Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhang, H.*; Mori, Shoji*; Hisano, Tsutomu*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 159, p.104342_1 - 104342_15, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:65.33(Mechanics) -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray fieldKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Terasaka, Yuta; Tomita, Hideki*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Uritani, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:88.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)We focus on the thickness and property controls of inorganic scintillators used for thermal neutron detection in intense  -ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20
-ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20 (a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF
(a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF :Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a
:Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron detection for GS20
-ray field, the neutron detection for GS20 with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a
with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron/
-ray field, the neutron/ -ray discrimination of GS20
-ray discrimination of GS20 was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(5), p.133 - 137, 2022/05
The effect of the corrosion inhibitor on the corrosion of steel under a thin solution layer was investigated. As a result of forming a thin solution layer with a thickness of 1.0-0.2 mm on the specimen, adding a mixed solution of sodium molybdate and aluminum lactate as a corrosion inhibitor, and performing electrochemical measurement, the corrosion inhibitor suppresses the anodic reaction. And in the thin solution layer, it was suggested that the morphology of the protective layer structure by the corrosion inhibitor changed according to the amount of liquid as compared with the bulk immersion.
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.121 - 125, 2022/04
The effect of solution layer thickness on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel was investigated using novel devices fabricated by a 3D printer. These novel devices allowed us to control the solution layer thickness precisely. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed under thickness-controlled solution layer, and oxygen diffusion limiting current density ( ) and anodic current density (
) and anodic current density ( ) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,
) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,  increased and
increased and  decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20
decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20 10
10 cm
cm s
s from the relationship between
from the relationship between  and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
Omori, Takazumi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Endo, Yasuichi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2021-015, 57 Pages, 2021/11
The JMTR reactor facility was selected as a decommissioning one in the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities formulated on April 1, 2017. Therefore, the decommissioning plan was submitted to Nuclear Regulation Authority on September 18, 2019, and the approval was obtained on March 17, 2021 after two amendments. Currently, preparations for decommissioning are underway. The JMTR reactor facility has been aged for more than 50 years since the first criticality in March 1968. However, some of the water piping systems has not been updated since its construction, and there is a possibility of pipe wall thinning due to corrosion, etc. Therefore, the integrity of the water piping was investigated for the facilities that circulate cooling water and pump radioactive liquid waste. In this investigation, the main circulation system of the reactor primary cooling system, the pool canal circulation system, the CF pool circulation system, the drainage system of the liquid waste disposal system, and the hydraulic rabbit irradiation system of the main experimental facility were measured for the pipe wall thickness using the Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement (UTM) method. These values satisfied the technical standards for research and test reactor facilities. No loss of integrity is expected to occur during the upcoming decommissioning period. In the future, we will periodically confirm that there is no wall thinning in the piping of the cooling water circulation and the water transmission system during the decommissioning period by using this result as basic data.
Sugita, Yutaka; Taniguchi, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Kanamaru, Shinichiro*; Okumura, Taisei*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(3), p.121 - 135, 2020/09
A series of structural analysis of disposal containers for direct disposal of spent fuel was carried out to provide preliminary estimates of the required pressure resistance thickness of the disposal container. Disposal containers were designed to contain either 2, 3 or 4 spent fuel assemblies in linear, triangular or square arrangements, respectively. The required pressure resistance thickness was evaluated using separation distance of the housing space for each spent fuel assembly as a key model parameter to obtain the required thickness of the body and then the lid of the disposal container. This work also provides additional analytical technical knowledge, such as the validity of the setting of the stress evaluation line and the effect of the model length on the analysis. These can then be referred to and used again in the future as a basis for conducting similar evaluations under different conditions or proceeding with more detailed evaluations.
Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Park, C. H.*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 146(Part A), p.285 - 288, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)Herein, the wall shear stress in a double contraction nozzle has been evaluated experimentally to produce a liquid lithium (Li) target as a beam target for intense fusion neutron sources such as the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), the Advanced Fusion Neutron Source (A-FNS), and the DEMO Oriented Neutron Source (DONES). The boundary layer thickness and wall shear stress are essential physical parameters to understand erosion-corrosion by the high-speed liquid Li flow in the nozzle, which is the key component in producing a stable Li target. Therefore, these parameters were experimentally evaluated using an acrylic mock-up of the target assembly. The velocity distribution in the nozzle was measured by a laser-doppler velocimeter and the momentum thickness along the nozzle wall was calculated using an empirical prediction method. The resulting momentum thickness was used to estimate the variation of the wall shear stress along the nozzle wall. Consequently, the wall shear stress was at the maximum in the second convergent section in front of the nozzle exit.
