Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
北條 智彦*; 小山 元道*; 熊井 麦弥*; Zhou, Y.*; 柴山 由樹; 城 鮎美*; 菖蒲 敬久; 齋藤 寛之*; 味戸 沙耶*; 秋山 英二*
ISIJ International, 65(2), p.284 - 296, 2025/02
被引用回数:0Stress and plastic strain distributions and those partitioning behaviors of ferrite and retained austenite were investigated in the medium manganese (Mn) and the transformation-induced plasticity-aided bainitic ferrite (TBF) steels, and the martensitic transformation behaviors of retained austenite during Luders elongation and work hardening were analyzed using synchrotron X-ray diffraction at SPring-8. The stress and plastic strain of retained austenite and volume fraction of retained austenite were remarkably changed during Luders deformation in the medium Mn steel, implying that the medium Mn steel possessed inhomogeneous deformation at the parallel part of the tensile specimen. On the other hand, the distributions of the stress, plastic strain and volume fraction of retained austenite were homogeneous and the homogeneous deformation occurred at the parallel part of the tensile specimen at the plastic deformation regime with work hardening in the medium Mn and TBF steels. The martensitic transformation of retained austenite at uders deformation in the medium Mn steel was possessed owing to the application of high stress and preferential deformation at retained austenite, resulting in a significant increase in the plastic deformation and reduction of stress in the retained austenite. The martensitic transformation of retained austenite at the plastic deformation regime with work hardening was induced by the high dislocation density and newly applied plastic deformation in retained austenite in the medium Mn steel whereas the TBF steel possessed gradual transformation of retained austenite which is applied high tensile stress and moderate plastic deformation.
広田 憲亮; 中野 寛子; 武田 遼真; 井手 広史; 土谷 邦彦; 小林 能直*
材料の科学と工学, 61(6), p.248 - 252, 2024/12
SUS304Lステンレス鋼の0.2%耐力に関する比較分析により、ひずみ速度が低下するほど、温度が上昇するほど、0.2%耐力は著しく低下することが明らかとなった。一方で結晶粒径を68.6 mから0.59
mから0.59 mに微細化した場合における低ひずみ速度下での0.2%耐力への強度低下率の影響は小さかった。しかし、結晶粒微細化は、室温に比べて原子炉運転温度下での0.2%耐力低下には影響を及ぼした。粒内応力腐食割れ(SCC)を促進する条件下での低ひずみ速度引張試験では、28.4
mに微細化した場合における低ひずみ速度下での0.2%耐力への強度低下率の影響は小さかった。しかし、結晶粒微細化は、室温に比べて原子炉運転温度下での0.2%耐力低下には影響を及ぼした。粒内応力腐食割れ(SCC)を促進する条件下での低ひずみ速度引張試験では、28.4 m以下の結晶粒径を持つSUS304Lに対しては、原子炉運転温度下での破断ひずみと同等の値を示したが、粗粒のSUS304Lでは破断ひずみが低下した。微細構造解析では、より結晶粒が微細な材料で87%以上の延性破面が観察され、特に0.59
m以下の結晶粒径を持つSUS304Lに対しては、原子炉運転温度下での破断ひずみと同等の値を示したが、粗粒のSUS304Lでは破断ひずみが低下した。微細構造解析では、より結晶粒が微細な材料で87%以上の延性破面が観察され、特に0.59 mの結晶粒径を持つSUS304Lでは{111}/
mの結晶粒径を持つSUS304Lでは{111}/ 3粒界が数多く存在する一方で、結晶粒径が大きくなるにつれてその割合が減少していた。これらの結果は、結晶粒微細化により、{111}/
3粒界が数多く存在する一方で、結晶粒径が大きくなるにつれてその割合が減少していた。これらの結果は、結晶粒微細化により、{111}/ 3粒界の増加を通じて、腐食の進行が遅延し、粒内SCCが抑制されたことを示唆している。
3粒界の増加を通じて、腐食の進行が遅延し、粒内SCCが抑制されたことを示唆している。
直江 翔太*; 田中 歩*; 神崎 訓枝; 竹中 伶樹*; 迫田 晃弘; 宮地 孝明*; 山岡 聖典*; 片岡 隆浩*
Acta Medica Okayama (Internet), 78(5), p.387 - 399, 2024/10
Radon is a known risk factor for lung cancer; however, it can be used beneficially, such as in radon therapy. We have previously reported the enhancement of antioxidant effects associated with trace amounts of oxidative stress as one of the positive biological effects of radon inhalation. However, the biological effects of radon inhalation are incompletely understood, and more detailed and comprehensive studies are required. Although several studies have used proteomics to investigate the effects of radon inhalation on body proteins, none has focused on brain proteins. In this study, we evaluated the expression status of proteins in murine brains using proteomic and multivariate analyses to identify those whose expressions changed following two days of radon inhalation at a concentration of 1,500 Bq/m . We found associations of radon inhalation with the expressions of seven proteins related to neurotransmission and heat shock. These proteins may be proposed as biomarkers indicative of radon inhalation. Although further studies are required to obtain the detailed biological significance of these protein alterations, this study contributes to the elucidation of the biological effects of radon inhalation as a low-dose radiation.
