Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 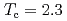 K for
K for 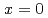 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 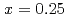 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 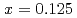 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 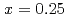 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 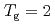 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 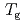 with a
with a 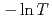 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
 Cs concentrations in coastal sediments off Fukushima
Cs concentrations in coastal sediments off FukushimaSuzuki, Shotaro*; Amano, Yosuke*; Enomoto, Masahiro*; Matsumoto, Akira*; Morioka, Yoshiaki*; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Kaeriyama, Hideki*; Miura, Hikaru*; Tsumune, Daisuke*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 831, p.154670_1 - 154670_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.93(Environmental Sciences)Tsunoda, Naofumi*; Otsuka, Takaharu; Takayanagi, Kazuo*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Suzuki, Toshio*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Sota*; Ueno, Hideki*
Nature, 587, p.66 - 71, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:92.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Hideki*; Suzuki, Rikie*; Yang, W.*; Ikawa, Hiroki*; Inoue, Tomoharu*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Kim, Y.*
Polar Data Journal (Internet), 2, p.14 - 29, 2018/11
The Arctic and boreal regions have been experiencing a rapid warming in the 21st century. It is important to understand the dynamics of boreal forest at the continental scale under the climate and environmental changes. While the role of understory vegetation in boreal forest ecosystems on carbon and nutrient cycling cannot be ignored, they are still one of least understood components in boreal ecosystems. Spectroscopic measurements of vegetation are useful to identify species and their biochemical characteristics. In this data paper, we present spectral reflectances of 44 typical understory formations and five 30-m long transects. The spectral reflectance covers the spectral region of visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared (350-2500 nm). For the transect measurements, we decided the length of transect at 30 m, similar to the scale of one pixel of a Landsat type satellite imagery. The photographs at all positions, where spectral reflectances were obtained, are included to understand the structure and status of each sample. The data set contains six dwarf shrubs (blueberry (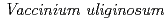 ), cowberry (
), cowberry (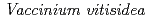 ), feltleaf willow (
), feltleaf willow (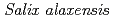 ), young birch (
), young birch (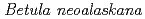 ), young aspen (
), young aspen ( ), and young black spruce (
), and young black spruce ( )), two herbaceous (cottongrass (
)), two herbaceous (cottongrass ( ) and marsh Labrador tea (
) and marsh Labrador tea ( )), three mosses (Sphagnum moss, splendid feather moss (
)), three mosses (Sphagnum moss, splendid feather moss ( ), and polytrichum moss (
), and polytrichum moss ( )), and reindeer lichen (
)), and reindeer lichen ( ). Spectral reflectances from several non-vegetative such as snow, litter, and soil are also included. This spectral and photographic data set can be used for understanding the spectral characteristics of understory formations, designing newly planned spectral observations, and developing and validating the remote sensing methodology of large scale understory monitoring.
). Spectral reflectances from several non-vegetative such as snow, litter, and soil are also included. This spectral and photographic data set can be used for understanding the spectral characteristics of understory formations, designing newly planned spectral observations, and developing and validating the remote sensing methodology of large scale understory monitoring.
