottom. Therefore, case studies including sensitivity analyses of spray cone angle and prolonged combustion of droplets on the floor are conducted. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the dynamics of sodium combustion and safety measures in sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Usami, Hiroshi; Yoshinaga, Kyohei*; Fujikawa, Keigo*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(5), p.295 - 299, 2025/05
, 67(5), p.295 - 299, 2025/05
no abstracts in English
Fuyushima, Takumi; Sayato, Natsuki; Otsuka, Kaoru; Endo, Yasuichi; Tobita, Masahiro*; Takemoto, Noriyuki
JAEA-Testing 2024-008, 38 Pages, 2025/03
In Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), irradiation tests had been conducted by loading specimens into capsules for irradiating fuels and materials. The thermal design calculation of capsules is significant to irradiate various types of specimens at the target temperature. The decommissioning plan of JMTR was approved in March 2021, and the Department of Waste Management and Decommissioning Technology Development is currently working on irradiation plans by foreign testing reactors as an alternative for JMTR. A one-dimensional thermal calculation code "GENGTC", which was developed at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in U.S., is used for capsule design and irradiation tests. GENGTC has been repeatedly improved as improvements of computer performance, but there were some defects in calculation function. Therefore, we investigated the cause of the problem and changed the program from the currently used FORTRAN77 language program to a Visual Basic language program that uses the macro calculation function of Excel. In addition, the program was improved to make it easier to use the calculation code.
Abe, Kazuhide
JAEA-Review 2024-065, 26 Pages, 2025/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency's research reactor, JRR-3, resumed operations on February 26, 2021, after nearly a decade. As a shared-use facility, JRR-3 is operated to accommodate external users as well. The procedures, from research proposal submissions to final report submissions, are conducted through the online system JRR-3 RING (Research Information NaviGator) (https://jrr3ring.jaea.go.jp/). RING enables integrated management of proposal submissions, schedule adjustments, data sharing, and report submissions, and it has been upgraded in preparation for the resumption of JRR-3 operations. RING is specifically designed to enhance the convenience of beamline users, featuring simplified application processes, improved flexibility in schedule coordination, and enhanced data management capabilities. With the implementation of this system, users can conduct their research more efficiently and securely. Moving forward, JRR-3 aims to expand its role as a platform for neutron research, accessible to a diverse range of researchers both domestically and internationally. The resumption of operations and the expansion of RING mark a significant step toward revitalizing neutron research and fostering collaboration with industries and academia.
Nuclear Backend Technology Development
JAEA-Evaluation 2024-002, 86 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (hereinafter referred to as "JAEA") consulted the "Evaluation Committee on Research and Development Activities for Decommissioning" (hereinafter referred to as "Committee") about the in-advance evaluation of research themes which had started after FY2021 of R&D plan for the 4th medium- and long-term objectives period concerning "Decommissioning of nuclear facilities and development of technologies for the treatment of related radioactive waste" project in accordance with the "Guideline for evaluation of government R&D activities". In response, the Committee evaluated to the evaluation points of view made by JAEA.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) and -MOX lattice calculations
and -MOX lattice calculationsFujita, Tatsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study estimated the influence of implicit effect on the k-infinity uncertainty in the PWR-UO and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n,
and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n, ) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO
) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For
and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For  Pu and
Pu and  Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Miyamoto, Yuta; Mori, Norimasa; Iwai, Hiroki; Tezuka, Masashi; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Tagawa, Akihiro; Takasaki, Koji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.308 - 316, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Guembou Shouop, C. J.; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170189_1 - 170189_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.60(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fujita, Tatsuya; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(2), p.179 - 196, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study newly established a direct coupling code system consisting of the nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 2, and the three-dimensional heterogeneous transport code GENESIS (FRENDY-V2/GENESIS) for easy implementation of the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification considering the implicit effect due to nuclear cross-section (XS) perturbations. The multi-group macroscopic XSs prepared for GENESIS were generated by FRENDY version 2, where the Dancoff factor was calculated by the neutron current method. Then the background XSs were evaluated based on the Carlvik two-term rational approximation. The infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) and the fission reaction rate distribution in UO and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
Matsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kondo, Kazuhiro*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113791_1 - 113791_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)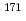 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Usami, Hiroshi; Ito, Rintaro; Tagawa, Akihiro
JAEA-Review 2024-045, 49 Pages, 2024/12
The decommissioning of the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station is a long-term project, and the training of young engineers and researchers who will be responsible for future decommissioning is a necessary and urgent task. Since 2016, Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science has been continuously organizing "Conferences for R&D Initiative on Nuclear Decommissioning Technology by the Next Generation (NDEC)" for students who are engaged in research activities for decommissioning. NDEC is a forum for students to present their research for the purpose of human resource development and networking among young researchers, and to increase their motivation for decommissioning research. NDEC-9 was held at "Manabi-no-Mori" in Tomioka-machi, Fukushima Prefecture, from March 21-22, 2024. This proceeding compiles the contents of report papers in the conference.
Miura, Taito*; Miyamoto, Shintoro*; Maruyama, Ippei*; Aili, A.*; Sato, Takumi; Nagae, Yuji; Igarashi, Go*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 21, p.e03571_1 - e03571_14, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology) )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 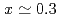
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
Hanari, Toshihide; Nakamura, Keita*; Imabuchi, Takashi; Kawabata, Kuniaki
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(6), p.1537 - 1549, 2024/12
This paper describes three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction processes introducing the image selection method for efficiently generating a 3D model from an image sequence. To obtain suitable images for efficient 3D reconstruction, we tried to apply the image selection method to remove the redundant images in the image sequence. By the proposed method, the suitable images were selected from the image sequence based on optical flow measures and a fixed threshold. As a result, the proposed method can reduce the computational cost for the 3D reconstruction processes based on the image sequence acquired by the camera. We confirmed that the computational cost of the 3D reconstruction processes can reduce while keeping the 3D reconstruction accuracy at a constant level.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.