Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Uto, Nariaki; Uto, Nariaki
JNC TN9400 2003-040, 67 Pages, 2003/06
A program of disposition of Russian weapon-grade plutonium by containing the plutonium in vibropacked MOX fuel subassemblies and burning them in the BN-600
Yamadate, Megumi; Yamaguchi, Hiroyuki; Naganuma, Masayuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Takaki, Naoyuki
JNC TN9400 2002-065, 131 Pages, 2002/12
Phase-II of the Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System in Japan (F/S) has been started since April 2001 and the design studies of various FR and recycle concepts are being conducted. In this report the JFY2001 studies of sodium cooled FR with mixed oxide fuel are summarized. The main results are as following. (1) Large scale reactors (1,500 MWe) (a) As for the large scale homogeneous ABLE type fuel core, we aimed to improve the effective average burn-up (that includes contribution of blankets) in order to reduce the fuel cycle cost. The specifications of Phase-I core and fuel were modified, which results in reducing the numbers of radial blanket sub-assemblies. As a result, the effective average burn-up was improved from 63 GWd/t to 77GWd/t. (b) As for the inner-duct sub-assembly core, the thickness of inner-duct was decided according to the evaluation of inner-duct expansion. As a result, the core reveals greater burn-up swing by about 0.6%  k/kk' than that of the ABLE type fuel core. (c) As for the heterogeneous core, the inner-blanket shuffling concept was studied in order to improve the effective average burn-up and the thermal hydraulic characteristics, As a result, though the breeding ratio decreases in some extent, the possible improvement is obtained in the effective average burn-up (from 56 GWd/t to 80 GWd/t) and core thermal hydraulic design. (2) Medium scale reactors (500 MWe) (a) As for the medium scale core, with the aim of an attractive core concept the high internal conversion ration core was studied. As a result, the obtained typical core concept reveals around 1.05 of breeding ratio with core diameter 10% greater than conventional one and without radial blanket. The core achieves over 100 GWd/t of the effective average burn-up with the potential capability of long operation cycle.
k/kk' than that of the ABLE type fuel core. (c) As for the heterogeneous core, the inner-blanket shuffling concept was studied in order to improve the effective average burn-up and the thermal hydraulic characteristics, As a result, though the breeding ratio decreases in some extent, the possible improvement is obtained in the effective average burn-up (from 56 GWd/t to 80 GWd/t) and core thermal hydraulic design. (2) Medium scale reactors (500 MWe) (a) As for the medium scale core, with the aim of an attractive core concept the high internal conversion ration core was studied. As a result, the obtained typical core concept reveals around 1.05 of breeding ratio with core diameter 10% greater than conventional one and without radial blanket. The core achieves over 100 GWd/t of the effective average burn-up with the potential capability of long operation cycle.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Sugino, Kazuteru; Takaki, Naoyuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2002-074, 143 Pages, 2002/11
In the Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System in Japan (F/S), two types of Helium gas cooled FBR core (Coated particle type fuel core and Pin type fuel core) have been studied. One of the main issues of this study is considered to be consistent achievement both of core performance and safety features. Therefore, in this study we conducted the parametric study on the issue to choose the directions of core and fuel design, and studied the designs of the two core concepts. In conclusion, the following results have been obtained. [Coated Particle Type Fuel Core] The parametric study shows that the increase of fuel volume fraction results in not only core breeding capability improvement but also safety feature improvement, which is due to the reduction of depressurization reactivity. Therefore, a core with the maximum acceptable fuel volume fraction (16.2%) is designed based on the sub-assembly thermal hydraulic considerations. The core reveals about 1.1 of breeding ratio with 150 GWd/t of discharge average burn-up and possible safety features of core meltdown proof in "depressurization accident without scram and forced convection". [Pin Type Fuel Core] The parametric study shows that it is difficult for pin type fuel core to achieve core meltdown proofin "depressurization accident without scram and forced convection", because a pin type fuel core has low heat capacity and low Doppler coefficient. Therefore, a core with passive shutdown mechanism for depressurization events is designed. The core that applies Si Zr
Zr as core material reveals about 1.1 of breeding ratio with 150 GWd/t of discharge average burn-up and possible safety features of core meltdown proof in "depressurization accident with passive shutdown and without forced convection". Based on the results, a coated particle type fuel is selected as a core concept to be studied with more priority in the JFY2002 design study.
as core material reveals about 1.1 of breeding ratio with 150 GWd/t of discharge average burn-up and possible safety features of core meltdown proof in "depressurization accident with passive shutdown and without forced convection". Based on the results, a coated particle type fuel is selected as a core concept to be studied with more priority in the JFY2002 design study.