Kadowaki, Masanao; Katata, Genki*; Terada, Hiroaki; Suzuki, Takashi; Hasegawa, Hidenao*; Akata, Naofumi*; Kakiuchi, Hideki*
Atmospheric Environment, 184, p.278 - 291, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.77(Environmental Sciences)The long-lived radioactive iodine ( I) is a useful geochemical tracer in the atmospheric environment. We recently observed clear seasonal trends in air concentration and deposition of
I) is a useful geochemical tracer in the atmospheric environment. We recently observed clear seasonal trends in air concentration and deposition of  I in Japan. Using these data, we developed a global atmospheric
I in Japan. Using these data, we developed a global atmospheric  I transport model to reveal key processes for the global atmospheric
I transport model to reveal key processes for the global atmospheric  I cycle. The model generally reproduced the observed seasonal change in air concentration and deposition of
I cycle. The model generally reproduced the observed seasonal change in air concentration and deposition of  I in Japan, and the global distribution of
I in Japan, and the global distribution of  I concentration in rain as presented in past literature. Numerical experiments changing the intensity of anthropogenic and natural sources were conducted to quantify the impact of anthropogenic sources on the global
I concentration in rain as presented in past literature. Numerical experiments changing the intensity of anthropogenic and natural sources were conducted to quantify the impact of anthropogenic sources on the global  I cycle. The results indicated that the atmospheric
I cycle. The results indicated that the atmospheric  I from the anthropogenic sources was deposited in winter and can be accumulated mainly in the northern part of Eurasia. In contrast, the atmospheric
I from the anthropogenic sources was deposited in winter and can be accumulated mainly in the northern part of Eurasia. In contrast, the atmospheric  I from the natural sources dominated the deposition in summer. These results suggested that the re-emission process of
I from the natural sources dominated the deposition in summer. These results suggested that the re-emission process of  I from the Earth's surface may be important as a secondary impact of
I from the Earth's surface may be important as a secondary impact of  I in the global-scaled environment. Furthermore, although wet deposition dominated the total deposition in the Northern hemisphere, dry deposition regionally and seasonally contributed to the total deposition over arctic and northern part of Eurasia in winter, suggesting that the dry deposition may play a key role in the seasonal change of
I in the global-scaled environment. Furthermore, although wet deposition dominated the total deposition in the Northern hemisphere, dry deposition regionally and seasonally contributed to the total deposition over arctic and northern part of Eurasia in winter, suggesting that the dry deposition may play a key role in the seasonal change of  I deposition in the Northern hemisphere high latitudes.
I deposition in the Northern hemisphere high latitudes.
Kobayashi, Hideki*; Nagai, Shin*; Kim, Y.*; Yan, W.*; Ikeda, Kyoko*; Ikawa, Hiroki*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Suzuki, Rikie*
Remote Sensing, 10(7), p.1071_1 - 1071_19, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:51.57(Environmental Sciences)Plant phenology timings, such as spring green-up and autumn senescence, are essential state information characterizing biological responses and terrestrial carbon cycles. Current efforts for the in situ reflectance measurements are not enough to obtain the exact interpretation of how seasonal spectral signature responds to phenological stages in boreal evergreen needleleaf forests. This study shows the first in situ continuous measurements of canopy scale (overstory + understory) and understory spectral reflectance and vegetation index in an open boreal forest in interior Alaska. Two visible and near infrared spectroradiometer systems were installed at the top of the observation tower and the forest understory, and spectral reflectance measurements were performed in 10 min intervals from early spring to late autumn. We found that canopy scale normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) varied with the solar zenith angle. On the other hand, NDVI of understory plants was less sensitive to the solar zenith angle. Due to the influence of the solar geometry, the annual maximum canopy NDVI observed in the morning satellite overpass time (10-11 am) shifted to the spring direction compared with the standardized NDVI by the fixed solar zenith angle range (60-70 degree). We also found that the in situ NDVI time-series had a month-long high NDVI plateau in autumn, which was completely out of photosynthetically active periods when compared with eddy covariance net ecosystem exchange measurements. The result suggests that the onset of an autumn high NDVI plateau is likely to be the end of the growing season. In this way, our spectral measurements can serve as baseline information for the development and validation of satellite-based phenology algorithms in the northern high latitudes.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-030, 115 Pages, 2015/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2014. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Goto, Ichiro*; Kibe, Satoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-040, 115 Pages, 2015/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-041, 115 Pages, 2014/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2012, from 1st April 2012 to 31st March 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Hemmi, Tsutomu; Harjo, S.; Kajitani, Hideki; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Abe, Jun; Gong, W.; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
KEK Progress Report 2013-4, p.45 - 47, 2013/11
The gradual degradation was observed in the results for ITER CS conductor samples. To investigate its origin, the internal strain in the sample after the testing was successfully measured using a neutron diffraction technique non-destructively. Up to now, the transverse electromagnetic loading has been considered as an origin of the degradation due to the local bending at the high loading side (HLS). However, as a result of the neutron diffraction measurement, the large bending at the LLS of the HFZ was found. The large bending was considered as an origin of the strand buckling due to the large void generated by the transverse electromagnetic loading and the thermally induced residual compressive strain. For the improvement of the conductor performance on the strand buckling, the shorter twisting pitch (STP) can be considered. The result of the SULTAN testing of the conductor sample with STP found very effective, and the performance degradation was negligible.
