Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
谷川 聖史; 瀬谷 和仁*; 浅川 直也*; 林 宏幸*; 堀籠 和志; 向 泰宣; 北尾 貴彦; 中村 仁宣; Henzlova, D.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-014, 63 Pages, 2025/02
プルトニウム転換技術開発施設の廃液処理工程で発生したスラッジ中のPu量を評価する上で、スラッジは生成上、多くの不純物(Na, Fe, Ni等)を含み不均質であるため、従来の破壊分析ではサンプリングによる代表性が乏しく、Pu量測定に係る測定不確かさが大きかった(約24%)。この測定不確かさを低減させるために、日本原子力研究開発機構と米国ロスアラモス国立研究所は共同で中性子を利用した非破壊測定装置のPlutonium Scrap Multiplicity Counter (PSMC)を用いた測定技術の開発を進めた。MOX粉末を用いた模擬スラッジやモンテカルロ法により検証等を行いPSMC検出器パラメーター(predelay, doubles gatefraction等)を最適化し、高分解能ガンマ線分光分析を組み合わせて測定した結果、含有不純物の影響はないことが確認でき、従来法と比べ新たに設定した非破壊測定方法における測定不確かさは約6.5%まで低減できた。さらに、PSMC測定値の妥当性を評価するため、IAEA立ち合いの下、ガンマ線を測定しPu量を評価するIn Situ Object Counting System (ISOCS)を用いた比較測定した結果、ISOCSとPSMCの測定値は両方の測定不確かさの範囲内で一致したため、PSMCによる測定値の妥当性が確認された。これらの結果より、本非破壊測定技術はスラッジのように不純物を多く含み、サンプリングの代表性が乏しいアイテムに有効であり、スラッジの計量管理に適用することが認められた。
Lee, J.; Rossi, F.; 児玉 有; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 佐野 忠史*; 松尾 泰典*; 堀 順一*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.111017_1 - 111017_7, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Silica glass has been used as a base and host material in vitrified radioactive waste and lithium glass scintillator for neutron detection because of its superb transparency, high heat resistance, and excellent chemical inertness. Therefore, an accurate total cross section of the silica glass is important to evaluate the criticality safety for the vitrified wastes and to understand the neutron response for lithium glass scintillators accurately. In the present study, to provide the accurate total cross section in the thermal and epithermal energy range, the neutron transmission measurements were carried out by a pulsed neutron beam with the time-of-flight method at the Kyoto University Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science - Linear Accelerator. We obtained the neutron total cross section of the silica glass in the energy region from 0.002 eV to 25 eV. The obtained results were compared and discussed with the previous results and the evaluated data.
田崎 真樹子; 清水 亮; 木村 隆志; 須田 一則
JAEA-Review 2024-043, 91 Pages, 2024/12
2018年度から開始した「非核化達成のための要因分析と技術的プロセスの研究」の一環で、朝鮮民主主義人民共和国(以下、「北朝鮮」という。)の核開発及び非核化の事例を調査し(ただし2018年に米朝交渉が開始される前まで)、8つの非核化要因((1)核開発の動機、(2)非核化を決断した際の内外情勢、(3)核開発の進捗度、(4)制裁の効果、(5)非核化の国際的枠組み、(6)非核化のインセンティブ、(7)非核化の方法、(8)非核化の検証者、検証方法)から分析し、得られる非核化の教訓を考察した。北朝鮮は朝鮮戦争以降、国家安全保障の確保、国家の威信及び金体制の維持・強化のため、核開発を進めて外交交渉を北朝鮮の有利に導く切り札としての核兵器を取得し、現在まで計6回の核実験を実施するに至った。その間国際社会は、南北朝鮮間の「朝鮮半島非核化宣言」、米朝間の「合意された枠組み」、さらに六者会合による「第4回六者会合に関する共同声明」及び左記声明に基づく「初期段階の措置」と「第二段階の措置」等に基づく北朝鮮の非核化に向けた国際的枠組みを形成した。加えて国連安全保障理事会(以下、「国連安保理」という。)決議に基づく経済制裁や、米国トランプ政権も「最大限の圧力」政策に基づく制裁で北朝鮮の非核化を推進しようとしたが、いずれも結果的には成功しなかった。2024年時点では北朝鮮が既に核兵器を保有していることから、同国の非核化は決して容易ではなく、北朝鮮をそのための外交交渉のテーブルに着かせることさえ難しいと思われる。しかし国際社会は、北朝鮮に対して核不拡散に係る国際規範の遵守の必要性を粘り強く主張すると共に、国連安保理常任理事国である5核兵器国の協調・協力による「抜け穴」を生じさせない強固な制裁の履行や、六者会合で示された「約束対約束、行動対行動」の原則に基づく北朝鮮の非核化の措置に即応し、確実な検証を伴った制裁の段階的な解除の実施など、将来的な「完全、検証可能かつ不可逆的な非核化(CVID: Complete, Verifiable, and Irreversible Dismantlement)」の実現に向けた措置を1つ1つ確実・着実に実施して行くための努力を継続していくことが必要となろう。
田崎 真樹子; 清水 亮; 木村 隆志; 須田 一則
JAEA-Review 2024-041, 88 Pages, 2024/11