Takaki, Naoyuki; Naganuma, Masayuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2002-067, 109 Pages, 2002/08
In the Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems (FS), transmutation technology of Long-Lived Fission Product (LLFP) using commercial fast reactors has been studied as a measure to reduce the environmental burden of nuclear waste. During phase-I of the FS (1999-2000), neutronic studies such as transmutation properties, effect by impurities, etc. had been mainly carried out and in the succeeding phase-II(2001) design studies on the LLFP target assembly and the core had been performed. The targeted long-lived isotopes for transmutation were  I,
I,  Tc and
Tc and  Cs. It was assumed that those LLFPs with neutron moderator were recycled into the core of sodium cooled fast reactor after recovering from the spent fuel by element wise separation technology. Concerning Cs, it was found out that the efficient transmutation was extremely difficult to be achieved due to the existence of considerable amount of stable isotope
Cs. It was assumed that those LLFPs with neutron moderator were recycled into the core of sodium cooled fast reactor after recovering from the spent fuel by element wise separation technology. Concerning Cs, it was found out that the efficient transmutation was extremely difficult to be achieved due to the existence of considerable amount of stable isotope  Cs that generates new
Cs that generates new  Cs through successive neutron captures, in addition to the large production rate for
Cs through successive neutron captures, in addition to the large production rate for  Cs. In the design study of the core loaded with LLFP assemblies of I and Tc, two types of LLFP assembly with zirconium hydride as neutron moderator were investigated. One was intended for core-region loading and the other was for radial blanket-region loading. The former has Tc layer in the peripheral region of the assembly to avoid thermal peak in the adjacent fuel assemblies. The integrity evaluation for LLFP assemblies led a conclusion that the most significant design limiting feature was ascribed to the temperature of the moderator pins that determines the dissociated hydrogen penetration rate. To ensure the sufficient cooling for moderator pins, 6-7% of the primary system coolant flow rate had to be distributed to the LLFP assemblies. Design modifications such as subdividing of coolant flow partition and flattening of power distribution were required for the core loaded with LLFP assemblies.
Cs. In the design study of the core loaded with LLFP assemblies of I and Tc, two types of LLFP assembly with zirconium hydride as neutron moderator were investigated. One was intended for core-region loading and the other was for radial blanket-region loading. The former has Tc layer in the peripheral region of the assembly to avoid thermal peak in the adjacent fuel assemblies. The integrity evaluation for LLFP assemblies led a conclusion that the most significant design limiting feature was ascribed to the temperature of the moderator pins that determines the dissociated hydrogen penetration rate. To ensure the sufficient cooling for moderator pins, 6-7% of the primary system coolant flow rate had to be distributed to the LLFP assemblies. Design modifications such as subdividing of coolant flow partition and flattening of power distribution were required for the core loaded with LLFP assemblies.
Takaki, Naoyuki; Uto, Nariaki
JNC TN9400 2002-053, 194 Pages, 2002/08
In the feasibility study on commercialized reactor cycle systems (FS), the design study on small fast reactors has been launched aiming at two main features of "long-life core" and "enhanced passive safety". The small reactors examined in the first stage of FS included (1)natural circulation Pb-Bi cooled reactor, (2)natural circulation sodium cooled reactor (3)forced circulation sodium cooled reactor and (4)forced circulation sodium cooled reactor controlled by movable radial reflector. The core cooled by natural circulation of Pb-Bi or sodium coolant has two extremely different Pu enrichment zones: lower in the inner and higher in the outer zone. This core showed small reactivity swing less than 1%  k/kk' and sufficient cooling capability through the core life time by the "self-following" flow rate of coolant responding to the power distribution change. As for forced circulation sodium cooled reactors, two types of core were studied. One is controlled by reflector with the height to diameter ratio (H/D)
k/kk' and sufficient cooling capability through the core life time by the "self-following" flow rate of coolant responding to the power distribution change. As for forced circulation sodium cooled reactors, two types of core were studied. One is controlled by reflector with the height to diameter ratio (H/D) 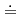 l and the other is having reduced void worth by minimizing H/D to around 0.4. All of the four cores indicated high passive safety behavior under Anticipated Transient Without Scram (ATWS) events with no need for installing Self Actuated Shutdown System (SASS). In the succeeding year 2001, the Pb-Bi core was modified from a united core to assembly wise core and the thermal rating of the sodium cooled core was tripled with keeping the core size in order to reduce the total plant cost. The safety analyses to simulate ATWS events indicated that these cores had potentials for passive shutdown by reactivity feedback effect due to the thermal expansion of core support plate and control rod, and also by controlling the flow coast down.