Takasaki, Koji; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Suzuki, Hideki; Ushigome, Sadaharu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(3), p.255 - 261, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)The wide-range krypton-85 detector was developed for monitoring of krypton-85 gas, which was discharged from the stack of a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant and varied largely in concentration. The detector combined a current-mode-operated plastic scintillation counter with a gated photomultiplier. The discrimination voltage of gated photomultiplier was determined, and the effects of temperature and humidity were examined on the background measurement. The detector was calibrated by krypton-85 gas and the decision threshold was estimated. These examinations showed that the wide-range krypton-85 detector worked in the measurement range as wide as 10 -10
-10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm in linearity and the decision threshold of krypton-85 concentration was 1.3
in linearity and the decision threshold of krypton-85 concentration was 1.3 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm for 10-minute measurement. The parallel measurement was made between this detector and a GM counter in the reprocessing laboratory. Both concentrations showed a good agreement with each other.
for 10-minute measurement. The parallel measurement was made between this detector and a GM counter in the reprocessing laboratory. Both concentrations showed a good agreement with each other.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Agostini, P.*; Ara, Kuniaki; Cevolani, S.*; Chida, Teruo*; Ciotti, M.*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Garin, P.*; Gessii, A.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.1007 - 1014, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:76.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes the latest design of liquid lithium target system in IFMIF. Design requirement of the Li target is to provide a stable Li jet with a speed of 20 m/s to handle an averaged heat flux of 1 GW/m . A double reducer nozzle and a concaved flow are applied to the target design. On Li purification, a cold trap and two kinds of hot trap are applied to control impurities below permissible levels. Nitrogen concentration shall be controlled below 10 wppm by one of the hot trap. Tritium concentration shall be controlled below 1 wppm by an yttrium hot trap. To maintain reliable continuous operation, various diagnostics are attached to the target assembly. Among the target assembly, a back-plate made of RAFM is located in the most severe region of neutron irradiation (50 dpa/y). Therefore, two design options of replaceable back wall and their remote handling systems are under investigation.
. A double reducer nozzle and a concaved flow are applied to the target design. On Li purification, a cold trap and two kinds of hot trap are applied to control impurities below permissible levels. Nitrogen concentration shall be controlled below 10 wppm by one of the hot trap. Tritium concentration shall be controlled below 1 wppm by an yttrium hot trap. To maintain reliable continuous operation, various diagnostics are attached to the target assembly. Among the target assembly, a back-plate made of RAFM is located in the most severe region of neutron irradiation (50 dpa/y). Therefore, two design options of replaceable back wall and their remote handling systems are under investigation.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Izaki, Kenji; Suzuki, Hideki; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Ozeki, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Research 2007-009, 40 Pages, 2007/03
Criticality Accident Alarm System (CAAS) has been used in Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories for about 20 years, and there is occurrence of the abnormal signal called "Single Detection", as an operational problem of CAAS. Radiation Protection Division has investigated the causes affecting "Single Detection", as well as reducing the influence of noises such as electromagnetic waves and power source variations. This report shows the result of the long-term observation with detectors of CAAS and describes that cosmic rays have high possibility to cause "Single Detection".
