Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Onuma, Toshiharu*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Iwasawa, Misako*
Heisei-21-Nendo Sentan Kenkyu Shisetsu Kyoyo Sokushin Jigyo "Chikyu Shimyureta Sangyo Senryaku Riyo Puroguramu" Riyo Seika Hokokusho, p.21 - 27, 2010/07
Silicon carbide, being a wide-band-gap semiconductor, is an attractive material in the development of electronic devices operated under extreme conditions such as high power, high temperature, and high radiation. SiC is particularly attractive for use in MOS technology because among the compound semiconductors only silicon carbide has the thermal oxide SiO , which is a good insulator. However, it is known that SiO
, which is a good insulator. However, it is known that SiO /SiC interfaces have a higher density of interface traps than SiO
/SiC interfaces have a higher density of interface traps than SiO /Si interfaces and that the channel mobility of MOS devices is much lower than theoretically expected values. In order to improve these characteristics, it is important to understand the thermal oxidation process at the SiO
/Si interfaces and that the channel mobility of MOS devices is much lower than theoretically expected values. In order to improve these characteristics, it is important to understand the thermal oxidation process at the SiO /SiC interface. We performed large-scale first-principles molecular dynamics simulations of the SiO
/SiC interface. We performed large-scale first-principles molecular dynamics simulations of the SiO /SiC interface oxidation process. We also performed large-scale first-principles molecular dynamics simulations to generate amorphous SiO
/SiC interface oxidation process. We also performed large-scale first-principles molecular dynamics simulations to generate amorphous SiO /SiC interface.
/SiC interface.
 Sr in highly radioactive liquid waste by alkaline precipitation separation/liquid scintillation counting technique
Sr in highly radioactive liquid waste by alkaline precipitation separation/liquid scintillation counting techniqueOnuma, Takashi; Surugaya, Naoki; Hiyama, Toshiaki
Bunseki Kagaku, 58(7), p.633 - 638, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)An analytical method with a liquid scintillation counting technique for the determination of  Sr in the presence of other elements was developed by deriving a calculation formula to remove their influence. Generally the analysis of
Sr in the presence of other elements was developed by deriving a calculation formula to remove their influence. Generally the analysis of  Sr is performed using the radioactive equilibrium of a generation process of
Sr is performed using the radioactive equilibrium of a generation process of  Y with
Y with  Sr separated from a sample. In this study, a new disintegration calculating formula that enable us remove influences by the coexistence nuclides to analyze
Sr separated from a sample. In this study, a new disintegration calculating formula that enable us remove influences by the coexistence nuclides to analyze  Sr in highly radioactive liquid wastes of spent-fuel reprocessing plants was derived and the formula was validated by experimental approaches. It was found that
Sr in highly radioactive liquid wastes of spent-fuel reprocessing plants was derived and the formula was validated by experimental approaches. It was found that  Sr was analyzed without any influences when a sample contains nuclides that have a long half life and radioactive equilibrium is small enough compared with a generation of
Sr was analyzed without any influences when a sample contains nuclides that have a long half life and radioactive equilibrium is small enough compared with a generation of  Y. The relative standard deviation of the analysis by the proposed method was equal to or less than 3%.
Y. The relative standard deviation of the analysis by the proposed method was equal to or less than 3%.
 /SiC interface structure by the first-principles molecular dynamics simulation
/SiC interface structure by the first-principles molecular dynamics simulationMiyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Materials Science Forum, 556-557, p.521 - 524, 2007/00
SiC semiconductor devices are expected to be used in severe environments. However, SiC devices don't present the theoretically expected performance. This is considered to be attributed to the SiO /SiC interface defects that reduce electrical characteristics of devices. To generate the real device interface structure with the computer simulation, it is important to construct the a-SiO
/SiC interface defects that reduce electrical characteristics of devices. To generate the real device interface structure with the computer simulation, it is important to construct the a-SiO structure on SiC. The slab model using 444 atoms for a-SiO
structure on SiC. The slab model using 444 atoms for a-SiO on a 4H-SiC (0001) crystal layer was constructed by using first-principles MD simulation. The heating and rapid quenching method was carried out to make an a-SiO
on a 4H-SiC (0001) crystal layer was constructed by using first-principles MD simulation. The heating and rapid quenching method was carried out to make an a-SiO /SiC interface structure. The heating temperature, the heating time and the speed of rapid quenching is 4000 K, 3.0 ps and -1000 K/ps, respectively. The interatomic distance and the bond angles of SiO
/SiC interface structure. The heating temperature, the heating time and the speed of rapid quenching is 4000 K, 3.0 ps and -1000 K/ps, respectively. The interatomic distance and the bond angles of SiO layers agreed well with the most probable values in bulk a-SiO
layers agreed well with the most probable values in bulk a-SiO , and there were no coordination defects in the neighborhood of the SiC substrate.