l and the other is having reduced void worth by minimizing H/D to around 0.4. All of the four cores indicated high passive safety behavior under Anticipated Transient Without Scram (ATWS) events with no need for installing Self Actuated Shutdown System (SASS). In the succeeding year 2001, the Pb-Bi core was modified from a united core to assembly wise core and the thermal rating of the sodium cooled core was tripled with keeping the core size in order to reduce the total plant cost. The safety analyses to simulate ATWS events indicated that these cores had potentials for passive shutdown by reactivity feedback effect due to the thermal expansion of core support plate and control rod, and also by controlling the flow coast down.
;
JNC TN9400 2002-051, 130 Pages, 2002/08
"Helium Gas Cooled Coated Particle Fue1 FBR" is one of attractive core concepts in the Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System in Japan, and the design study is presently proceeded. As one of key technologies of this concept, the coated layer material is important, and ceramics is considered to be a candidate material because of the superior refractory. Based on existing knowledge, TiN is regarded to be a possible candidate material, to which some property tests and evaluations have been conducted. In this study, preliminary tests about the high temperature property and the capability of thick layer coating of TiN have been conducted. Results of these tests come to the following conclusions. (1)Heating tests of two kinds of TiN layer specimens coated by PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) were conducted. As a result, as for CVD coating specimens, remarkable change was not observed on the layer up to 2,000 C, therefore we concluded that the layer by CVD had applicability up to high temperature of actual operation level. On the other hand, as for PVD coating specimens, an unstable behavior that the layer changed to a mesh like texture was observed on a 2,000
C, therefore we concluded that the layer by CVD had applicability up to high temperature of actual operation level. On the other hand, as for PVD coating specimens, an unstable behavior that the layer changed to a mesh like texture was observed on a 2,000 C heated specimen, therefore the applied PVD method is not considered to be promising as the coating technique. (2)The surface conditions of some parts inside CVD device were investigated in order to evaluate possibility of TiN thick coating (
C heated specimen, therefore the applied PVD method is not considered to be promising as the coating technique. (2)The surface conditions of some parts inside CVD device were investigated in order to evaluate possibility of TiN thick coating ( 100
100 m). As a result, around 500
m). As a result, around 500 m of TiN coating layer was observed on the condition of multilayer. Therefore, we conclude that CVD has capability of coating up to thick layer in actual coated particle fuel fabrication.
m of TiN coating layer was observed on the condition of multilayer. Therefore, we conclude that CVD has capability of coating up to thick layer in actual coated particle fuel fabrication.
Sugino, Kazuteru
JNC TN9400 2002-050, 49 Pages, 2002/07
In the former study on the nuclear parameters of gas-cooled fast reactor cores, thier mechanisms and knowhows for the evaluation have scacely been investigated in Japan. Therefore heterogeneity and transport effects of the criticality and depressurization reactivity for three gas-cooled fast reactor cores which are selected in the feasibility study first phase on the fast reactor fuel cycle development have been evaluated in order to improve the prediction accuracy of the nuclear parameters. For the evaluation on the heterogeneity effect the Monte Carlo method was applied and subsequent results were divided into the axial-neutron-streeming and another effects. Further in order to evaluate the transport effect whole core calculations were performed based on the diffusion and transport theories. Concerning the heterogeneity effect, analysis on the heterogeneity effect was tried by dividing into axial-neutron-streeming effect and another effect with applicatlon of the axially-infinite core model. As a result it is cralified that total heterogeneity effect of the criticality tends to be negative because absolute value of the axial neutron streeming effect of gas-cooled reactor core is larger than that of sodium-cooled reactor cores. However total heterogeneity effect of the CO -cooled reactor core is nearly zero due to the cancellation of above mentioned two heterogeneity effects. In addition it is found that the uncertainty of the heterogeneity of the depressurizatlon reactivity is comparable to the heterogeneity effect itself but that is not so large in terms of the correction on the design parameters. What related to the transport effect, those of the criticality and depressurizatlon reactivity are considerable for gas-cooled fast reactor cores. It is cralified that main reason is the diffusion approximation error due to the diluteness of the control rod follower region. Therefore calculation without composition change in the control rod region is ...
