Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and O
and O in a reaction cell in triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
in a reaction cell in triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKazama, Hiroyuki; Konashi, Kenji*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Maeda, Koji; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Onishi, Takashi; Abe, Chikage*; Shikamori, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(8), p.1676 - 1681, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Analytical)Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
Koyama, Shinichi; Nakagiri, Toshio; Osaka, Masahiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Takano, Masahide; et al.
Hairo, Osensui Taisaku jigyo jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 144 Pages, 2021/08
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy and Thermal Behavior Estimation of Fuel Debris))" in 2020JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management.
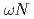 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.35(Physics, Nuclear)Sato, Isamu; Maeda, Koji; Suto, Mitsuo; Osaka, Masahiko; Usuki, Toshiyuki; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(4), p.580 - 587, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Penetration behavior of radionuclides such as  Cs into dried concrete material, dried mortar material and epoxy paint for a few dozen days was observed using a solution containing fission products extracted from irradiated fuels to obtain fundamental information on the radionuclide penetration rate and depth. Hardly any radionuclides could penetrate into the epoxy paint. The radionuclide solution penetrated into concrete and mortar materials to a depth of a few millimeters for a few dozen days. The penetration behavior observed near the surface of concrete and mortar materials was similar to the diffusion of nuclides in media such as water-saturated concrete, bentonite and cement materials.
Cs into dried concrete material, dried mortar material and epoxy paint for a few dozen days was observed using a solution containing fission products extracted from irradiated fuels to obtain fundamental information on the radionuclide penetration rate and depth. Hardly any radionuclides could penetrate into the epoxy paint. The radionuclide solution penetrated into concrete and mortar materials to a depth of a few millimeters for a few dozen days. The penetration behavior observed near the surface of concrete and mortar materials was similar to the diffusion of nuclides in media such as water-saturated concrete, bentonite and cement materials.
Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Inoue, Masaki; Maeda, Koji
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2014/10
In the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, seawater was temporarily injected into the spent fuel pools since water cooling and feeding functions were lost. For fuel assemblies which experienced seawater immersion, surface corrosion due to seawater constituents and the resultant degradation of mechanical property are of concern. Therefore, in order to assess the integrity of fuel assemblies (especially cladding tubes), the effects of seawater immersion on corrosion behavior and mechanical properties for as-recieved and irradiated Zircaloy-2 cladding tubes were investigated in the present study. As a result, no obvious surface corrosion and no significant degradation in the tensile strength property were observed after both artificial and natural seawater immersion tests for both steels. This suggests that the effects of seawater immersions on corrosion behavior and mechanical property (especially tensile property) for Zircaloy-2 cladding tubes are probably negligible.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
JAEA-Testing 2014-001, 29 Pages, 2014/05
The penetration tests with solution containing radioactive nuclides were experimented to understand basic data for floor and wall materials of Fukushima Daiichi reactor buildings. The solution prepared from irradiated fuels was used as solution containing radioactive nuclides. The solution was applied to surface of epoxy paint, dried concrete and mortar used as specimens. Dose-rate profiles of direction of depth were given by radiation measurement and grinding of the specimens. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for epoxy paint specimens were not clearly observed and the penetration depths would be within 0.4 mm. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for dried concrete specimens proceeded. The penetration rates were substantially decreased when 16 days have elapsed from start. The dose rates of penetrated dried concrete specimens were reduced to background by grinding-2.0 mm.  -ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
-ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
Yamagata, Ichiro; Hayashi, Takehiro; Mashiko, Shinichi*; Sasaki, Shinji; Inoue, Masaki; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Maeda, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2013-004, 23 Pages, 2013/11
In the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Co. accompanying the Great East Japan Earthquake, fuel assemblies kept in the spent fuel pool of reactor units 1-4, were exposed to the inconceivable environment such as falling and mixing of rubble, especially seawater were injected into unit 2-4. In order to evaluate the integrity of the fuel assemblies in spent fuel pools, and in the long-term storage after transported to the common storage pool, the immersion tests were performed using zircaloy-2 fuel cladding tubes irradiated in the advanced thermal reactor Fugen. The immersion liquid was prepared with doubling dilution of artificial seawater, which temperature was 80  C and immersion time was about 336 hours, as assuming the situation of the pool. The results indicated zircaloy-2 cladding tubes had no significant corrosion and no influence on mechanical property by immersion tests with artificial seawater conditions of this work.
C and immersion time was about 336 hours, as assuming the situation of the pool. The results indicated zircaloy-2 cladding tubes had no significant corrosion and no influence on mechanical property by immersion tests with artificial seawater conditions of this work.
