Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Nakanishi, Tomoaki*; Nakayama, Takenori*; Sakashita, Shinji*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2005-001, 224 Pages, 2004/02
For repository container material of high-level radioactive waste, titanium and nickel-base alloys have been investigated as high corrosion resistance metal. In this study, the effects of environmental and material factors on hydrogen absorption of titanium were investigated experimentally. As for nickel-base allys, previous studies on corrosion behavior were serched.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2004-017, 71 Pages, 2004/02
Research on changes of nitrate by interactions with metals under the wastes disposal environment containing TRU nuclide
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2004-016, 194 Pages, 2004/02
Research on Changes of Nitrate by Chemical Interactions with Metals under the wastes Disposal Environment Contaioning TRU Nucride
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Nakanishi, Tomoaki*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Inoue, Takao*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-092, 246 Pages, 2003/02
Titanium is being studied for the high-level radioactive waste package material. Titanium has good corrosion resistance, however there is the possibility of hydrogen embrittlement with absorption of hydrogen in reducing condition. Experimental studies were performed to evaluate the hydrogen absorption behaviors of titanium in reducing condition. The failure model of the titanium overpack was also examined from the viewpoint of fracture mechanism in order to evaluate the fracture behavior of the titanium overpack caused by the hydrogen absorption. (1) Scratch test was conducted in reduce condition. The surface films on the titanium specimen were analyzed to examine the changes of the existing films and the growth phenomena of the regenerated films on the titanium specimen. (2)The long-term reaction test of the titanium specimen using the glass-seal ampoules maintaining reducing condition was conducted and analyses of the hydrogen gas generation and absorption quantitative as well as the generated film evaluation were performed. (3) Under reducing condition, the electrochemical acceleration tests of the titanium specimen were conducted. The effect of acceleration rate on the hydrogen absorption and surface film was evaluated, and the prediction as to the hydrogen absorption behavior at a natural state was also made. (4) The prediction of the maximum residual stress and the evaluation of crack growth of the titanium overpack based on the previous studies were performed. Feasibility of the modeling of fracture phenomenon with existing analysis technique was examined and the items to be developed were also discussed.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-080, 153 Pages, 2003/02
There exists the waste including a nitrate ion as a salt in the TRU waste materials. This nitrate ion can be transferred to the nitrite ion and/or ammonia by reducing materials such as metals in the waste disposal environment, and has the possibility to affect on the disposal environment and nuclide transfer parameters.Therefore, electrochemical tests were conducted to evaluate the reaction rate parameters of the nitrate ion and metals under the low oxygen environment. The long-term reaction test using the glass-seal vessel was also conducted to grasp precisely the nitrate ion transition reaction rate and the gas generation rate caused by the reaction of metal and the nitrate ion coexist solution. (1) Reaction rate constants under various environments were obtained performing the potentiostatic holding tests with the parameters of the solution pH, temperature, and the nitrate and nitrite ion concentrations. The formula of the nitrate ion transition reaction rate was also examined based on these obtained data. (2) Conducting the immersion tests under the environment of the low oxygen and high-pH rainfall underground water site, the long-term reaction rate data were obtained on the reaction products (ammonia, hydrogen gas etc.) of metals (carbon steel, stainless steel and zircaloy etc.) with nitrate ion. The tests under the same conditions as in the past were also conducted to evaluate the test accuracy and error range of the long-term reaction test with the glass-seal vessels.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-079, 252 Pages, 2003/02
There exists the waste including a nitrate ion as a salt in the TRU waste materials. This nitrate ion can be transferred to the nitrite ion and/or ammonia by reducing materials such as metals in the waste disposal environment, and has the possibility to affect on the disposal environment and nuclide transfer parameters. Therefore, electrochemical tests were conducted to evaluate the reaction rate parameters of the nitrate ion and metals under the low oxygen environment. The long-term reaction test using the glass-seal vessel was also conducted to grasp precisely the nitrate ion transition reaction rate and the gas generation rate caused by the reaction of metal and the nitrate ion coexist solution. (1)}Reaction rate constants under various environments were obtained performing the potentiostatic holding tests with the parameters of the solution pH, temperature, and the nitrate and nitrite ion concentrations. The formula of the nitrate ion transition reaction rate was also examined based on these obtained data. (2) Conducting the immersion tests under the environment of the low oxygen and high-pH rainfall underground water site, the long-term reaction rate data were obtained on the reaction products (ammonia, hydrogen gas etc.) of metals (carbon steel, stainless steel and zircaloy etc.) with nitrate ion. The tests under the same conditions as in the past were also conducted to evaluate the test accuracy and error range of the long-term reaction test with the glass-seal vessels.