, and there were no coordination defects in the neighborhood of the SiC substrate.
 /4H-SiC(0001) interface oxidation process; From first-principles
/4H-SiC(0001) interface oxidation process; From first-principlesOnuma, Toshiharu*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Iwasawa, Misako*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*
Materials Science Forum, 556-557, p.615 - 620, 2007/00
We performed the dynamical simulation of the SiO /4H-SiC(0001) interface oxidation process using first-principles molecular dynamics based on plane waves and the slab model supercells method. The heat-and-cool method is used to prepare the initial interface structure. In this structure, there is no transition oxide layer or dangling bond at the SiO
/4H-SiC(0001) interface oxidation process using first-principles molecular dynamics based on plane waves and the slab model supercells method. The heat-and-cool method is used to prepare the initial interface structure. In this structure, there is no transition oxide layer or dangling bond at the SiO /SiC interface. As the trigger of the oxidation process, the carbon vacancy is introduced in the SiC layer near the interface. The oxygen molecules are added one by one to the empty sphere in the SiO
/SiC interface. As the trigger of the oxidation process, the carbon vacancy is introduced in the SiC layer near the interface. The oxygen molecules are added one by one to the empty sphere in the SiO layer near the interface in the oxidation process simulation. The molecular dynamics simulation is carried out at 2500 K. The oxygen molecule is dissociated and forms bonds with the Si atom in the SiO
layer near the interface in the oxidation process simulation. The molecular dynamics simulation is carried out at 2500 K. The oxygen molecule is dissociated and forms bonds with the Si atom in the SiO layer. The atoms of Si in the SiC layer at the SiO
layer. The atoms of Si in the SiC layer at the SiO /4H-SiC(0001) interface are oxidized. Carbon clusters are formed in the interface layer. Oxygen molecules react with the carbon clusters and formed CO molecules.
/4H-SiC(0001) interface are oxidized. Carbon clusters are formed in the interface layer. Oxygen molecules react with the carbon clusters and formed CO molecules.
Kinoshita, Motoyasu*; Geng, H. Y.*; Chen, Y.*; Kaneta, Yasunori*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 2006 International Meeting on LWR Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2006) (CD-ROM), p.248 - 254, 2006/10
The New Crossover Project (NXO) is studying effect of fission irradiation on fuel material that research activity is crossing over universities, national and private laboratories. Simulation studies are being performed to find principal and triggering processes of the rim-structure formation in high burnup LWR fuel pellet, using accelerator irradiation and computational calculations. Accelerator irradiation, high energy electron irradiation, fission energy particle beam and ion implantation (ragegas atoms) and combined overlapping irradiations are being performed. For the target of irradiation, CeO isused as simulation of nuclear fuel. The initial results were such as planar structure made by Oxygen defects created by high energy electrons, and surface modification similar to grain-sub-division created by high fluence high energy particle irradiations.
isused as simulation of nuclear fuel. The initial results were such as planar structure made by Oxygen defects created by high energy electrons, and surface modification similar to grain-sub-division created by high fluence high energy particle irradiations.