Komiyama, Daisuke; Amaya, Masaki
JAEA-Research 2016-013, 20 Pages, 2016/08
The boric acid in the coolant may precipitate on the fuel cladding surface in the case that the blockage of coolant flow path etc. occurs and/or the cooling of fuel becomes insufficient during a LOCA (Loss-Of-Coolant Accident) in PWRs. While there is much knowledge about the compatibility between Zircaloy-4 and boric acid under normal operation conditions, such knowledge under high temperature condition, e.g. LOCA, has not been sufficient. In this study, isothermal heating tests were carried out by using Zircaloy-4 plates with solid boric acid in various atmospheres at up to 900 C; and the stability of boric acid, the reaction between Zircaloy-4 and boric acid and the effect of solid boric acid on the high temperature oxidation behavior of Zircaloy-4 were investigated. From the results obtained, it was suggested that, if boric acid anhydride remained on the surface of Zircaloy-4, the boric acid anhydride prevented the surface of Zircaloy-4 from contacting oxidizing atmosphere and mitigated the high-temperature oxidation of Zircaloy-4. In the case that solid boric acid adhered to the surface of pre-oxidized Zircaloy-4 and they have been heated up to high temperature, it was indicated that the solid boric acid penetrated into the gaps in the pre-oxide layer and the penetrated solid boric acid mitigated the oxidation of Zircaloy-4 thereafter.
C; and the stability of boric acid, the reaction between Zircaloy-4 and boric acid and the effect of solid boric acid on the high temperature oxidation behavior of Zircaloy-4 were investigated. From the results obtained, it was suggested that, if boric acid anhydride remained on the surface of Zircaloy-4, the boric acid anhydride prevented the surface of Zircaloy-4 from contacting oxidizing atmosphere and mitigated the high-temperature oxidation of Zircaloy-4. In the case that solid boric acid adhered to the surface of pre-oxidized Zircaloy-4 and they have been heated up to high temperature, it was indicated that the solid boric acid penetrated into the gaps in the pre-oxide layer and the penetrated solid boric acid mitigated the oxidation of Zircaloy-4 thereafter.
Harada, Masahide; Watanabe, Noboru; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 539(1-2), p.345 - 362, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutronic studies of decoupled hydrogen moderators were performed by calculations taking into account para hydrogen content, decoupling energy, moderator dimensions/shapes and reflector material. Low-energy parts of calculated spectral intensities with different para hydrogen contents were analyzed by a modified Maxwell function to characterize neutron spectra. The result shows that a 100% para hydrogen moderator gives the highest pulse peak intensity together with the narrowest pulse width and the shortest decay times. Pulse broadening with a reflector was explained by time distributions of source neutrons entering into the moderator through a decoupler. Material dependence of time distribution was studied. A decoupling energy higher than 1 eV does not bring about a large improvement in pulse widths and decay times, even at a large penalty in the peak intensity. The optimal moderator thickness was also discussed for a rectangular parallelepiped shape and a canteen shape moderators.
Nakahira, Masataka; Takeda, Nobukazu; Urata, Kazuhiro*
JAERI-Tech 2004-069, 55 Pages, 2004/12
This report summarizes the study on dynamic behavior of ITER tokamak scaled model according to the parametric analysis of base plate thickness, in order to find a solution to give the sufficient rigidity without affecting the dynamic behavior. For this, modal analyses were performed changing the base plate thickness from the present design of 55mm to 100, 150 and 190 mm. It was found that the thickness of 150mm gives well fitting of 1st natural frequency about 90% of ideal rigid case. Thus, the modification study was performed to find out the adequate plate thickness. Considering the material availability, transportation and weldability, it was found that the 300mm thickness would be a limitation. The analysis result of 300mm thickness case showed 97% fitting of 1st natural frequency to the ideal rigid case. It was however found that the bolt length was too long and it gave additional twisting mode. As a result, it was concluded that the base plate thickness of 150mm or 190mm gives sufficient rigidity for the dynamic behavior of the scaled model.
Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Watanabe, Noboru; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.657 - 666, 2003/07
Neutronic design studies were carried out on the J-PARC coupled H moderator. The highest time- and energy- integrated intensity below 15 meV, pulse peak intensity at 2 meV and 10 meV, were given by 100% para-H
moderator. The highest time- and energy- integrated intensity below 15 meV, pulse peak intensity at 2 meV and 10 meV, were given by 100% para-H moderators, but the optimal moderator thickness was different for each: more than 220 mm, about 120 mm and 80 mm, respectively. Finally, we concluded 140 mm was the optimal thickness for the 100% para-H
moderators, but the optimal moderator thickness was different for each: more than 220 mm, about 120 mm and 80 mm, respectively. Finally, we concluded 140 mm was the optimal thickness for the 100% para-H coupled moderator. Cold neutron distributions on the moderator viewed surface were found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. This rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use. The intensity decreases along with beam-extraction angle to the normal direction down to about 70% at 25.4
coupled moderator. Cold neutron distributions on the moderator viewed surface were found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. This rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use. The intensity decreases along with beam-extraction angle to the normal direction down to about 70% at 25.4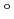 . Then, we propose a cylindrical shape coupled moderator which brings about a slight intensity decrease for 0
. Then, we propose a cylindrical shape coupled moderator which brings about a slight intensity decrease for 0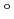 but a increase in the averaged intensity over the angles of interest.
but a increase in the averaged intensity over the angles of interest.
Oba, Toshihiro; Suetsugu, Hidehiko*; Yano, Masaya*; Kato, Chiaki; Yanagihara, Takao
JAERI-Tech 2002-082, 47 Pages, 2003/01
The demonstration test for evaluating reliability of the acid recovery evaporator at Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant has been carried out at JAERI. For the nondestructive measurement of the thickness of heat transfer tubes of the acid recovery evaporator in corrosion test, we have developed thickness measurement apparatus for heat transfer tubes by ultrasonic immersion method with high resolution. The ultrasonic prove in a heat transfer tube can be moved vertically and radially. The results obtained by this apparatus coincident well with those obtained by a destructive method using an optical microscope.
 detection system in the indoor environments of concrete buildings
detection system in the indoor environments of concrete buildingsTsutsumi, Masahiro; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; Sakamoto, Ryuichi; Yoshida, Makoto
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(12), p.1109 - 1114, 2001/12
In order to predict the indoor background spectra to gamma detection systems, the gamma radiation field in a concrete building is studied by the Monte Carlo simulations. The parameters of wall thickness, room shape and dimensions were considered in the modeling. The indoor source geometry was simulated by a spherical layer model with the intention of easy and effective calculations. The model was applied to an unshielded germanium detector and the detection system with a more complex shielding configuration. As the results, we found that the indoor radiation field in concrete buildings can be predicted well with the source geometry of a spherical concrete layer of 25cm thickness and with the source of the natural major three components of the  U series,
U series,  Th series and
Th series and  K that are homogeneously distributed. The simulation model is useful for designing and optimizing gamma detection systems or shielding assemblies.
K that are homogeneously distributed. The simulation model is useful for designing and optimizing gamma detection systems or shielding assemblies.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*; Baba, Yuji
Surface Science, 454-456, p.363 - 368, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.82(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Atomic Collision Research in Japan, No.24, p.118 - 119, 1998/11
no abstracts in English
Tamada, Masao; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Hosoi, Fumio; Suwa, Takeshi
Thin Solid Films, 315(1-2), p.40 - 43, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hideo; ; Kukita, Yutaka*; ; ; Maekawa, Hiroshi
Eighth Int. Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics (NURETH-8), 3, p.1268 - 1275, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Yagyu, Junichi; Ogiwara, Norio; Saido, Masahiro; Okabe, Tomokazu; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Takeshita, Hidefumi; Aoki, Yasushi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 241-243, p.579 - 584, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:75.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; Naito, Yoshitaka; Komuro, Yuichi
JAERI-M 88-160, 37 Pages, 1988/08
no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 24(11), p.897 - 905, 1987/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English