Wada, Ryutaro*; *; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-007, 86 Pages, 2003/02
The overpack for the high-level radioactive waste disposal is expected to maintain the long-term integrity and the corrosion behavior model of the overpack has been developed so far. To verify the adequacy and conservatism of the model, in this study, measurements of hydrogen absorption regarding hydrogen embrittlement of carbon steel, one of the candidate materials, were carried out in the compacted bentonite coexistence environment. The definite research programs to be performed in the future were also established for the important subjects as the extralong tests: (1)The hydrogen penetration-measuring device was designed to measure the penetrated hydrogen caused by the corrosion of carbon steel in the buffer material (compacted bentonite). (2)Out of generated hydrogen by the corrosion of carbon steel in the buffer material, the penetrated hydrogen volumes into carbon steel were measured. (3) Research programs on the four laboratory test themes and the three site test themes were established as the extralong test themes to be performed in the future.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-077, 156 Pages, 2002/02
Some TRU wastes contain nitrate ions as salt.The nitrate ions might transform into NO2- and NH3, etc. in the disposal site environment because of reducing agent such as metals, possibly changing disposal site environment or affecting nuclide migration parameters.Therefore, we investigated of chemical interaction between NO3- and metals in a low oxygen environment that corresponds to the disposal site environment.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-076, 300 Pages, 2002/02
Some TRU wastes contain nitrate ions as salt.The nitrate ions might transform into NO2- and NH3, etc. in the disposal site environment because of reducing agent such as metals, possibly changing disposal site environment or affecting nuclide migration parameters. Therefore, we investigated of chemical interaction between NO3- and metals in a low oxygen environment that corresponds to the disposal site environment.
Wada, Ryutaro*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2002-002, 111 Pages, 2002/02
In geologic disposal system of high-level radioactive waste, confinement by waste container must be assured over a thousand years. Titanium is one of the candidate materials, so it is important to clarify hydrogen embrittlement property under geological environment for the container lifetime prediction. The purpose of this study is to investigate hydrogen embrittlement behavior of titanium under reducing condition. Hydrogen was absorbed into titanium test pieces by electrochemical method, and tensile bending and impact tests were performed for mechanical property research. Under 1000ppm concentration of hydrogen, while distinct degradation of mechanical properties by hydrogen embrittlement occurred on dynamic stress, micro cracks induced by hydride were observed in fracture, but distinct degradation of mechanical properties by hydrogen embrittlement did not occur on static stress. Under low oxygen circumstances, corrosion rates of titanium were estimated 10 micrometer/year by hydrogen absorption method, on the contrary to 10
micrometer/year by hydrogen absorption method, on the contrary to 10 micrometer/year by gas evolution method. These results indicated hydrogen generated by corrosion of titanium under reducing condition, is almost absorbed into material. Carbon steel is regarded as reinforcement of the titanium nuclear fuel waste container. Magnetite, corrosion product of carbon steel, is considered to accelerate corrosion rate. Contribution of hydrogen evolution reaction to its acceleration is estimated to ca.60%.
micrometer/year by gas evolution method. These results indicated hydrogen generated by corrosion of titanium under reducing condition, is almost absorbed into material. Carbon steel is regarded as reinforcement of the titanium nuclear fuel waste container. Magnetite, corrosion product of carbon steel, is considered to accelerate corrosion rate. Contribution of hydrogen evolution reaction to its acceleration is estimated to ca.60%.