-cooled reactor core is nearly zero due to the cancellation of above mentioned two heterogeneity effects. In addition it is found that the uncertainty of the heterogeneity of the depressurizatlon reactivity is comparable to the heterogeneity effect itself but that is not so large in terms of the correction on the design parameters. What related to the transport effect, those of the criticality and depressurizatlon reactivity are considerable for gas-cooled fast reactor cores. It is cralified that main reason is the diffusion approximation error due to the diluteness of the control rod follower region. Therefore calculation without composition change in the control rod region is ...
;
JNC TN9400 2002-032, 318 Pages, 2002/03
Design studies of "Helium Gas Cooled Coated Particle FueI FBR" are being conducted since it has the following superior features, and it is considered to be one of the most promising concepts in Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System in Japan (F/S). (1)Helium gas as coolant is applicable to a high temperature direct gas turbine cycle with high thermal efficiency, (2)Large heat capacity and large Doppler coefficient induced by coated layer material may achieve the attractive core safety characteristic such as so-called "melt down proof" at the sever accident ("Depressurization accident + Without scram + Natural circulation"). As for the conventional design of coated particle fuel, TRISO fuel with SiC as main layer and PyC as buffer and surface protect layers has expressed a lot of excellent achievements in High Temperature Gas Reactor studies. However, it is impossible to directly use this fuel design in FBR, because high burn-up ( 150GWd/t) aimed for economics demands higher strength, and high fast neutron fluence makes it difficult to adopt PyC as surface protect layer due to its dimensional instability in fast neutron spectrum. Therefore, materials with higher strength for main layer and alternative material for surface protect layer are necessary. Nevertheless, at present situation usable data of strength of coat ceramics besides SiC is scarce, and refractory metals as possible candidates of surface protect layer have little experience in fabrication. Based on these backgrounds, we have investigated characteristics of potential candidate coat materials (for main layer and surface protect layer) to understand the possibility of coating applications to the above described design concept in F/S, have selected some potential candidates, and have conducted tests of strength properties for main layer materials and tests of vapor deposition properties for surface protect layer materials. The results of these examinations come to ...
150GWd/t) aimed for economics demands higher strength, and high fast neutron fluence makes it difficult to adopt PyC as surface protect layer due to its dimensional instability in fast neutron spectrum. Therefore, materials with higher strength for main layer and alternative material for surface protect layer are necessary. Nevertheless, at present situation usable data of strength of coat ceramics besides SiC is scarce, and refractory metals as possible candidates of surface protect layer have little experience in fabrication. Based on these backgrounds, we have investigated characteristics of potential candidate coat materials (for main layer and surface protect layer) to understand the possibility of coating applications to the above described design concept in F/S, have selected some potential candidates, and have conducted tests of strength properties for main layer materials and tests of vapor deposition properties for surface protect layer materials. The results of these examinations come to ...
; Sasaki, Makoto; *; *;
JNC TN9400 2001-113, 219 Pages, 2001/09
In the phase-I of the Feasibility Studies (F/S) on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems from July 1999 to the end of FY2000, technology candidates of various commercialized fast reactor (FR) recycle concepts were investigated, in response to the JNC middle long term enterprise plan. This report describes about the core concept study of sodium-cooled oxide-fuel fast breeder reactors as a part of the investigation. The major results of JFY2000 are as follows: (1)One of the promising candidates of large and medium scale Na cooled oxide cores is radial heterogeneous core with axial blanket partial elimination driver fuel sub-assemblies, which achieves re-criticality free and high breeding capability. Core thermal hydraulic design is one of the technical matters of this concept to be investigated in detail. (2)There are concerns of core breeding capability of large scale Na cooled oxide core with the inner-duct sub-assembly concept. 0ne of the possible solutions of the concerns is selection radial heterogeneous core concept with inner-duct sub-assembly. (3)Results of core shielding analysis showed that feasible radial shielding thickness is 2 sub-assemblies layer for the core with radial blanket and 3 sub-assemblies layer for the core without radial blanket.
; Sasaki, Makoto; *; *;
JNC TN9400 2001-112, 174 Pages, 2001/09
As a part of phase-I of the Feasibility Studies of Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems (F/S), fast reactor core characteristics sensitivity study has been performed to understand the relationship between core performances of candidate concepts in the F/S and fuel specification variations, which correspond to the candidates of advanced fuel cycle technology concepts in the F/S, including fuel isotopic compositions. The major results of JFY2000 study are as follows: (1)It is indicated by neutronic calculation that change of core characteristic is not significant even the cases of variation of TRU composition and residual fission products in the recycled fuel which corresponds to advanced fuel cycle candidates. And such change is within a range in which significant modification of core design would not be required. (2)The core characteristic sensitivity study with oxide fuel concept options such as pellet, vi-pack, etc. indicated that the fuel smeared density variation has certain contribution to the core characteristic, especially to the breeding ration. The breeding ratio was calculated to be below l.2 even in the radial heterogeneous core if the fuel smeared density is as low as 80%TD. (3)Accessibility of irradiated radial blanket sub-assembly is evaluated in a viewpoint of proliferation resistance of core concept with radial blanket. The results showed that the heavy shielding and remote handling, similar to the general reprocessing plants, are indispensable to handle the irradiated radial blanket even after 5 years cooling.