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:89.22(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hiroo; Riccardi, B.*; Loginov, N.*; Ara, Kuniaki*; Burgazzi, L.*; Cevolani, S.*; Dell'Ocro, G.*; Fazio, C.*; Giusti, D.*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.202 - 207, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.09(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), being developed by EU, JA, RF and US, is a deuteron-lithium (Li) reaction neutron source for fusion materials testing. In the end of 2002, 3 year Key Element technology Phase (KEP) to reduce the key technology risk factors has been completed. This paper describes these KEP tasks results. To evaluate Li flow characteristics, a water and Li flow experiments have been done. To develop Li purification system, evaluation of nitrogen and tritium gettering materials have been done. Conceptual design of remote handling and basic experiment have been donde. In addition, safety analysis and diganostics design have been done. In the presentation, the latest design and future prospects will be also summarized.
Morita, Suguru; Tanizawa, Teruaki*; Masayuki, Morifuji,; Takasaki, Koji; Suzuki, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kazunori; Kobayashi, Hirohide
JNC TN8410 2004-011, 83 Pages, 2004/07
In the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF), after reconstruction was completed, the examination for advanced hydrometallurgy reprocessing was carried out from December 2002 to March 2004. In this examination, Kr were discharged from the stack. Discharge of
Kr were discharged from the stack. Discharge of Kr was measured and estimated by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector.GM Gas monitor of the CPF stack monitor was exchanged for the wide range radioactive Krypton detector in fiscal 1994. In discharge monitoring of this examination for advanced hydrometallurgy reprocessing,
Kr was measured and estimated by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector.GM Gas monitor of the CPF stack monitor was exchanged for the wide range radioactive Krypton detector in fiscal 1994. In discharge monitoring of this examination for advanced hydrometallurgy reprocessing, Kr gas were detected for the first time by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector of CPF. In this examination, the temporary gas monitor of the conventional GM detector was installed, and the result of measurement and inventory were compared.In this report the discharge of
Kr gas were detected for the first time by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector of CPF. In this examination, the temporary gas monitor of the conventional GM detector was installed, and the result of measurement and inventory were compared.In this report the discharge of Kr is indicated by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector. As a result of comparative evaluation, it was confirmed that the discharge monitoring by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector was appropriate.
Kr is indicated by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector. As a result of comparative evaluation, it was confirmed that the discharge monitoring by the wide range radioactive Krypton detector was appropriate.
Kobayashi, Hirohide; ; ; Maruo, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Kenjiro; *
JNC TN8410 2002-006, 82 Pages, 2002/08
The stationary gaseous effluent monitor is equipment intended for continuously monitoring radioactivity in gaseous effluents released from the nuclear facilities. This monitor consists of sampling, detection and control assemblies. The sampling pump is a most integral part of the sampling assembly and required to be operated with an appropriate pressure to keep the continuous monitoring. However, in 1998, the failures of sampling pumps had successively occurred.This was due to the overload in pressure at the intake or the outlet. To prevent from the failures of sampling pumps, the overload characteristics and the mean time between failures (MTBF) were investigated. The following results were obtained. (1)The performance and tolerance tests with rapid increase of air pressure were carried out. The sampling pumps could withstand two or three times higher pressure than the regularly operating pressure during a few minutes. But, after that, the pump suddenly fell down by an over-current relay (OCR). (2)The MTBF were analyzed on the basis of the maintenance and repair records over a period from 1988 to 1998. The MTBF of a sampling pump were in the range from 7,600 to 35,500 hours. For a preventive maintenance, the consumption parts, such as a carbon blade and a bearing of rotor shaft, etc., should be replaced periodically.
Nishi, Masataka; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; et al.
Materialovedenie (Russian Science of Materials) No.2, p.42 - 45, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Ohira, Shigeru; Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Tadokoro, Takahiro*; Nakamura, H.*; Ito, Takeshi*; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Iwai, Yasunori; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 40(3Y), p.519 - 525, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:59.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English