Wada, Ryutaro*; *; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; *; *; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*
JNC TJ8400 2002-001, 71 Pages, 2002/02
The overpack is expected to have long-term soundness, and corrosion behavior models of the overpack have been constructed. To verify validity and maintainability of the models, this study conducted a research on a super-long-term test of overpack materials for several decades. (1)We designed a testing device that would allow long-term monitoring of the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, an overpack candidate material, and the condition in the buffer material in an environment corresponding to the environment immediately after disposal. (2)We examined and prototyped a test container that would allow long-term immersion tests of carbon steel without maintenance operations such as solution exchange. (3)We proposed super-long-term tests (about 20 years) that would contribute to future geological disposal projects and safety rules. (4)We investigated a method for managing and preserving the records of the super-long-term test for the test period (20 years).
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*
JNC TN8400 2001-011, 62 Pages, 2001/03
The corrosion of metallic materials used in natural environment are sometimes affected by microbial action. It is apprehended that microorganism living in deep underground or brought from ground surface during excavation makes an impact on overpack material for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) is known to be one of the most representative microorganism which affects the corrosion of metals. In this study, the behavior of growth of SRB was investigated at first under the presence of bentonite as a main component of buffer material which encloses the overpack. The results of the tests showed that the population of SRB after the culture in synthetic sea water mixed with bentonite decreased with increasing the ratio of bentonite/solution. SRB was hardly grown in medium whose bentonite/solution ratio exceeded 1000g/l. As a conservative case, the effects of sulfide on the corrosion of overpack materials were also studied assuming high activity of SRB. Carbon steel, copper and titanium specimens were immersed in synthetic sea water purging 0.1MPa H S gas and the corrosion behavior was compared with the results in N
S gas and the corrosion behavior was compared with the results in N gas purging environment. Obvious effect of sulfide on the corrosion of carbon steel was not observed, but the corrosion rates of copper specimens were accelerated several hundred times by purging H
gas purging environment. Obvious effect of sulfide on the corrosion of carbon steel was not observed, but the corrosion rates of copper specimens were accelerated several hundred times by purging H S gas. The absorption of hydrogen into titanium specimens was not affected by purging H
S gas. The absorption of hydrogen into titanium specimens was not affected by purging H S gas, but the difference of hydrogen absorption between pure titanium and titanium alloy containing 0.06%-Pd was observed.
S gas, but the difference of hydrogen absorption between pure titanium and titanium alloy containing 0.06%-Pd was observed.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-040, 171 Pages, 2000/02
In order to evaluate the hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of metallic materials contained in TRU wastes, the ampoule type immersion tests (the test specimen and test solution are enclosed into a glass ampoule) have been performed following the last year. The gas generation tests on zircaloy, stainless steel and carbon steel were performed under the aerobic condition in this year. (1)The hydrogen gas generation rates due to the corrosion of stainless steel (SUS304) in simulated underground water (pH8 13.5) were 0.01
13.5) were 0.01 0.15
0.15 m/y (oxygen concentration = 20%) and
m/y (oxygen concentration = 20%) and  0.1
0.1 m/y (oxygen concentration = 1%). (2)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of carbon steel (SPHC) in simulated underground water (pH8
m/y (oxygen concentration = 1%). (2)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of carbon steel (SPHC) in simulated underground water (pH8 13.5) ranged in equivalent corrosion rate of about 0.02
13.5) ranged in equivalent corrosion rate of about 0.02 12
12 m/y (oxygen concentration = 20%) and
m/y (oxygen concentration = 20%) and  0.3
0.3 m/y(oxygen concentration = 1%) depending on the composition of test solution, and the ranking by pH of solution was pH8
m/y(oxygen concentration = 1%) depending on the composition of test solution, and the ranking by pH of solution was pH8 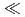 pH10
pH10  pH13.5
pH13.5  pH12.5. (3)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of zircaloy in simulated underground water (pH10
pH12.5. (3)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of zircaloy in simulated underground water (pH10 13.5) decreased with the immersion time, and the equivalent corrosion rate after immersion of 30
13.5) decreased with the immersion time, and the equivalent corrosion rate after immersion of 30 180 days was
180 days was  0.004
0.004 m/y. (4)The corrosion rates of zircaloy, stainless steel and carbon steel based on oxygen were higer than that on the hydrogen gas generation.