; Hayashi, Hideyuki; ; ; ; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-070, 146 Pages, 2000/03
Feasibility studies(F/S) have been undertaken since July, 1999 in order to determine promising concepts of a commercialized fast reactor cycle system and to define the related necessary R&D tasks. ln the phase l(FYs of 1999-2000) of this F/S, a number of conceptual FBR candidates are evaluated. As for this study, a parameter survey on core characteristics of lead cooled fast breeder reactors (FBRs) has been performed. This report describes the intermediate results obtained in the first FY of the phase l. BREST-300 (Russia) is selected as one example for the parameter survey by using the JNC original analysis method, because it is easy to obtain enough information of the core design and its characteristics. The comparison of core characteristics has been performed under the same thermo-hydraulic conditions between lead cooled FBRs and sodium cooled ones. As a result, problems to be resolved have been listed up, and their core characteristics have been evaluated from the target review points of the F/S. The results have been obtained are as follows: (1)High breeding (internal conversion ratio  1) of BREST-300 is mainly due to loading nitride fuel, though the effect of reflecting neutrons is high in the lead coolant. (2)lt may be difficult to reach 150GWd/t due to surface erosion and FCMl of fuel claddings. (3)The maximum fuel cladding temperature of lead cooled FBRs becomes about 40
1) of BREST-300 is mainly due to loading nitride fuel, though the effect of reflecting neutrons is high in the lead coolant. (2)lt may be difficult to reach 150GWd/t due to surface erosion and FCMl of fuel claddings. (3)The maximum fuel cladding temperature of lead cooled FBRs becomes about 40 C higher than sodium cooled ones under the same cooling condition. (4)Fuel pin pitch of lead cooled FBRs becomes larger than that of sodium cooled ones, under the coolant flow condition where
C higher than sodium cooled ones under the same cooling condition. (4)Fuel pin pitch of lead cooled FBRs becomes larger than that of sodium cooled ones, under the coolant flow condition where  T
T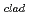 and bundle pressure drop are the same for both cases. Therefore, breeding of the former is not always superior to the latter. From this study core characteristics of lead cooled FBRs, about which we had no experience of design studies so far, was almost clear.
and bundle pressure drop are the same for both cases. Therefore, breeding of the former is not always superior to the latter. From this study core characteristics of lead cooled FBRs, about which we had no experience of design studies so far, was almost clear.
; Hayashi, Hideyuki; ; ; *; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-068, 337 Pages, 2000/03
Feasibility studies(F/S) have been undertaken since July, 1999 in order to determine promising concepts of a commercialized fast reactor cycle system and to define the related necessary R&D tasks. ln the phase l(FYs of 1999-2000) of this F/S, a number of conceptual candidates are selected from the following 5 viewpoints: (a)ensuring safety, (b)economic competitiveness to future LWRs, (c)efficient utilization of resources, (d)reduction of environmental burden, (e)enhancement of nuclear non-proliferation. As for this study based on the above viewpoints, core characteristics of sodium-cooled fast breeder reactors have been surveyed and classified in the combinations of fuels (MOX, metal and nitride). and power output scales. As a result, R&D items to be performed have been proposed, a data base to select candidate reactor concepts has been prepared. The intermediate results obtained in the first FY of the phase l are as follows: (1)There is a limitation in expansion of operation duration for large scale FBRs with MOX fuel. ln case of the reactor with a short doubling time, it is possible to obtain doubling time less than 30 years. (2)The MA transmutation ratio per cycle is about 11% in case of MOX fuel with 5 weight% MA. The difference of this ratio among MOX, metal and nitride fuels is small. (3)A low decontamination fuel with 2 volume% FP may be possible to be used in FBR core designs. (4)The concept of re-criticality prevention may be possible by adoption of a fuel assembly with partly removed axial blanket fuel and a radial heterogeneous core. (5)There is no significant difference of core haracteristics between metal fuel and nitride one, which are suitable for the targets of the F/S.