Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
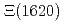 and
and 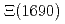 resonances in
resonances in 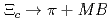 decays
decaysMiyahara, Kenta*; Hyodo, Tetsuo*; Oka, Makoto; Nieves, J.*; Oset, E.*
Physical Review C, 95(3), p.035212_1 - 035212_12, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:89.74(Physics, Nuclear)Nonleptonic weak decays of 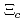 into
into 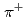 and a meson-baryon final state,
and a meson-baryon final state, 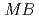 , are analyzed from the viewpoint of probing
, are analyzed from the viewpoint of probing 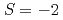 baryon resonances, i.e.
baryon resonances, i.e. 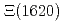 and
and 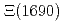 . We argue that the weak decay of
. We argue that the weak decay of 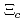 is dominated by a single quark-line diagram. The decay process has an advantage of being free from meson resonances in the
is dominated by a single quark-line diagram. The decay process has an advantage of being free from meson resonances in the 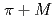 invariant mass distribution. The invariant mass distribution of the meson-baryon final state is calculated, assuming that the
invariant mass distribution. The invariant mass distribution of the meson-baryon final state is calculated, assuming that the 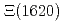 and
and 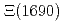 resonances have
resonances have 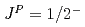 . It is found that a clear peak for the
. It is found that a clear peak for the 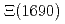 is seen in the
is seen in the 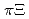 and
and 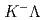 spectra. We also suggest that the ratios of the
spectra. We also suggest that the ratios of the 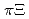 ,
, 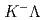 and
and 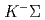 final states are useful to distinguish whether the peak is originated from the
final states are useful to distinguish whether the peak is originated from the 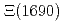 resonance or it is a
resonance or it is a 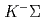 threshold effect.
threshold effect.
Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto*; Inagaki, Manabu*; Koo, Shigeru*; Shibata, Masahiro; Itazu, Toru; Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Miyahara, Kaname; Apted, M. J.*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1665, p.39 - 45, 2014/07
In Japan, the likelihood of uplift/erosion on repository performance and waste isolation can be typically greatly reduced or excluded by careful siting, however, the inability to completely exclude the uplift/erosion scenario may require an analysis of the consequences of such a scenario. For this purpose, an assessment approach has been developed to more realistically treat the effect of uplift/erosion for a hypothetical repository located in sedimentary host rock. A key advantage to this approach is the extrapolation of the geohistory of modern analogue sites to develop credible initial inputs for future volunteer sites that may be poorly characterized at the initial stages of site investigation. In addition, the approach provides a systematic basis for bounding the range of possible evolution in thermal-hydrological-mechanical-chemical conditions of a repository experiencing different uplift/ erosion rates.
Miyahara, Kaname; Kawamura, Makoto*; McKinley, I. G.*; Inagaki, Manabu*; Ebina, Takanori*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(7), p.1069 - 1076, 2011/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)In Japan, uplift/erosion scenarios must be analysed even if they occur far in the future, as no assessment cut-off times have yet been defined. For this purpose, the geological record of river terrace formation and their long term evolution has been studied further, with the aim of constructing a more realistic fluvial erosion model compared with the original, rather simple cyclic fluvial erosion model developed in a previous study. The model allows the consequences of erosion of the repository to be assessed, as before using comparisons with natural radionuclide fluxes. This paper describes a conceptual model based on a generalization of field observations in relevant settings and discusses resultant analyses, which again illustrate the effectiveness and robustness of the reference HLW disposal system.
Itazu, Toru; Inagaki, Manabu; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebina, Takanori*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Review 2009-015, 59 Pages, 2009/07
The project of high-level radioactive waste disposal is in the stage of site selection in Japan, and the site-specific performance assessment using the methodology of site-generic study has been developed after the publication of the second progress report (H12). In the same way, biosphere assessment using the behavior of radionuclides, which depends on the site-specific condition, has been started. In this paper, the following issues have been addressed. (1) Survey of the foreign literature relating to the surface and near- surface hydrology for biosphere assessments. (2) Survey of the domestic literature of flow and transport in subsurface systems valuable for biosphere assessments. (3) Trial of transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment of the model site. (4) The setting and boundary conditions of model used for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis. About the fist issue, from literature of Sweden, we studied the calculation of the dose with account to radionuclides migration in the Quaternary. Concerning the second item, collecting and compiling the useful information for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis from literature related to groundwater flow and pollution survey in Japan, we learned about the environmental tracer method and so on. Concerning the third point, transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment using site-specific data for sensitivity analysis after this has been carried out to check out the influence of some parameters on transport phenomena, and the relative high sensitivity of the difference of the source positions were shown. Concerning the fourth item, we examined the setting and the boundary conditions of model whose outputs include groundwater flow and transport rate into river, lake, sea. These outputs are used as inputs of biosphere assessment model.
Miyahara, Kaname; Inagaki, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebina, Takanori*; McKinley, I. G.*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.177 - 184, 2009/05
Uplift and erosion cannot be generally precluded in Japan, therefore needs to be treated. In particular, uplift and erosion will cause major disruption of the engineered and natural barriers when the repository is exposed at the ground surface, although erosion of the repository should be excluded for very long times by careful siting and design. In Japan, uplift/erosion scenarios must be analysed, even if they occur far in the future as no assessment cut-off times have yet been defined. For this purpose, an argumentation method is being developed to allow sensible scenarios to be constructed. This paper discusses procedures to derive relevant conceptual models and resultant analyses in a credible manner which illustrates the effectiveness and robustness of the HLW disposal system, using relevant yardsticks based on natural radionuclide fluxes.
Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Inagaki, Manabu; Koo, Shigeru*; Shibata, Masahiro; Itazu, Toru; Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Research 2008-117, 36 Pages, 2009/03
It is considered that it is possible to avoid the effect of the uplift and denudation process on geological disposal system by siting and a repository design. However, since the uplift/denudation continues far into the future, it is important to enhance the confidence of the methodology to evaluate such an effect, based on the understanding of geohistorical information and potential impact on the disposal system. This paper presents an evolution pattern of the geological environment and the influence analysis in terms of system performance affected by the uplift and denudation process based on the relevant conceptual models for groundwater scenarios of the disposal system for a hypothetical sedimentary rock. As a result, it is indicated that the conceptual model is capable to identify a specific combination of patterns of system evolution of the geological environment in terms of features on the uplift and denudation process, and also provides technical basis for setting up parameters of nuclide migration model and the subsequent influence analysis. Consequently, it is also indicated that the evaluation methodology applied in this study is valuable to evaluate the uplift/denudation phenomena with specific geological environment, and the results obtained by the analysis could be valuable information for site investigation and/or the prediction of a future change trend for the uplift/denudation.
Miyahara, Kaname; Inagaki, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebina, Takanori*
Proceedings of 2008 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2008) (CD-ROM), p.593 - 599, 2008/09
This paper illustrated how to conduct "what if?" calculations in a transparent manner based on a developed formal procedure in order to treat perturbations of disruptive fault movement on a HLW disposal system. Calculation cases are defined due to stepwise combination of loss of key safety functions as what if? assumptions. The calculation results show effectiveness and robustness of the multibarrier system, even considering the most extreme combination of what if assumptions.
Kawamura, Makoto; Oi, Takao; Makino, Hitoshi; Umeda, Koji; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Kawachi, Susumu; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Seo, Toshihiro; Ebina, Takanori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-039, 60 Pages, 2007/01
This report is to outline a 5-year plan of research and development (R&D) for performance assessment of potential effect of natural phenomena on a geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in JAEA. In each research plan, objectives based on the necessity and the significance of the research plan are clarified in the section of "Objectives and the past progresses", with summarizing the progresses of H12: Project to establish the scientific and technical basis for HLW disposal in Japan (Second Progress Report), and H17: Development and management of the technical knowledge base for the geological disposal of HLW (H17 report). In addition, next five year plan is described in the section.
Miyahara, Kaname; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oi, Takao; Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Maekawa, Keisuke; Kawamura, Makoto; Kato, Tomoko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-015, 29 Pages, 2006/03
This report is to outline a 5-year plan of research and development (R&D) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in JAEA. This 5-year plan is based on JAEA's mid-term plan which follows the R&D policy specified in "Framework for Nuclear Energy Policy" issued by Japan Atomic Energy Commission. Moreover, research plans for safety regulation issued by Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan should be taken into account. The contents of this 5-year plan follows a framework of R&D issues for performance assessment field established in "the R&D map", i.e. the mid and long term R&D plan for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, developed by JNC (predecessor of JAEA) and other relevant R&D organizations. In each research plan, objectives based on the necessity and the significance of the research plan are clarified in the section of "Objectives and the past progresses", with summarizing the progresses of H12: Project to establish the scientific and technical basis for HLW disposal in Japan (Second Progress Report), and H17: Development and management of the technical knowledge base for the geological disposal of HLW (H17 report). In addition, next five year plan is described in the section of "5-year plan (up to Fiscal year Heisei-22)".
Shimizu, Makoto*; Kimuro, Harumi*; Ayabe, Muneo*; Kouno, Yasumasa*; Miyahara, Shuji*; Yamashita, Saburo*; Kanazawa, Kazuo*; Hayashi, Mitsuo*; Yoshizaki, Masato*
PNC TJ118 83-05VOL2, 222 Pages, 1984/03
None
Shimizu, Makoto*; Kimuro, Harumi*; Ayabe, Muneo*; Kouno, Yasumasa*; Miyahara, Shuji*; Yamashita, Saburo*; Kanazawa, Kazuo*; Hayashi, Mitsuo*; Yoshizaki, Masato*
PNC TJ118 83-05VOL1, 42 Pages, 1984/03
None
Kojima, Takuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Haruyama, Yasuyuki; Haneda, Noriyuki; Sunaga, Hiromi*; Miyahara, Makoto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyahara, Makoto*; Kojima, Takuji; Sunaga, Hiromi*; Maitani, Tamio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Manabu; Ebina, Takanori*; Oi, Takao; Kawamura, Makoto; Kawachi, Susumu; Miyahara, Kaname
no journal, ,
A study of extraction of scenarios which considered the realistic geological environment and site - design options.
Miyahara, Kaname; Kawamura, Makoto*; McKinley, I. G.*; Inagaki, Manabu; Ebina, Takanori*; Apted, M.*
no journal, ,
In Japan, uplift/erosion scenarios must be analysed even if they occur far in the future, as no assessment cut-off times have yet been defined. For this purpose, the geological record of river terrace formation and its evolution in a very long term has been studied further, with the aim of constructing a more realistic river erosion model compared with the original, rather simple cyclic river erosion model developed in a previous study. The model allows the consequences of erosion of the repository to be assessed, again using comparisons with natural radionuclide fluxes. This paper describes a conceptual model based on a generalization of field observations in relevant settings and discusses resultant analyses, which again illustrate the effectiveness and robustness of the reference HLW disposal system.