 Am content on homogenization of denatured Pu with broad range of neutron energy based on U irradiation test in the experimental fast reactor Joyo
Am content on homogenization of denatured Pu with broad range of neutron energy based on U irradiation test in the experimental fast reactor JoyoShiba, Tomooki*; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Han, C. Y.*; Saito, Masaki*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 51, p.74 - 80, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The design consideration of DU-Am oxide fuel pin was performed for Pu denaturing in the framework of the protected plutonium production based on the irradiation analyses of the depleted U (DU) samples irradiated in the environment of broad range of neutron energy in the experimental fast reactor Joyo. From the results of irradiation analyses of DU, it was confirmed that there is a strong dependence of transmutation behavior of DU on the resonance neutron ratio even in a fast reactor. Also, it was confirmed that there is a strong effect of sample material form and shape on generated Pu nuclide inventory especially near the reflector area ( 20% resonance neutron ratio), because of the intensive self-shielding of
20% resonance neutron ratio), because of the intensive self-shielding of  U, though less is expected for
U, though less is expected for  Am. Sensitivity study of hypothetical DU-Am oxide fuel pellet irradiation on neutron energy and burn-up was performed to evaluate significant gradient of radial
Am. Sensitivity study of hypothetical DU-Am oxide fuel pellet irradiation on neutron energy and burn-up was performed to evaluate significant gradient of radial  Pu isotopic composition profile (e.g., from 12 to 18% distribution in 3% Am doping, in 30% resonance neutron ratio and in 4.0
Pu isotopic composition profile (e.g., from 12 to 18% distribution in 3% Am doping, in 30% resonance neutron ratio and in 4.0 10
10 [n/cm
[n/cm ] of neutron fluence inside a large pellet with softened neutron spectrum), and vulnerability of the fuel pellet surface in terms of Pu denaturing was revealed. Design consideration of radial zoning of
] of neutron fluence inside a large pellet with softened neutron spectrum), and vulnerability of the fuel pellet surface in terms of Pu denaturing was revealed. Design consideration of radial zoning of  Am content was introduced to flatten the radial distribution of isotopic composition of Pu. The results of radial zoning of
Am content was introduced to flatten the radial distribution of isotopic composition of Pu. The results of radial zoning of  Am (4% and 3% of Am in the outer and inner zone of DU-Am oxide fuel pellet) in hypothetical irradiation neutronics analysis showed the radial profile of produced Pu is over 15 at.% of
Am (4% and 3% of Am in the outer and inner zone of DU-Am oxide fuel pellet) in hypothetical irradiation neutronics analysis showed the radial profile of produced Pu is over 15 at.% of  Pu isotopic composition in any zone and meets the criteria of Kimura et al. based on decay heat of Pu to impede utilization to fission explosive devices.
Pu isotopic composition in any zone and meets the criteria of Kimura et al. based on decay heat of Pu to impede utilization to fission explosive devices.
 -spectrometry (Contract research)
-spectrometry (Contract research)Maeda, Shingo*; Hirano, Takahiro*; Shimada, Taro; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAEA-Technology 2008-066, 35 Pages, 2008/10
Bulk in-situ  -spectroscopy is effective for a slightly and uniformly contaminated surface such as a room surrounded by concrete walls. The time-consuming scoping scanning survey for the entire surface is essential to ensure the slight and uniform contamination prior to the bulk in-situ measurement. However, the scoping scanning survey is omissible if the conservative procedure is acceptable. The count rate, cps, for the material of interest can be obtained by in-situ Ge detector will be converted to the radioactivity using conversion factor, Bq/cps, which depends on the distance from the detector to the furthest point. The radioactive concentration, Bq/g, is evaluated by dividing the radioactivity by the "measurement unit" of 100 kg. This procedure could certainly produce a conservative value. If the value obtained by this procedure is lower than the regulated clearance level, the material of interest can be cleared without the prior scoping scanning survey.
-spectroscopy is effective for a slightly and uniformly contaminated surface such as a room surrounded by concrete walls. The time-consuming scoping scanning survey for the entire surface is essential to ensure the slight and uniform contamination prior to the bulk in-situ measurement. However, the scoping scanning survey is omissible if the conservative procedure is acceptable. The count rate, cps, for the material of interest can be obtained by in-situ Ge detector will be converted to the radioactivity using conversion factor, Bq/cps, which depends on the distance from the detector to the furthest point. The radioactive concentration, Bq/g, is evaluated by dividing the radioactivity by the "measurement unit" of 100 kg. This procedure could certainly produce a conservative value. If the value obtained by this procedure is lower than the regulated clearance level, the material of interest can be cleared without the prior scoping scanning survey.
