Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamano, Hidemasa; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Takano, Kazuya; Kikuchi, Shin; Kondo, Toshiki; Umeda, Ryota; Shirakura, Shota*
Dai-27-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/09
This project studies investigation on safety design guideline and risk assessment technology for sodium-cooled fast reactor with the molten-salt heat storage system, development of evaluation method for heat transferring performance between sodium and molten-salt and improvement of the performance, and evaluation of chemical reaction characteristic between sodium and molten-salt and improvement of its safety. The project overview is presented in this report.
 O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) measured by aerodynamic levitation
measured by aerodynamic levitationKondo, Toshiki; Toda, Taro*; Takeuchi, Junichi*; Kikuchi, Shin; Kargl, F.*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Oishi, Yuji*
High Temperatures-High Pressures, 52(3-4), p.307 - 321, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Thermodynamics)In order to establish an evaluation method/numerical simulation for nuclear reactor safety under severe accidental conditions, it is necessary to obtain the physical properties, especially fluidity of the relevant molten materials at very high temperatures. In this study, thermophysical properties such as density and viscosity were obtained for (Fe O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) , which is a representative composition in the early stage of severe accident. (Fe
, which is a representative composition in the early stage of severe accident. (Fe O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) is produced by the contact between the molten oxide of steel, which is the main component of the reactor, and SiO
is produced by the contact between the molten oxide of steel, which is the main component of the reactor, and SiO , which is the main component of concrete. As a result, the physical properties of the (Fe
, which is the main component of concrete. As a result, the physical properties of the (Fe O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) mixture were almost the same as those of Fe
mixture were almost the same as those of Fe O
O obtained in previous studies, and it could be concluded that a small amount of SiO
obtained in previous studies, and it could be concluded that a small amount of SiO (about 5 mol.%) did not significantly affect the fluidity of Fe
(about 5 mol.%) did not significantly affect the fluidity of Fe O
O .
.
Emura, Yuki; Takai, Toshihide; Kikuchi, Shin; Kamiyama, Kenji; Yamano, Hidemasa; Yokoyama, Hiroki*; Sakamoto, Kan*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamano, Hidemasa; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Takano, Kazuya; Kikuchi, Shin; Kondo, Toshiki; Umeda, Ryota; Shirakura, Shota*; Hayashi, Masaaki*
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on New Energy and Future Energy Systems (NEFES 2023) (Internet), p.27 - 34, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0This project studies investigation on safety design guideline and risk assessment technology for sodium-cooled fast reactor with the molten-salt heat storage system, development of evaluation method for heat transferring performance between sodium and molten-salt and improvement of the performance, and evaluation of chemical reaction characteristic between sodium and molten-salt and improvement of its safety. The project overview is presented in this report.
 , (FeO
, (FeO )
)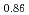 -(ZrO
-(ZrO )
)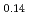 and (FeO
and (FeO )
)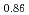 -(UO
-(UO )
)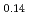
Kondo, Toshiki; Toda, Taro*; Takeuchi, Junichi*; Kargl, F.*; Kikuchi, Shin; Muta, Hiroaki*; Oishi, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1139 - 1148, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Shin; Koga, Nobuyoshi*
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 147(7), p.4635 - 4643, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.32(Thermodynamics)In a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) may probably occur when liquid sodium from cooling system spilled into the floor may lead to fail the steel liner as protector of the structural concretes. The structural concretes of SFR comprises siliceous concreate as main body of reactor structure and perlite concrete placed between the steel liner and the siliceous concrete serving as a protector and an insulator, respectively. Therefore, the reaction behaviour between the perlite concrete and liquid sodium in the early stage of SCR should be focused. In this study, for the first step of elucidation on SCR, thermal behaviour of sodium-calcium hydroxide reaction was investigated using a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). It was revealed that the reaction between Na(l) and Ca(OH) (s) initiates at approximately 550 K, producing the product layer composed of CaO(s) and NaOH(s), which is evident from XRD pattern of solid product after DSC measurement. The kinetic consideration of the cited reaction was carried out to obtain the activation energy.
(s) initiates at approximately 550 K, producing the product layer composed of CaO(s) and NaOH(s), which is evident from XRD pattern of solid product after DSC measurement. The kinetic consideration of the cited reaction was carried out to obtain the activation energy.
