Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Morishita, Kazuki; Marufuji, Takato; Ishikawa, Takashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2023-016, 41 Pages, 2023/09
This report summarizes the results of the stabilization treatments of post-experiment nuclear materials in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) from August 2018 to March 2021. Based on the management standards for nuclear materials enacted after the contamination accident that occurred at PFRF on June 6, 2017, the post-experiment nuclear materials containing plutonium (Pu): samples mixed with organic substances that cause an increase in internal pressure due to radiolysis (including X-ray diffraction samples mixed with epoxy resin and plutonium powder which caused contamination accidents), carbides and nitrides samples which is reactive in air, and chloride samples which may cause corrosion of storage containers, were selected as targets of the stabilization. The samples containing organic materials, carbides and nitrides were heated in an air flow at 650  C and 950
C and 950  C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500
C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500  C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
Nakanishi, Takumi*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Sato, Hiroyasu*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Munakata, Koji*; Ohara, Takashi; Okazawa, Atsushi*; Shimada, Rintaro*; Sakamoto, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 145(35), p.19177 - 19181, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hayashi, Hirokazu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Sato, Takumi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(3), p.97 - 107, 2023/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has chosen nitride fuel as the first candidate for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven systems (ADS). The pyrochemical method has been considered for reprocessing spent MA nitride fuels, because their decay heat should be very large for aqueous reprocessing. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of decay heat on the pyrochemical reprocessing of MA nitride fuels. On the basis of the estimated decay heats and the temperature limits of the materials that are to be handled in pyrochemical reprocessing, quantities adequate for handling in argon gas atmosphere were evaluated. From these considerations, we proposed that an electrorefiner with a diameter of 26 cm comprising 12 cadmium (Cd) cathodes with a diameter of 4 cm is suitable. On the basis of the size of the electrorefiner, the number necessary to reprocess spent MA fuels from 1 ADS in 200 days was evaluated to be 25. Furthermore, the amount of Cd-actinides (An) alloy to produce An nitrides by the nitridation-distillation combined reaction process was proposed to be about one-quarter that of Cd-An cathode material. The evaluated sizes and required numbers of equipment support the feasibility of pyrochemical reprocessing for MA nitride fuels.
Nakanishi, Takumi*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Sato, Hiroyasu*; Wu, S.-Q.*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Munakata, Koji*; Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Osamu*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 25(17), p.12394 - 12400, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.86(Chemistry, Physical) -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd using cadmium chloride
using cadmium chlorideHayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.503 - 510, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)The formation of MPd (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu -type GdPd
-type GdPd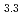 (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) and NpPd
0.0001 nm) and NpPd (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi
0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi -type NpPd
-type NpPd . Chlorination of the MPd
. Chlorination of the MPd (M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl
(M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl formation.
formation.
 O
O -pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawater
-pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawaterMizumachi, Takumi*; Sato, Minami*; Kaneko, Masashi; Takeyama, Tomoyuki*; Tsushima, Satoru*; Takao, Koichiro*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(16), p.6175 - 6181, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Based on unique 5-fold equatorial coordination of UO
 , water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H
, water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
 in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
 /CO
/CO
 , pH 8), saldian
, pH 8), saldian shows the strongest complexation with UO
shows the strongest complexation with UO
 to form UO
to form UO (saldian) (log
(saldian) (log
 = 28.05
= 28.05  0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
 from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
Morishita, Kazuki; Sato, Takumi; Onishi, Takashi; Seki, Takayuki*; Sekine, Shinichi*; Okitsu, Yuichi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-024, 27 Pages, 2021/10
In the case of Plutonium (Pu)-bearing organic materials, organic materials are decomposed by alpha rays emitted mainly from Pu to generate hydrogen gas and other substances. Therefore, to safely store Pu-bearing organic materials for an extended period of time, organic materials must be eliminated. In addition, carbide and nitride fuels must be converted into oxides for safe storage in order to prevent the exothermal reaction of these fuels with oxygen/moisture in air. A survey of the literature on the stabilization treatment of Pu-bearing organic materials confirmed that organic materials can be decomposed and removed by heating at 950  C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950
C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950  C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950
C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950  C was lower than 2.1
C was lower than 2.1 10
10 Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950
Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950  C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
 O
O ; Application of Raman imaging technique to uranium compound
; Application of Raman imaging technique to uranium compoundKusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Yomogida, Takumi; Takano, Masahide; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(6), p.629 - 634, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:66.68(Nuclear Science & Technology) Se
Se ultrathin films on van der Waals ferromagnet Cr
ultrathin films on van der Waals ferromagnet Cr Si
Si Te
Te
Kato, Takemi*; Sugawara, Katsuaki*; Ito, Naohiro*; Yamauchi, Kunihiko*; Sato, Takumi*; Oguchi, Tamio*; Takahashi, Takashi*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Saito, Eiji; Sato, Takafumi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 4(8), p.084202_1 - 084202_6, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tateno, Haruka; Sato, Takumi; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Hirokazu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.224 - 235, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fuel cycle technology for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MAs) using an accelerator-driven system has been developed using the double-strata fuel cycle concept. A mononitride solid solution of MAs and Pu diluted with ZrN is a prime fuel candidate for the accelerator-driven transmutation of MAs. Pyro-reprocessing is suitable for recycling the residual MAs in irradiated nitride fuel with high radiation doses and decay heat. Spent nitride fuel is anodically dissolved, and the actinides are recovered simultaneously into a liquid cadmium cathode via molten salt electrorefining. The process should be designed to achieve the target recovery yield of MAs and the acceptable impurity level of rare earths in the recovered material. We evaluated the material balance during the pyro-reprocessing of spent nitride fuel to gain important insight on the design process. We examined the effects of changing processing conditions on material flow and quantity of waste.