 /SiC interface
/SiC interfaceMiyashita, Atsumi; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Kano, Takuma; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Sakai, Takayuki*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Soneda, Naoki*
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2004 - March 2005, p.287 - 291, 2005/12
Silicon carbide semiconductor device is expected to be used under a severe environment like the nuclear reactor and the space environment. On the semiconductor device interface, the electric charge state of the defect decides an electric characteristic. To emulate interfacial structure the 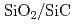 interface structure is generated and the electronic geometry is decided by the first-principle molecular dynamics simulation with the earth simulator. The amorphous
interface structure is generated and the electronic geometry is decided by the first-principle molecular dynamics simulation with the earth simulator. The amorphous 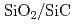 interface structure is made by medium-scale model of about 400 atoms. The heating temperature is 4000K, the heating time is 3.0ps, the speed of rapid cooling is -1000K/ps, and SiC movable layers in the interface are assumed to be 4 layers. In temperature 2200K the
interface structure is made by medium-scale model of about 400 atoms. The heating temperature is 4000K, the heating time is 3.0ps, the speed of rapid cooling is -1000K/ps, and SiC movable layers in the interface are assumed to be 4 layers. In temperature 2200K the 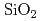 terminal was opened to make the
terminal was opened to make the 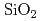 layer more amorphous. The model has almost abrupt interface, however, some defects energy levels were still observed in the band gap. The energy levels are originated from interfacial oxygen. The localized electronic distribution of the dangling bond causes defect energy levels.
layer more amorphous. The model has almost abrupt interface, however, some defects energy levels were still observed in the band gap. The energy levels are originated from interfacial oxygen. The localized electronic distribution of the dangling bond causes defect energy levels.
Hirai, Takashi; Tanai, Kenji; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Shigeno, Yoshimasa*; Namikawa, Tsutomu*; Takaji, Kazuhiko*; Onuma, Satoshi*
JNC TN8400 2003-034, 158 Pages, 2004/02
The objective of this report is to make a proposal of the proper constitutive models and parameters for the evaluation of the long term mechanical behavior of the buffer material in the engineered barrier system. In the second progress report by JNC, it was reported that the well designed engineered barrier system is stable and safety on mechanical support of the overpack to ensure stability and stress which acts on the overpack by using analysis which based on the popular constitutive models for the general caly soils. However, the buffer material which has swelling characteristics is considered not to be ordinary clay soils. So it is necessary to select the reliable constitutive models again. Therefor the proper models were selected again systematically in the several models which have been used for the assessment of the behavior of clay soils and the simulation analysis on the laboratory tests were carried out by using these models. From the result of the simulation analysis it appeared that the selected two models were alike to assess the behavior of the buffer material and the parameters which need to simulate the consolidation tests are different from those for the triaxial compression tests. Finally the analysis was conducted to evaluate the effect of the swelling of the overpack by the collosion and the self weight which causes the sedimentation of the overpack. From the analytical result, it was clarified that two kinds of parameter sets are necessary to evaluate the deformation and the stress of the buffer material in the engineered barrier system.
Hirai, Takashi; Tanai, Kenji; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Takaji, Kazuhiko*; Onuma, Satoshi*
JNC TN8400 2003-031, 48 Pages, 2004/02
The objective of this report is to clarify the characteristics of the bearing capacity of the buffer material against the deformation of the overpack in the engineered barrier system. In the second progress report by JNC, it was reported that the well designed engineered barrier system is stable and safety on mechanical support of the overpack to ensure stability and stress which acts on the overpack by some analysis. However, the degree of the capacity to the ultimate state and the background datas of the design are not necessary clarified in the report. Therefore it is considered to be mportant to assess the ultimate state and make the relationship clear between deformation and bearing capacity of the overpack in the engineered barrier system. So the scale test and the simulation analysis were carried out for the longitudinal deformation of the overpack in the saturated buffer material constrained by the host rock. From the result of the scale test and the analysis it appears that the bearing capacity is increasing with the deformation of the overpack even if the bearing capacity is over the yielding force and the relationship between deformation and bearing capacity can be approximately expressed by the simple fanction.