. We found associations of radon inhalation with the expressions of seven proteins related to neurotransmission and heat shock. These proteins may be proposed as biomarkers indicative of radon inhalation. Although further studies are required to obtain the detailed biological significance of these protein alterations, this study contributes to the elucidation of the biological effects of radon inhalation as a low-dose radiation.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 相澤 一也; 山崎 倫昭*; 川崎 卓郎
日本材料学会第58回X線材料強度に関するシンポジウム講演論文集, p.58 - 60, 2024/07
The experiment and analysis procedures for a sample exhibiting multimodal structures were outlined. The sample, a Mg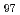 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy, initially comprised two phases: the HCP
alloy, initially comprised two phases: the HCP  matrix (
matrix ( Mg) and the long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO), constituting approximately 25% of the volume. Through hot extrusion at 623 K with an extrusion ratio (R) of 5.0, the alloy was rendered multimodal. Specifically, at an R value of 5.0, dynamic recrystallization occurred partially within the
Mg) and the long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO), constituting approximately 25% of the volume. Through hot extrusion at 623 K with an extrusion ratio (R) of 5.0, the alloy was rendered multimodal. Specifically, at an R value of 5.0, dynamic recrystallization occurred partially within the  Mg phase, resulting in a bimodal microstructure. This microstructure consisted of a deformed
Mg phase, resulting in a bimodal microstructure. This microstructure consisted of a deformed  Mg component and a recrystallized
Mg component and a recrystallized  Mg component. An analysis employing Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) data facilitated multimodal characterization, enabling successful determination of stresses within the individual
Mg component. An analysis employing Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) data facilitated multimodal characterization, enabling successful determination of stresses within the individual  Mg components, as well as the LPSO phase stress.
Mg components, as well as the LPSO phase stress.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
日本材料学会第58回X線材料強度に関するシンポジウム講演論文集, p.51 - 54, 2024/07
In-situ neutron diffraction was used to study tensile deformation in an extruded AZ31 alloy. The aim was to validate existing methods and develop new ones for stress evaluation in magnesium alloys. Results showed varied increases in lattice strains among grains, posing challenges for conventional procedures. A new method, considering grain volume fraction and multiple orientations, proved highly accurate. When simultaneous hk.l peaks weren't available, the 12.1 peak was recommended for stress evaluation, showing a linear relationship with applied stress throughout deformation.
Li, S.; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
Flaws due to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) were recently detected in welded joints of austenitic stainless steel piping lines in pressurized water reactors. Welding-induced high hardness and tensile residual stress are known as one of the main factors affecting SCC. In this work, thermal-elastic-plastic coupled three-dimensional finite element analyses were performed to investigate the distributions of welding residual stress and hardness in butt-welded joints of Type 316 stainless steel. Different heat inputs were applied to the pipe welds, including normal heat input, high heat input and very high heat input. Two different constraint conditions were considered for the welded joints, i.e., both ends free or clamped, the latter indicating that the welded joint is constrained by the surrounding piping system. Simulation results were compared with experimental data such as welding thermal cycle, axial shrinkage and residual stress for validation. The effects of heat input and constraint condition on the welding residual stress and hardness at different sections of the welded joints including the weld start/end location were discussed in detail.