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Marufuji, Takato; Sato, Takumi; Ito, Hideaki; Suzuki, Hisashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2019-006, 22 Pages, 2019/05
Radioactive contamination incident occurred at Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) in Oarai Research and Development Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency on June 6, 2017. During inspection work of storage container containing nuclear fuel materials, the PVC bag packaging in the storage container ruptured when a worker opened the lid in the hood, and a part of contents was spattered over the room. The cause of the increase of internal pressure of the storage container was gas generation by alpha radiolysis of the epoxy resin mixed with nuclear fuel materials. Opening inspection of about 70 similar containers stored in PFRF has been planned to confirm the condition of the contents and to stabilize the stored materials containing organic compounds. For safe and reliable open inspection of the storage containers with high internal pressure in the glove box, it is necessary to develop a pressure-resistant chamber in which the storage containers are opened and the contents are inspected under gastight condition. This report summarizes the concerns and countermeasures of the chamber design and the design results of the chamber.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
NEA/NSC/R(2017)3, p.427 - 432, 2017/11
Transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides including minor actinides (MA: Np, Am, Cm) has been studied in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Pb-Bi cooled sub-critical accelerator-driven system (ADS) is regarded as one of the powerful tools for transmutation of MA under the double strata fuel cycle concept. Uranium-free MA-Pu nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate for MA transmutation. Reprocessing of spent ADS fuel and reusing MA recovered from the spent ADS fuels is necessary to improve the transmutation ratio. A pyrochemical process has been proposed as the first candidate for reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel for MA transmutation, because this technique has some advantages over aqueous process, such as the resistance to radiation damage, which is an important issue for the fuels containing large amounts of highly radioactive MA, and feasibility for recovering expensive N-15 in the spent fuels to be reused. This paper overviews the current status of the technology development, including our recent study. Development of the anode suitable for electro-refining of nitride fuels and that of the apparatus for renitridation of the metals recovered in Cd cathode for 100g-Cd scale cold tests are main topics. Evaluation of the batch sizes of each process, which is necessary for estimating the scale of the engineering-apparatus, with considering the decay heat of MA and FP, will also be introduced.
 and (U,Zr)O
and (U,Zr)O solid solution using MoCl
solid solution using MoCl
Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Takano, Masahide; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1253 - 1258, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to explore the applicability of the chlorination by MoCl as a potential pretreatment technique for waste treatment of fuel debris by pyrochemical methods, chlorination experiments of UO
as a potential pretreatment technique for waste treatment of fuel debris by pyrochemical methods, chlorination experiments of UO and (U
and (U Zr
Zr )O
)O simulated fuel debris were carried out in two steps: the first one is a chlorination reaction by homogeneous heating, the second one is a volatilization of molybdenum by-product by heating under temperature gradient condition. Most of UO
simulated fuel debris were carried out in two steps: the first one is a chlorination reaction by homogeneous heating, the second one is a volatilization of molybdenum by-product by heating under temperature gradient condition. Most of UO and (U
and (U Zr
Zr )O
)O powder were converted to UCl
powder were converted to UCl or UCl
or UCl and ZrCl
and ZrCl mixture at 573 K, respectively. In the case of (U
mixture at 573 K, respectively. In the case of (U Zr
Zr )O
)O sintered particle, most of sample was converted to the chlorides because the products evaporated and be separated from sample surface at 773 K, while only the surface of the sample disk was converted to the chlorides at 573 and 673 K. Most of molybdenum by-product and ZrCl
sintered particle, most of sample was converted to the chlorides because the products evaporated and be separated from sample surface at 773 K, while only the surface of the sample disk was converted to the chlorides at 573 and 673 K. Most of molybdenum by-product and ZrCl were separated from UCl
were separated from UCl by volatilization at 573 K.