2018年度から開始した「非核化達成のための要因分析と技術的プロセスの研究」の一環で、イランの核開発及び非核化(包括的共同作業計画まで)の事例を調査し、それらを8つの非核化要因((1)核開発の動機、(2)非核化を決断した際の内外情勢、(3)核開発の進捗度、(4)制裁の効果、(5)非核化の国際的枠組み、(6)非核化のインセンティブ、(7)非核化の方法、(8)非核化の検証者、検証方法)から分析し、他国の非核化との比較も交えて得られる非核化の教訓を導いた。パーレビ国王下のイランは、米国の支援を得て研究炉等を導入し、商用原子炉の建設や自国でのウラン濃縮の実施等、原子力プログラムの推進を企図したが、1979年のイラン・イスラム革命で原子力計画は一時停止した。しかしイラン・イラク戦争で、イラクから化学兵器の攻撃を受け、国際社会からもイランが望んだ対応を得られなかったこと等から、秘密裡の核開発に舵を切り、パキスタンの「核の供給ネットワーク」から遠心分離機等を調達すると共に、ナタンズに秘密裡のウラン濃縮施設を建設し、アラクに重水炉の建設も企図した。加えて、後に「イランの核プログラムの軍事的側面の可能性」と呼ばれることになる核兵器開発に繋がる活動も実施したとされる。しかし、2002年のイラン反体制派によりそれまでの秘密裡の活動が暴露され、イランは核開発よりもウラン濃縮活動の維持と継続を優先した。IAEAとの協力を維持して外交交渉で事態打開を目指し国連安全保障理事会への付託や経済制裁を避けるとの「現実的アプローチ」を採ることとして、2002年からEU3か国(仏独英)と、また2006年からは5核兵器国を交えてEU3/E+3(中仏独露英米とEU)と非核化交渉を開始した。そして2015年に包括的共同作業計画の合意に至った。イランの非核化事例の教訓としては、非核化には、国際社会の非核化に向けたモメンタム、5核兵器国の協調・協力(当事国全ての国による合意の遵守も含まれる)、制裁の有効的な活用、非核化対象国の非核化に対するインセンティブを損なわないための原子力平和利用の保証が重要であり、非核化の検証方法や手段、制裁解除の条件の明確化等が必要であることが挙げられる。
今村 有里
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
本報告では、国家・非国家主体による武力攻撃が発生した際、条約に基づく対応がとられ得る原子力施設の範囲を明確にする。敵対者による攻撃時における原子力施設の保護等を規定する既存の条約において、対象とされる原子力施設の範囲は条約毎に異なっている。そのため、当該保護規定を有する条約上の原子力施設についての定義を確認することで、どのような原子力施設が各条約により保護され得るのかを整理し、将来の議論に資する。
田崎 真樹子
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
露国によるウクライナへの軍事侵攻及び原子力施設に対する攻撃等に起因し、国家主体による武力攻撃からの原子力施設の保護に関して、有識者等からの見解が示されている。それらについてのまとめ及び考察結果を報告する。
加藤 優弥
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
一般に核セキュリティと核軍縮は異なる概念として理解されるが、ICONS2024の各国ステートメントから同じ文脈で両者を捉える国家が複数存在することが判明した。本発表の目的は、核セキュリティと核軍縮の関連性を強調する国々の考え方を整理することである。複数国における核セキュリティと核軍縮の関連性についての考え方を整理する際には、ICONS2024で発出された各国ステートメントだけでなく、NPT運用検討会議等の資料も用いる。
江口 綾*; 相楽 洋*; 三星 夏海; 長谷 竹晃
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 2 Pages, 2024/11
次世代高速炉用燃料には、ウランおよびプルトニウムに加え、マイナーアクチノイドやランタノイド等の核分裂生成物が含まれ、新燃料であっても核物質以外を由来とする中性子およびガンマ線の高いバックグラウンドが想定されている。本研究では、次世代高速炉用燃料中のプルトニウム定量のために、同時計数法、Differential Die Away Self Interrogation (DDSI)法を用いたパッシブ中性子非破壊測定技術の適用可能性を評価することを目的とする。
清水 亮
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
イランは、2019年5月以降、JCPOAの合意の履行を段階的に停止し、濃縮ウランの保有量及びウラン濃縮度の制限を超えたウラン濃縮活動を行っている。現在、イランは追加議定書の暫定的適用を停止しており、IAEA事務局長報告等から得られる情報は限られているが、イランの遠心分離機、濃縮能力、ブレイクアウトタイム及び今後の推移について分析を行った結果を報告する。
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Wei, T.*; 余語 覚文*; et al.
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a non-destructive method applicable for measuring nuclear material using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. To realize a high resolution compact NRTA system, use of a short-pulsed neutron source is essential. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) are well-suit for generating such neutron beams due to their short pulse width. The advances in laser technology will further reduce the system's size and improve practicality. In this study, we demonstrate the measurement of a neutron transmission TOF spectrum of a sample containing indium and silver using the LDNS of the Osaka University. The obtained spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, showcasing for the first time the potential of an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.21916_1 - 21916_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:64.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) can generate strong short-pulse neutron beams, which are valuable for scientific studies and engineering applications. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a nondestructive technique used for determining the areal density of each nuclide in a material sample using pulsed thermal and epithermal neutrons. Herein, we report the first successful NRTA performed using an LDNS driven by the Laser for Fast Ignition Experiment at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. The key challenge was achieving a well-resolved resonance transmission spectrum for material analysis using an LDNS with a limited number of laser shots in the presence of strong background noise. We addressed this by employing a time-gated  Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to
Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to  In and
In and  Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
木村 祥紀; 松本 哲也*; 山口 知輝
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3541 - 3551, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)This study discusses the application of a deep metric learning model based on a convolutional neural network to scanning electron microscope image analysis to determine UOC samples. One of the unique features of this technique is that it can detect a sample that comes from an unknown material not listed in the reference for comparison, in addition to the classification of a sample based on surface characteristics captured in the microscopic images. It was confirmed that the present technique could detect hypothetical unknown samples with  0.8 of Area Under the ROC Curve, and it can effectively provide preliminary observations in nuclear forensics analysis.
0.8 of Area Under the ROC Curve, and it can effectively provide preliminary observations in nuclear forensics analysis.
Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; 早川 岳人*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 小泉 光生; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:75.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The temperature measurement of material inside of an object is one of the key technologies for control of dynamical processes. For this purpose, various techniques such as laser-based thermography and phase-contrast imaging thermography have been studied. However, it is, in principle, impossible to measure the temperature of an element inside of an object using these techniques. One of the possible solutions is measurements of Doppler brooding effect in neutron resonance absorption (NRA). Here we present a method to measure the temperature of an element or an isotope inside of an object using NRA with a single neutron pulse of approximately 100 ns width provided from a high-power laser. We demonstrate temperature measurements of a tantalum (Ta) metallic foil heated from the room temperature up to 617 K. Although the neutron energy resolution is fluctuated from shot to shot, we obtain the temperature dependence of resonance Doppler broadening using a reference of a silver (Ag) foil kept to the room temperature. A free gas model well reproduces the results. This method enables element(isotope)-sensitive thermometry to detect the instantaneous temperature rise in dynamical processes.
 Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method
Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 持丸 貴則*; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 小泉 光生
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169465_1 - 169465_9, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The response of a gamma-ray spectrometer is generally determined by analyzing full-energy peaks. However, full-energy peaks cannot be measured easily in the case of scintillation detectors that consist of light elements, such as glass scintillators. Only a strong Compton plateau appears in the spectrum of such detectors. Therefore, Compton edgers were used to evaluate the response of these detectors. The response of a low-resolution  Li-glass detector to gamma rays was measured for the first time by a coincidence method with a high-resolution LaBr
Li-glass detector to gamma rays was measured for the first time by a coincidence method with a high-resolution LaBr :Ce detector using cascade gamma rays (2.75 and 1.37 MeV) from a
:Ce detector using cascade gamma rays (2.75 and 1.37 MeV) from a  Na source. Coincidence gates were applied at the peaks of the spectrum of the LaBr
Na source. Coincidence gates were applied at the peaks of the spectrum of the LaBr :Ce detector at the 0.51 MeV annihilation peak, and the sum peaks of a gamma ray and a backscattered gamma ray. By analyzing the gated spectra of the
:Ce detector at the 0.51 MeV annihilation peak, and the sum peaks of a gamma ray and a backscattered gamma ray. By analyzing the gated spectra of the  Li-glass detector, the energy-dependent detector response (i.e., the output strength and its dispersion) was determined.
Li-glass detector, the energy-dependent detector response (i.e., the output strength and its dispersion) was determined.
Rossi, F.; Lee, J.; 児玉 有; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 佐野 忠史*
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
Various non-destructive assay techniques are being used to verify different nuclear material. However, one of the difficulties of current NDA is the measurement of highly radioactive materials. Since 2015, the JAEA has been working on the development of various active non-destructive assay techniques to address some of the current challenges in nuclear safeguards. Among the various technologies proposed, the Neutron Resonance Analysis system combines signatures from NRTA, NRCA and the newly proposed NRFNA. The combination of those techniques can provide accurate information on the small fissile content in a sample. Neutrons are generated by a pulsed neutron source and slowed down into the moderator. Neutrons are collimated using lead and borated polyethylene to reach the sample, where various neutron-induced reactions occur. n/g PSD plastic scintillators are used to measure the captured gamma rays and fission neutrons at sample location. GS20 is used to collect the transmitted neutrons downstream of the source-sample beamline. A first measurement campaign was performed using natural uranium sample. The possibility of using NRFNA to identify fissile materials within a sample was clearly demonstrated, but the detectors used were not sufficient to achieve a good n/g PSD. New PSD scintillators were introduced. A first measurement campaign was performed in 2023. The acquired data are currently being analyzed, but preliminary results show distinct fission resonance peaks of increasing intensity with varying thicknesses of the same natural uranium samples. Currently, an assembly of multiple scintillators is being investigated to provide a better signal. The new setup will be tested starting in early 2024. In this paper, we will describe in detail the NRA project development and the latest results from experimental campaign. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like"
Kyffin, J.*; Dia, A.*; Nkosi, G.*; Nizhnik, V.*; 林 昭彦; 長谷 竹晃
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
In collaboration with the Japan Safeguards Office, the Nuclear Material Control Centre, and the JAEA, the IAEA Department of Safeguards is implementing a new neutron detector system for the verification of plutonium hold-up in process gloveboxes at MOX fuel fabrication facilities in Japan. The previous verification technique utilised the so-called Super Glove Box Assay System (SBAS), which, while capable of detecting partial defects, is a heavy and bulky detector system that requires both significant operator support for safe assembly and positioning, and long measurement times. The recent development of a detector system based on two Plutonium Neutron Coincidence Collar (PNCL) miniature neutron slabs provides the capability of detecting gross defects with semi-quantitative plutonium mass measurement, and is sufficient in respect to inspections for timeliness purposes. For regular use, the Mini-slab detector offers several advantages, including improved safety, reduced operator support requirements and shorter measurement times. The Mini-slab detector satisfies the required verification role with a quarter of the inspector-days compared to SBAS. Furthermore, it has the capability to measure in tighter spaces, with the need for such use expected to grow as parts of these facilities begin decommissioning.