Ozawa, Tatsuya; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Nakayama, Shinichi; Hotta, Katsutoshi*
JAEA-Technology 2006-001, 11 Pages, 2006/02
Melting treatment is a candidate solidification technique for nonflammable low-level radioactive wastes including metals, incineration ashes, and glasses. Simulated incineration ashes of a wide range of chemical compositions were molten at 1,600 C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 32(7), p.635 - 650, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Americium isotopes generated in the MOX fuel irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO were analyzed by applying a sophisticated radiochemical technique. Americium was isolated from the irradiated MOX fuel by a combination method of anion-exchange chromatography and oxidation of Am. The isotopic ratio of americium and its content were determined by thermal ionization mass spectroscopy and alpha-spectrometry, respectively. The americium isotopic ratio was similar for all the specimens, but was significantly different from that of PWR-MOX. On the basis of present analytical results, the accumulation and transmutation behavior of americium nuclides in a fast reactor was discussed from viewpoints of neutron spectrum dependence and the isomeric ratio of  Am capture reaction Am for the capture reaction. The estimated isomeric ratio was about 87 %, which was close to recently evaluated value. A rapid estimation method of Am content by using
Am capture reaction Am for the capture reaction. The estimated isomeric ratio was about 87 %, which was close to recently evaluated value. A rapid estimation method of Am content by using  Pu to
Pu to  Pu index was adopted and was proved to be valid for the spent fuel irradiated in the fast reactor.
Pu index was adopted and was proved to be valid for the spent fuel irradiated in the fast reactor.
 Ni migration through crushed rock media
Ni migration through crushed rock mediaTanaka, Tadao; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Radiochimica Acta, 92(9-11), p.725 - 729, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Migration experiments of  Ni for crushed rocks, granite and tuff, were performed under the coexistent condition with a humic acid and a fulvic acid of 0-30 mg/l in concentration, which are Nordic humic substances supplied from International Humic Substance Society. Migration experiments of Ni had been performed by a column system, to investigate migration behavior of Ni through a column packed crushed rock. The Ni concentration in the effluent passed through the column was corresponding to the fractional percentage of Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution. This result suggests that the Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution was flowed out from the column without any effective interactions with the rock media. The migration behavior of Ni could be expressed by a migration model taking account of the complexation kinetics of Ni with humic substance in the aqueous phase.
Ni for crushed rocks, granite and tuff, were performed under the coexistent condition with a humic acid and a fulvic acid of 0-30 mg/l in concentration, which are Nordic humic substances supplied from International Humic Substance Society. Migration experiments of Ni had been performed by a column system, to investigate migration behavior of Ni through a column packed crushed rock. The Ni concentration in the effluent passed through the column was corresponding to the fractional percentage of Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution. This result suggests that the Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution was flowed out from the column without any effective interactions with the rock media. The migration behavior of Ni could be expressed by a migration model taking account of the complexation kinetics of Ni with humic substance in the aqueous phase.
; ; Koyama, Shinichi
JNC TN9400 2002-001, 155 Pages, 2002/01
Uranium-plutonium mixed nitride, (U,Pu)N, has been developed as advanced fuels for fast reactors. Compare with MOX fuel, it has an advantage of larger fissile density and higher thermal conductivity. In order to investigate the irradiation behavior under a fast reactor condition, post irradiation examinations were conducted for (U,Pu)N fuels as a part of the JAERI-JNC joint research program entitled "Basic Irradiation Test of Carbide and Nitride Fuels for Fast Reactors". The (U,Pu)N fuels were irradiated up to 40GWd/t at maximum linear power of 76kW/m in the fast test reactor JOY0. In the center part of fuels, the porosity and the pore size were increased compared with the peripheral region. But there were not observed the drastic structure change such as the formation of central hole and columnar grains. It was shown that the concentration of retained FP gas in any region was extremely high by the measurements of Xe radial distribution in the fuels. These results mentioned above indicated that the fuel temperature was low because of high thermal conductivity of (U,Pu)N.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Ogawa, Hiromichi
JAERI-Review 2001-001, 25 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Fujine, Sachio; Murata, Mikio; Abe, Hitoshi; Takada, Junichi; Tsukamoto, Michio; Miyata, Teijiro*; Ida, Masaaki*; Watanabe, Makio; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Asakura, Toshihide; et al.
JAERI-Research 99-056, p.278 - 0, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
Kinoshita, Chiken*; Abe, Hiroaki; *; Fukumoto, Kenichi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 219, p.152 - 160, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:76.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Maeda, Koji; Koyama, Shinichi; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Kurosawa, Makoto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Yamada, Fumika; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Sakamoto, Yoshifumi*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Tadao; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Kimura, Yuichiro; Taki, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Takeshi; Ueda, Masato*; Mukai, Masayuki; Yamada, Fumika; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English