by volatilization at 573 K.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Sato, Takumi; Kurata, Masaki
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.1811 - 1817, 2015/09
Transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides including minor actinides (MA: Np, Am, Cm) has been studied in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Accelerator-driven system (ADS) is regarded as one of the powerful tools for transmutation of MA under the double strata fuel cycle concept. Uranium-free nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate fuel for MA transmutation using ADS. To improve the transmutation ratio of MA, reprocessing of spent fuel and reusing MA recovered from the spent fuels is necessary. Our target is to transmute 99% of MA arisen from commercial power reactor fuel cycle, with which the period until the radiotoxicity drops below that of natural uranium can be shorten from about 5000 years to about 300 years. A pyrochemical process has been proposed as the first candidate for reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel. This paper overviews the current status of the nitride fuel cycle technology. Our recent study on fuel fabrication, fuel property measurements, reprocessing of spent fuel, development of the property database of MA nitride fuel, and fuel behavior simulation code are introduced. Our research and development (R&D) plan based on the roadmap of the development is also introduced.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki
NEA/NSC/R(2015)2 (Internet), p.360 - 367, 2015/06
Uranium-free nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate for transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven system (ADS) under the double strata fuel cycle concept by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The advantages of nitride fuel are good thermal properties and large mutual solubility among actinide elements. A pyrochemical process is proposed as the first candidate for the reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel, because this technique has some advantages over aqueous process, such as the resistance to radiation damage, which is an important issue for the fuels containing large amounts of highly radioactive MA. This paper overviews the recent progress and future R&D plan of the study on the nitride fuel cycle technology in JAEA.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
Science China; Chemistry, 57(11), p.1427 - 1431, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:5.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nitride fuels have several advantages, such as high thermal conductivity and high metal density like metallic fuels, and high melting point and isotropic crystal structure like oxide fuels. Since the late 1990s, the partitioning and transmutation of minor actinides (MA) has been studied to decrease the long term radio-toxicity of high level waste and mitigate the burden on the final disposal. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been proposing dedicated transmutation cycle using the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) with the nitride fuels containing MA. We have been developing the nitride fuel cycle including pyrochemical process. Our focus is on electrolysis of nitride fuels and refabrication of nitride fuel from the recovered actinides because other processes are similar to the technology for the metal fuel treatment and have been studied elsewhere. In this paper, we summarized our activity on developments of the pyrochemical treatment of the spent nitride fuels.
Sato, Takumi; Nishihara, Kenji; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Kurata, Masaki*; Arai, Yasuo
Proceedings of 11th OECD/NEA Information Exchange Meeting on Actinide and Fission Product Partitioning and Transmutation (Internet), 9 Pages, 2012/00
Nitride fuel cycle for transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MAs) has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) under the double-strata nuclear fuel cycle concept. This study aims at developing the process flow diagram with the material balance sheet of the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nitride fuel for ADS to evaluate the technological feasibility of the fuel cycle. Three process flow diagrams were proposed in this work: (1) the currently-proposed process with the molten salt electrorefining of spent nitride fuel, (2) the process with the molten salt electrorefining of the actinide-cadmium alloy after the chemical dissolution of spent nitride fuel, and, (3) the process combining the chemical dissolution of spent nitride fuel and the multi-stage counter current extraction. Moreover, the material balance was evaluated for the process (1) by use of the calculated and experimental data of the nitride fuel for ADS.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Iwai, Takashi; Nishihara, Kenji; Arai, Yasuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/12
R&D on the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) by the accelerator-driven system (ADS) using nitride fuels is underway at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In regard to reprocessing technology, pyrochemical process has several advantages in case of treating spent fuel with large decay heat and fast neutron emission, and recovering highly enriched N-15. In the pyrochemical reprocessing, plutonium (Pu) and MA are dissolved in LiCl-KCl eutectic melts and selectively recovered into liquid cadmium (Cd) cathode by molten salt electrorefining. The recovered Pu and MA are converted to nitrides by the nitridation-distillation combined method, in which the Cd alloys containing Pu and MA are heated in nitrogen gas stream. The authors have investigated its elemental technologies such as electrorefining and renitridation. On the other hand, development of the process flow diagram with the material balance sheet of the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nitride fuel for ADS is in progress. This paper summarized recent progress of the study which aims to prove the technological applicability of pyrochemical process to the nitride fuel cycle for transmutation of MA.