m/y. (4)The corrosion rates of zircaloy, stainless steel and carbon steel based on oxygen were higer than that on the hydrogen gas generation.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-039, 77 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Wada, Ryutaro*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Taniguchi, Naoki;
JNC TN8400 99-077, 58 Pages, 1999/10
As a part of evaluation of corrosion life of carbon steel overpack, the experimental studies have been performed on the effects of bacteria on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel in compacted bentonite using iron bacteria (IB) as a representative oxidizing bacteria and sulphur reducing bacteria (SRB) as a representative reducing bacteria. The results of the experimental studies showed that ; (1)The activity of SRB was low in compacted bentonite in spite of applying suitable condition for the action of bacteria such as temperature and nutritious solution. (2)Although the corrosion behavior of carbon steel was affected by the existence of bacteria in simple solution, the corrosion rates of carbon steel in compacted bentonite were several  m/year
m/year  10
10 m/year irrespective of coexistence of bacteria and that the corrosion behavior was not affected by the existence of bacteria. According to these results, it was concluded that the bacteria would not affect the corrosion behavior of carbon steel overpack under repository condition.
m/year irrespective of coexistence of bacteria and that the corrosion behavior was not affected by the existence of bacteria. According to these results, it was concluded that the bacteria would not affect the corrosion behavior of carbon steel overpack under repository condition.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Inaba, Masayuki*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 99-014, 47 Pages, 1999/02
In order to evaluate the hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of metallic materials contained in TRU wastes, the ampoule type immersion tests (the test specimen and test solution are enclosed into a glass ampoule) have been performed following the last year. The gas generation tests on single metal of zircaloy and stainless steel were continued for longer immersion time, and the gas generation tests on single metal of carbon steel and dissimilar metals were added in this year. (1)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of zircaloy in simulated underground water (pH10 3.5) decreased with the immersion time, and the equivalent corrosion rate after immersion of 230 days ranged in 10
3.5) decreased with the immersion time, and the equivalent corrosion rate after immersion of 230 days ranged in 10
 10
10
 m/y. (2)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of stainless steel (SUS304) in simulated underground water (PH10
m/y. (2)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of stainless steel (SUS304) in simulated underground water (PH10 3.5) generally tended to decrease with immersion time, but increasing tendency was also recognized in the high pH range. The equivalent corrosion rate after immersion of 230 days ranged in 10
3.5) generally tended to decrease with immersion time, but increasing tendency was also recognized in the high pH range. The equivalent corrosion rate after immersion of 230 days ranged in 10
 10
10
 m/y. (3)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of carbon steel (SS400) in simulated underground water (pH10
m/y. (3)The hydrogen gas generation rate due to the corrosion of carbon steel (SS400) in simulated underground water (pH10 13.5) ranged in equivalent corrosion rate of about 0.02
13.5) ranged in equivalent corrosion rate of about 0.02 3
3  m/y depending on the composition of test solution, and the ranking by pH of solution was pH10
m/y depending on the composition of test solution, and the ranking by pH of solution was pH10 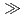 pH13.5
pH13.5  PH12.5. (4)The effects of electrical contact of zircaloy or stainless steel on the hydrogen gas generation rate from carbon steel have not remarkably been recognized. (5)By continuing these tests for longer time hereafter, the reliability of these data must furthermore be raised. In addition as a thema nearafter, gas generation rate under unsaturated condition considering the first stage of disposal should be evaluated.
PH12.5. (4)The effects of electrical contact of zircaloy or stainless steel on the hydrogen gas generation rate from carbon steel have not remarkably been recognized. (5)By continuing these tests for longer time hereafter, the reliability of these data must furthermore be raised. In addition as a thema nearafter, gas generation rate under unsaturated condition considering the first stage of disposal should be evaluated.
Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; Tomari, Haruo*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*
PNC TJ1074 98-002, 270 Pages, 1998/02
None
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; Tomari, Haruo*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*; Shimoda, Hideaki*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Nishimoto, Hidetoshi*; Oda, Masashi*
PNC TJ1058 98-002, 159 Pages, 1998/02
None