Rodriguez, D.; 赤松 駿介*; Rossi, F.; 鈴木 敏*; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
Under the MEXT subsidy to promote nuclear security related activities, we will present the preliminary results from the new Fission Signature Assay Instrument that was fabricated and fully installed in November 2023. We will describe the instrument within the context of the JAEA-JRC collaboration development and the experimental activities planned with it in the larger context of finishing off Phase-III development.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)We report on the findings of a quantitative nondestructive analysis of the natural isotopic abundances of hafnium and tungsten elements using nuclear resonance fluorescence. Commercial samples of hafnium and tungsten were irradiated to six quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six
-ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six  -ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total,
-ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total, 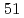 transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
田崎 真樹子; 木村 隆志; 清水 亮; 中谷 隆良; 須田 一則
JAEA-Review 2023-042, 121 Pages, 2024/03
2018年度に開始した「非核化達成のための要因分析と技術的プロセスに関する研究」の一環として、旧ソ連3か国(ベラルーシ、カザフスタン及びウククライナ)の非核化事例を調査して8つの非核化要因から分析すると共に、非核化の特徴及び教訓を考察した。3か国の非核化プロセスは国毎に異なり、特にウクライナの非核化プロセスは紆余曲折を経たが、共通項としては、核兵器国全てが安全の保証(assurance)を提供し、それをもって3か国は戦略核を露国に搬出し、非核兵器国として核兵器不拡散条約(NPT)に加入したこと、またその決断には、米露が非核化の経済的・物理的支援をしたことが功を奏したことが挙げられる。更にこの3か国の非核化の特徴としては、米国の巧みな非核化戦略を挙げることができる。米国は、この3か国が露国同様START-Iの当事国であるとの主張を支持して、最終的に第一次戦略兵器削減条約(START-I)の枠組みで3か国からの戦略核兵器の露国への搬出及びその後の露国での廃棄を達成した。また旧ソ連3か国の非核化からの教訓としては、非核化対象国への安全の保証(assurance)の提供は非核化の強力なインセンティブであるが、露国による2014年のクリミア併合及び2022年2月からのウクライナへの軍事侵攻を鑑みると、今後、将来的な非核化では、非核化対象国がより強固な安全の保証(guarantee)を求めるであろうと予想されることである。更に非核化に関しては、関係国の大統領・首脳の強力なイニシアティブが必要であること、また核兵器国が非核兵器国に非核化を求めるならば、核兵器国自身も核軍縮に対する積極的な取組を示す等の必要性があろう。
福井 康人
Journal of Conflict & Security Law, 29(1), p.129 - 142, 2024/01
核セキュリティ分野の国際法は、核物質防護条約改正等の条約を、各国が原子力施設等の防護措置を定める際の指針となる核セキュリティ文書等のいわゆるソフト・ローからなる文書等が補完する形態を取っている。また、将来の方向性を示す核セキュリティ・サミット文書のようなものもある。本稿では、核セキュリティ分野の国際法がなぜそのようなソフト・ローに補完された法体系になっているのかの理由を考察する。そこには、IAEA加盟国の多様な原子力施設に対応するため、国際法レベルではソフト・ローとなっていても、日本等では規制官庁の設置文書に明記された権限等を基に、こうしたソフト・ローがベースとなって強制力を持って許認可が行われ、強制執行力を有する規範に変質して実施されるというハードローに変質する興味深い傾向がある。