Li, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, K.*; Lacroix, V.*; Dulieu, P.*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 18 Pages, 2024/07
The stress intensity factor (SIF) solutions for subsurface flaws in flat plates are provided in Appendix A of ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section XI. A part of the SIF solutions was initially provided in the 2015 edition. The solutions were obtained for the fourth order polynomial stress distribution base on the influence function method. The solutions were expanded in the 2021 edition for subsurface flaws near the surface of the plate. The additional solutions were obtained based on the J-integral from the elastic finite element analyses. However, recent investigations have found that there is a minor discrepancy in trend between the two sets of SIF solutions because they were obtained by using different numerical methods. Although the discrepancy is very small, the change in trend causes some difficulties in engineering applications. In this work, the SIF solutions are recalculated using the same numerical method based on the J-integral from elastic finite element analyses. The results are compared with the solutions in the current Section XI, RSE-M, and are finally cross-checked with the results obtained from an independent numerical model. The results are useful to eliminate the discrepancy in trend in the SIF solutions for subsurface flaws in flat plates in the current edition of Section XI.
Li, L.*; 宮本 吾郎*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; 諸岡 聡; 及川 勝成*; 友田 陽*; 古原 忠*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation (DT) of austenite ( ) to ferrite (
) to ferrite ( ) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with
) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with  +
+ duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in
duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in  +
+ two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.
two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.  to
to  DT during isothermal compression and
DT during isothermal compression and  to
to  reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between
reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between  and
and  was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft
was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft  phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the
phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the  to
to  transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
三浦 靖史*; 鈴木 賢治*; 諸岡 聡; 菖蒲 敬久
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is expected as a reasonable structural integrity assessment method for nuclear components such as piping, whose main degradation phenomenon is stress corrosion cracking (SCC). Some input parameters are necessary for PFM analysis, and welding residual stress is one of the most important parameters because welding residual stress affects SCC initiation and propagation. Recently, a double exposure method (DEM) with synchrotron X-ray has been proposed, and the method is an expected candidate for the measurement of welding residual stress with a high spatial resolution. In this paper, the DEM was applied to measure the residual stress of the plate specimen, which was cut from the welded pipe using electrical discharge machining, and detailed stress maps under a plane stress state were obtained. Furthermore, the residual stress distributions of the welded pipe under a triaxial stress state were also evaluated using neutron diffraction. From these results, the method for obtaining a detailed stress map of the welded pipe by the complementary use of high-energy synchrotron radiation X-rays and neutrons was proposed.
Zhang, H.*; 梅原 裕太郎*; 吉田 啓之; 森 昌司*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 218, p.124750_1 - 124750_11, 2024/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:73.25(Thermodynamics)The interfacial shear stress and pressure drop of an upward vertical annular flow of nitrogen-water, HFC134a-water, and nitrogen-95% ethanol solution were comprehensively investigated considering the effect of the liquid-gas density ratio and surface tension. A direct link between the disturbance wave height and equivalent sand-grain roughness was noted through the analogy with the famous Moody chart for single-phase turbulent flows. A predictive model of the interfacial friction factor was developed based on this finding. To predict the pressure drop of the annular flow, a new model with good predictive performance for annular flows of various working fluids including steam-water under boiling water reactor operating condition (286 C and 7MPa) was proposed.
C and 7MPa) was proposed.
広田 憲亮; 中野 寛子; 藤田 善貴; 武内 伴照; 土谷 邦彦; 出村 雅彦*; 小林 能直*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
沸騰水型原子炉を模擬した高温高圧水中環境下では、溶存酸素量(DO)の変化により動的ひずみ時効(DSA)と粒界型応力腐食割れ(粒界SCC)がそれぞれ発生する。これらの現象の違いを明確に理解するために、その発生メカニズムを整理した。その結果、SUS304ステンレス鋼では、DOが1ppb未満の低濃度では粒内割れによるDSAが発生し、DOが100 8500ppbでは表面の酸化膜形成によりDSAは抑制されることがわかった。一方、DOが20000ppbまで上昇すると、皮膜が母材から剥離し、母材の結晶粒界に酸素元素が拡散し、粒界SCCが発生した。これらの結果から、DSAや粒界SCCによるクラック発生を抑制するためには、最適なDO濃度を調整する必要があることが示唆された。
8500ppbでは表面の酸化膜形成によりDSAは抑制されることがわかった。一方、DOが20000ppbまで上昇すると、皮膜が母材から剥離し、母材の結晶粒界に酸素元素が拡散し、粒界SCCが発生した。これらの結果から、DSAや粒界SCCによるクラック発生を抑制するためには、最適なDO濃度を調整する必要があることが示唆された。
松野 崇*; 藤田 大樹*; 松田 知子*; 柴山 由樹; 北條 智彦*; 渡邊 育夢*
Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 322, p.118174_1 - 118174_16, 2023/12
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:69.06(Engineering, Industrial)変態誘起塑性(TRIP)鋼の加工硬化における高応力三軸度の影響は、特にオーステナイト体積率の測定結果から幅広く知られている。プレス成形プロセスにおける材料の破壊予測のためには、このTRIP挙動を明らかにすることが重要である。しかし、高応力三軸度条件における流動応力の形成メカニズムは未解明である。本研究では、TRIP鋼の応力三軸度誘起による加工硬化挙動を調査するため、微小ノッチ付き丸棒を用いた新たな引張試験手法を開発した。測微法を用いて試験片をモデル化し、有限要素解析によって引張試験中の流動応力の同定に成功した。また、開発した引張試験手法と放射光X線回折を組み合わせ、応力形成挙動をその場測定した。TRIP型ベイニティックフェライト鋼では、流動応力と応力三軸性が不安定に増加し、加工硬化指数が低下して、より高い応力三軸性が誘起されることを明らかにした。一方、TRIP型マルテンサイト鋼は、鋭いノッチの場合、加工硬化指数の急激な減少によって特徴づけられる弱化挙動を示した。X線回折の結果から、鋼材内部の微視組織の不均一性がオーステナイト相に非常に高い静水圧応力をもたらすことで、これらの対照的な挙動が説明できると結論づけた。本研究結果は、応力三軸度を考慮したTRIP鋼のプレス成形プロセスに関する枠組みについて、新たに応力三軸度を考慮した枠組みが必要であることが示唆される。
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.32_1 - 32_13, 2023/12
Tensile deformation in situ neutron diffraction of an extruded AZ31 alloy was performed to validate conventional procedures and to develop new procedures for stress evaluation from lattice strains by diffraction measurements of HCP-structured magnesium alloys. Increases in the lattice strains with respect to the applied true stress after yielding largely vary among [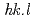 ] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [
] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [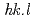 ] grains and evaluating them in many [
] grains and evaluating them in many [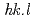 ] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple
] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple 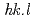 peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
 B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB wire using a pulsed neutron source
wire using a pulsed neutron source町屋 修太郎*; 長村 光造*; 菱沼 良光*; 谷口 博康*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.34_1 - 34_17, 2023/10
Measuring the actual strain on the MgB filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB
filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
Li, S.; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; Deng, D.*
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/07
In this work, a framework was proposed on the comprehensive assessment of hardness and welding residual stress in Type 316 austenitic stainless steel welded joints. Firstly, an 8-pass butt-welded joint made of Type 316 stainless steel was fabricated. Finite element analysis of the welded joint was performed to investigate hardness and welding residual stress distributions. The grain growth model was developed for the hardness prediction. The Chaboche combined isotropic-kinematic strain hardening model and time-temperature dependent annealing model were adopted. The relationships between the Vickers hardness and the uniaxial plastic strain as well as grain size were collected from published literatures. The simulation results of the grain size and accumulated equivalent plastic strain were used for the hardness prediction of the welded joint. The predicted hardness was compared with the experimental data of hardness mapping. The distribution of welding residual stress on the outer surface of the welded pipe was measured by using the X-ray diffraction method and strain gauge method, respectively. The predicted welding residual stresses were compared with the measurements. The results obtained showed that the developed numerical approach can predict the hardness and welding residual stress of Type 316 stainless steel welded joints with satisfactory accuracy. The effects of structural constraint and heat input on the hardness and welding residual stress will be investigated as further works, as described in the proposed framework.
 X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; 冨永 亜希; 菖蒲 敬久; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:94.81(Engineering, Mechanical)コバルトフリーのマルエージング鋼の強度特性を明らかにするために、高エネルギー放射光X線回折法を利用したその場引張試験を行った。マルテンサイト相とオーステナイト相からの回折プロファイルが得られ、それらの強度及び幅が負荷に伴い変化している様子が観察された。回折プロファイルを解析した結果、時効(as-aged)材では、低応力レベルにてマルテンサイトの含有量が緩やかに減少し、高応力レベルでは急激に減少した。一方、熱処理(as-solution)材では、応力の増加とともにオーステナイト相がマルテンサイト相に著しく転移変態している結果が得られた。これらのことがそれぞれの強度特性に起因していることを明らかにした。
山崎 泰広*; 篠宮 啓介*; 奥村 忠晴*; 鈴木 賢治*; 菖蒲 敬久; 中村 唯我*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
The suspension plasma spray (SPS) technique has attracted attention because of its various microstructures, which can be achieved by mixing submicron spray particles with a solvent to form a suspension. Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) with a columnar structure, which might achieve high strain tolerance, can be obtained using the SPS technique. In this study, the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC with different columnar structures was evaluated by hybrid measurement using high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis and laboratory low-energy X-rays. The effect of microstructure on the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC was discussed on the basis of the experimental results. In addition, the in-plane internal stress was decreased by decreasing the column diameter. The thin columnar microstructure of the SPS-TBC has superior strain tolerance. The internal stresses in the column of the SPS-TBC are periodic decrements caused by stress relaxation in porous layers.