Hirai, Takashi; Tanai, Kenji; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Suzuki, Hideaki*; *; Onuma, Satoshi*
JNC TN8400 2003-009, 56 Pages, 2003/03
The objective of this report is to clarify mechanical effect of engineered barrier system to the unavoidable fault movement. From the basic policy of the second progess report by JNC, natural phenomenon which affect strongly to the geological disposal system shoult be avoided. However, small faults as sliprate "C" far from principal fault zone, are difficult to be found out completely. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the influence of these fault movements and to clarify stability and safety of the engineered barrier system. Accordingly, the effect of a rock displacement across a deposition holl was considered and the midium scale test was carried out. Then midium scale test was simulated by Finit Element Method in which the constitutive model of Tresca was adopted to analyze elastoplastic behavior of buffer material. From the result of the midium scale test and the analysis, it was realized that the buffer material diminish shear stress acting on the overpack. Further analytical study was conducted to evaluate the real scale engineered barrier system designed in the second progress report by JNC. From the study, it was apeared that stress in buffer corresponded to the stress calculated for the midium scale test model. Consequently, it was obvious that rock displacement, 80% of buffer thickness, didn't affect overpack if velocity of fault movement was under 10 cm/sec.
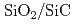 interface by the first-principles molecular dynamics simulation
interface by the first-principles molecular dynamics simulationMiyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Iwasawa, Misako*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*
no journal, ,
Silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductor devices are expected to be used under severe environments such as outer space and/or nuclear power plants. However, at this time, SiC devices don't present the predictable performance, since defects at 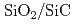 interface reduce electric characteristics of them. The relation among atomic structures, interfacial defects and electric characteristics is not clear. Therefore, we tried to solve these problems by the computer simulation. The SiO
interface reduce electric characteristics of them. The relation among atomic structures, interfacial defects and electric characteristics is not clear. Therefore, we tried to solve these problems by the computer simulation. The SiO /SiC interface structure is generated and the electronic geometry is decided by the first-principle molecular dynamics (MD) simulation with the Earth-Simulator. The amorphous
/SiC interface structure is generated and the electronic geometry is decided by the first-principle molecular dynamics (MD) simulation with the Earth-Simulator. The amorphous 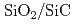 interface structure is made by heating and rapid quench calculation using 444 atoms model. The heating temperature is 4000K, the heating time is 3.0ps, and the speed of rapid quench is
interface structure is made by heating and rapid quench calculation using 444 atoms model. The heating temperature is 4000K, the heating time is 3.0ps, and the speed of rapid quench is 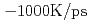 . After a rapid quench, the atomic structure became an almost perfect interfacial structure. However, a few defect energy levels were still observed in the band gap. The defect energy levels are originated from the localized electronic distribution of the interfacial oxygen.
. After a rapid quench, the atomic structure became an almost perfect interfacial structure. However, a few defect energy levels were still observed in the band gap. The defect energy levels are originated from the localized electronic distribution of the interfacial oxygen.
 thin films deposited on 4H-SiC(0001) substrates by capacitance-voltage method
thin films deposited on 4H-SiC(0001) substrates by capacitance-voltage methodYoshikawa, Masahito; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /SiC interface structure by the first-principles
/SiC interface structure by the first-principlesMiyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Sakai, Takayuki*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Kano, Takuma; Soneda, Naoki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /4H-SiC(0001) interface oxidation process; Formation of carbon cluster
/4H-SiC(0001) interface oxidation process; Formation of carbon clusterOnuma, Toshiharu*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Iwasawa, Misako*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /SiC interface by the simulation; First-principles molecular dynamics
/SiC interface by the simulation; First-principles molecular dynamicsMiyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /SiC interface structure by the first-principles, 2
/SiC interface structure by the first-principles, 2Miyashita, Atsumi; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /4H-SiC(0001) interface
/4H-SiC(0001) interfaceOnuma, Toshiharu*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Iwasawa, Misako*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 and UO
and UO
Nakamura, Jinichi; Kaneta, Yasunori*; Chen, Y.*; Geng, H.*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Kinoshita, Motoyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 and CeO
and CeO
Nakamura, Jinichi; Chen, Y.*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Kaneta, Yasunori*; Geng, H.*; Kinoshita, Motoyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English