Johnson, M.*; Delacroix, J.*; Journeau, C.*; Brayer, C.*; Clavier, R.*; Montazel, A.*; Pluyette, E.*; Matsuba, Kenichi; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/04
Fuel-coolant interactions in the event of molten fuel discharge to the lower plenum of a sodium cooled fast reactor is under investigation as part of a French-Japanese experimental collaboration on severe accidents. The MELT facility enables the X-ray visualisation of the quenching of molten core material jets in sodium at kilogram-scale. The SERUA facility, currently under preparation, is presented for the investigation of boiling heat transfer at elevated melt-coolant interface temperatures. In this article, the status of the collaboration using these facilities is presented.
 reaction; A Physicogeometrical kinetic approach toward the safety assessment of Na-cooled fast reactors
reaction; A Physicogeometrical kinetic approach toward the safety assessment of Na-cooled fast reactorsKoga, Nobuyoshi*; Kikuchi, Shin
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 61(7), p.2759 - 2770, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Chemical)Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamaji, Akifumi*
JAEA-Research 2021-006, 52 Pages, 2021/09
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (referred to as "FDNPS" hereafter) unit2 and unit3, failure of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and relocation of some core materials (CRD piping elements and upper tie plate, etc.) to the pedestal region have been confirmed. In boiling water reactors (BWRs), complicated core support structures and control rod drive mechanisms are installed in the RPV lower head and its upper and lower regions, so that the relocation behavior of core materials to pedestal region is expected to be also complicated. The Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method is expected to be effective in overviewing the relocation behavior of core materials in complicated RPV lower structure of BWRs, because of its Lagrangian nature in tracking complex interfaces. In this study, for the purpose of RPV ablation analysis of FDNPS unit2 and unit3, rigid body model, parallelization method and improved calculation time step control method were developed in FY 2019 and improvement of pressure boundary condition treatment, stabilization of rigid body model, and calculation cost reduction of debris bed melting simulation were achieved in FY2020. These improvements enabled sensitivity analyses of melting, relocation and re-distribution behavior of deposited solid debris in RPV lower head on various cases, within practical calculation cost. As a result of the analyses of FDNPS unit2 and unit3, it was revealed that aspect (particles/ingots) and distribution (degree of stratification) of solidified debris in lower plenum have a great impact on the elapsed time of the following debris reheat and partial melting and on molten pool formation process, further influencing RPV lower head failure behavior and fuel debris discharging behavior.
Kikuchi, Shin; Nakamura, Kinya*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(4), p.20-00542_1 - 20-00542_13, 2021/08
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B
C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B
C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B
C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B
C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
Kikuchi, Shin; Takai, Toshihide; Yamano, Hidemasa; Sakamoto, Kan*
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) may occur. Thus, behavior of B
C) and stainless steel (SS) may occur. Thus, behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, the reaction experiments using SS crucibles and the pellets of SS with low B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, the reaction experiments using SS crucibles and the pellets of SS with low B C concentration as samples were performed to simulate the state of the reaction interface in which the eutectic reaction and interdiffusion of B
C concentration as samples were performed to simulate the state of the reaction interface in which the eutectic reaction and interdiffusion of B C-SS have progressed to a certain extent. It was revealed that the rate constants of eutectic reaction between SS and SS with low B
C-SS have progressed to a certain extent. It was revealed that the rate constants of eutectic reaction between SS and SS with low B C concentration are smaller than that of B
C concentration are smaller than that of B C-SS eutectic reaction at high temperatures.
C-SS eutectic reaction at high temperatures.
Umeda, Ryota; Kondo, Toshiki; Kikuchi, Shin; Kurihara, Akikazu
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
In this study, in order to obtain the fundamental information on aerosol transport behavior between cells, the Multiple cells with Expandable connecting pipe Test facility (MET) was manufactured and preliminary experiments were performed. In the preliminary experiments, simulated particles were used in a test system with two cells connected horizontally or vertically, and their transport behavior was measured. As a result, it was possible to confirm the behavior of the simulated particles transporting to the horizontal or vertical cells from the results such as images and sedimentation data.
Umeda, Ryota; Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Kurihara, Akikazu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(4), p.234 - 244, 2020/12
Sodium-water reaction caused by failure of the steam generator tube of sodium-cooled fast reactor induce the wastage phenomenon, which has erosive and corrosive feature. In this report, the authors have performed the self-wastage experiments under high sodium temperature condition to evaluate the effect of wastage form/geometry by using two types of initial defect such as the micro fine pinhole and fatigue crack, and water leak rate on self-wastage rate. Based on the consideration of crack type influence, it was confirmed that self-wastage rate did not strongly depend on the initial defect geometry. As a mechanism of the self-plug phenomenon, it is speculated that sodium oxide intervenes and inhibits the progress of self-wastage. The dependence of initial sodium temperature on self-wastage rate was clearly observed, and new self-wastage correlation was derived considering the initial sodium temperature.