安江 歩夢*; 川上 真由*; 小林 謙祐*; Kim, J.*; 宮津 裕次*; 西尾 悠平*; 向井 智久*; 諸岡 聡; 兼松 学*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.15_1 - 15_14, 2023/05
Neutron diffraction is a noncontact method that can measure the rebar strain inside concrete. In this method, rebar strain and stress are calculated using the diffraction profile of neutrons irradiated during a specific time period. In general, measurement accuracy improves with the length of the measurement time. However, in previous studies, the measurement time was determined empirically, which makes the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results unclear. In this study, the relationship between the measurement time and the measurement standard deviation was examined for reinforced concrete specimens under different conditions. The aim was to clarify the accuracy of the measurement of rebar stress using the neutron diffraction method. It was found that if the optical setup of the neutron diffractometer and the conditions of the specimen are the same, there is a unique relationship between the diffraction intensity and the rebar stress standard deviation. Furthermore, using this unique relationship, this paper proposes a method for determining the measurement time from the allowable accuracy of the rebar stress, which ensures the accuracy of the neutron diffraction method.
鈴木 賢治*; 三浦 靖史*; 城 鮎美*; 豊川 秀訓*; 佐治 超爾*; 菖蒲 敬久; 諸岡 聡
材料, 72(4), p.316 - 323, 2023/04
Residual stresses in small-bore butt-welded pipe of austenitic stainless steel have never been measured. It is difficult to obtain a detailed residual stress map of the root welded part, because the gauge volume in neutron diffraction is large. The stress evaluation of the welded part by synchrotron X-rays was also difficult due to the dendritic structure. In this study, a double exposure method (DEM) with high-energy synchrotron X-rays was applied to measuring the details of the residual stress of the welded part, and we succeeded in obtaining the detailed axial and radius stress maps of the root welded part of the plate cut from the welded pipe, though the stress map was under the plane stress condition. The hoop stress map of the butt-welded pipe was obtained using the strain scanning method with neutrons under the triaxial stress state. The axial and radius stress maps under triaxial stress state were made up using the complementary use of the synchrotron X-ray and neutron. As a result, the detailed stress maps of the root welded part of the butt-welded pipe were obtained. The obtained map sufficiently explained the initiation and propagation of SCC.
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 東北大学*
JAEA-Review 2022-063, 86 Pages, 2023/02
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和3年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の廃炉等を始めとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、研究課題のうち、令和元年度に採択された「低線量・低線量率放射線被ばくによる臓器別酸化ストレス状態の検討」の令和元年度から令和3年度の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本課題は令和3年度が最終年度となるため3年度分の成果を取りまとめた。本研究は、廃炉作業を含めた原子力・放射線作業従事者の被ばくに該当するような低線量・低線量率放射線への長期被ばくのように、特に1F事故以降に社会的関心が高まっている放射線被ばく影響に関する知見を収集することを目的として実施した。本研究で解明を目指す被ばく線量域の影響解析試料は、1F事故後の旧警戒区域で被ばくした野生ニホンザルから収集した。また、野生動物試料解析結果を検証するために、放射性セシウムに曝露させて飼育した動物実験マウスから解析試料を作成した。放射線影響の指標として酸化ストレスマーカーを指標に体内の酸化ストレス状態とその防御機構の活性のバランスについて検討し、低線量放射線被ばくによる生体の応答反応について検討を行なった。野生ニホンザルの被ばく線量はモンテカルロシミュレーションおよび歯の電子スピン共鳴分析によって評価し、物理指標と生物指標の関連性から放射線影響について検討を行なった。酸化ストレス状態の変動と放射線影響との関連性を検討した学際共同研究である。