Kikuchi, Shin; Sakamoto, Kan*; Takai, Toshihide; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2020-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/09
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B
C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B
C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B C or SS with low B
C or SS with low B C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B
C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B
C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B C concentration were smaller than that of B
C concentration were smaller than that of B C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B
C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B C containing SS became small when decreasing the B
C containing SS became small when decreasing the B C concentration against SS.
C concentration against SS.
Negishi, Hitoshi; Kamide, Hideki; Maeda, Seiichiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Abe, Tomoyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(8), p.438 - 441, 2020/08
, 62(8), p.438 - 441, 2020/08
Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, Monju, was under decommission since April, 2018. It is the first time for Japan to make a sodium cooled reactor into decommission. It is significant work and will take 30 years. The Monju has provided wide spectrum and huge amount of findings and knowledge, e.g., design, R&D, manufacturing, construction, and operation up to 40% of full power over 50 years of development history. It is significant to utilize such findings and knowledge for the development and commercialization of a fast rector in Japan.
Kikuchi, Shin; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nakamura, Kinya*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2020/08
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B
C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B
C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B
C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B
C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
Kondo, Satoru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
JAEA-Research 2019-009, 382 Pages, 2020/03
The SIMMER-III computer code, developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA, the former Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation), is a two-dimensional, multi-velocity-field, multi-component fluid-dynamics code, coupled with a space- and time-dependent neutron kinetics model. The code is being used widely for simulating complex phenomena during core-disruptive accidents (CDAs) in liquid-metal fast reactors (LMFRs). In parallel to the code development, a comprehensive assessment program was performed in two phases: Phase 1 for verifying individual fluid-dynamics models; and Phase 2 for validating its applicability to integral phenomena important to evaluating LMFR CDAs. The SIMMERIII assessment program was participated by European research and development organizations, and the achievement of Phase 1 was compiled and synthesized in 1996. This report has been edited by revising and reproducing the original 1996 informal report, which compiled the achievement of Phase 1 assessment. A total of 34 test problems were studied in the areas: fluid convection, interfacial area and momentum exchange, heat transfer, melting and freezing, and vaporization and condensation. The problems identified have been reflected to the Phase 2 assessment and later model development and improvement. Although the revisions were made in the light of knowledge base obtained later, the original individual contributions by the participants, both positive and negative, are retained except for editorial changes.
Kikuchi, Shin; Koga, Nobuyoshi*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 137(4), p.1211 - 1224, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.34(Thermodynamics)In this study, two siliceous concretes with similar specification as structural concretes of SFR were selected for the comparative study of the thermal behavior. The thermal behavior of the structural concretes was investigated in a temperature range from room temperature to 1900 K using TG-differential thermal analysis (DTA) and other supplementary techniques. The softening and melting of the concretes initiated in the thermal decomposition product of the cement portion in the temperature range 1400-1600 K. Because the compositional difference between the cement portion of two different siliceous concretes was characterized by different Ca(OH) /CaCO
/CaCO ratios, the melting temperature ranges of those thermal decomposition products are not so significantly different. On the other hand, the melting of the aggregate is directly influenced by the initial composition of SiO
ratios, the melting temperature ranges of those thermal decomposition products are not so significantly different. On the other hand, the melting of the aggregate is directly influenced by the initial composition of SiO compounds.
compounds.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.2095 - 2107, 2019/08
Development of a sodium-cooled fast reactor has been implemented in Japan from the viewpoint of severe accident countermeasures. This paper describes the progress of research and development related to safety enhancement and the severe accident countermeasures. A volcanic PRA methodology was developed for the proper consideration of external hazards. Water and sodium experiments were carried out for the decay heat removal in a core disruptive accident (CDA), and also thermal hydraulic interactions between the core and upper plenum where dipped heat exchanger was operated. In order to elucidate the behavior of molten fuel during CDA, basic experiments of core melt fragmentation in deep and shallow sodium pools were carried out. X-ray visualization showed the liquid column of molten steel was intensively fragmented nearly simultaneously with a rapid expansion of sodium vapor.
Tsuruga Comprehensive Research and Development Center
JAEA-Technology 2019-007, 159 Pages, 2019/07
This report summarizes the history and achievements of the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. The development of Monju started in 1968 as a prototype reactor following the experimental fast reactor Joyo. The development covers all the activity related to the fast reactor; plant design, mockup tests, construction, operation, and plant management. This report summarizes the history and achievements for 11 technical areas: history and principal achievements, design and construction, operation test, plant safety, core physics, fuel, plant system, sodium technology, materials and mechanical design, plant management, and trouble management.