Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Araki, Shohei; Aizawa, Eiju; Murakami, Takahiko; Arakaki, Yu; Tada, Yuta; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 217, p.111323_1 - 111323_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has modified the STACY from a homogeneous system using solution fuel to a heterogeneous system using fuel rods in order to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris. The modification of the STACY was completed in December 2023. A series of performance inspections were conducted for the start of experimental operations. A new thermal power calibration is required for the performance inspections in order to operate at less than 200 W, which is the permitted thermal power. However, the thermal power measurement method and calibration data used in the former STACY is no longer available due to the modification of the modified STACY. We measured the thermal power of the STACY using the activation method that was improved to adapt to the measurement condition and calibrated the power meter system. Since the positions where activation foils could be installed were very limited, the thermal power was evaluated using numerical calculations supplemented by experimental data. Neutron flux data at the positions of the activation foil was measured by the activation method. Neutron distribution in the core was calculated by the Monte Carlo code MVP. A response function of the activation foil was calculated using the PHITS. The uncertainty of the thermal power measurement was conservatively estimated to be about 15%. Four operations were conducted for the thermal power measurement. The power meter was calibrated by using three operational data and tested with the one operational data. It was found that the indicated value of the meter adjusted by the STACY before the modification work would tend to overestimate the actual output by about 40%. In addition, the current calibration was able to calibrate the meter to within 3% accuracy.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2024-058, 179 Pages, 2025/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2023 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2024-057, 178 Pages, 2025/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2022 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Sono, Hiroki
Robutsuri No Kenkyu (Internet), (78), 12 Pages, 2025/03
The Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) was renovated from a "solution fuel reactor" to a "reactor using fuel rods and light water moderator", and restarted operation on August 2, 2024, after a hiatus of 13 years and 8 months. During that time, it took 8 years and 11 months to obtain its permission and approval, 3 years and 1 month for its construction, and 4 months for pre-operation inspections on the reactor performance. This article reports on the history of STACY from its birth to its restart of operation, as well as its future utilization.
Sono, Hiroki
Genshiryoku Kiko, Genken OB Kai Kaiho, (86), P. 2, 2025/01
The Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) was renovated from a "solution fuel reactor" to a "reactor using fuel rods and light water moderator", and restarted operation on August 2, 2024, after a hiatus of 13 years and 8 months. During that time, it took 8 years and 11 months to obtain its permission and approval, 3 years and 1 month for its construction, and 4 months for pre-operation inspections on the reactor performance. This article reports on the history of STACY from its birth to its restart of operation, as well as its future utilization.
Gunji, Satoshi
Robutsuri No Kenkyu (Internet), (77), 11 Pages, 2024/06
I participated in the international reactor physics conference PHYSOR2024 and summarized the overview and impressions of the conference.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2024) (Internet), p.227 - 236, 2024/04
It is considered that a large amount of fuel debris was generated in the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. In particular, the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris, including concrete components, which are products of molten core-concrete interaction (MCCI), have not been well investigated. In this study, to plan physical simulation in critical experiments at the critical assembly using pseudo fuel debris samples including concrete, we evaluated the sensitivity to the effective multiplication factor of the Si and Ca cross sections in the concrete-simulant sample based on the results of elemental analysis of the prototype. These sensitivity calculations were carried out for each sample loading method and composition. We focused on the energy profile of the sensitivity of the  Ca capture reaction and confirmed that the shape of the sensitivity energy profile changed depending on the sample compositions and neutron moderation conditions. We could know the characteristics of each experimental method by clarifying the trends of sensitivity obtained in different experimental cases. It was found that increasing the amount of concrete in the samples and changing the neutron moderation conditions in the experimental core configurations produced similar changes in the shape of the sensitivity energy profile. This result shows the possibility of reproducing the characteristics of MCCI products through practical critical experiments using concrete materials that do not contain fissile materials.
Ca capture reaction and confirmed that the shape of the sensitivity energy profile changed depending on the sample compositions and neutron moderation conditions. We could know the characteristics of each experimental method by clarifying the trends of sensitivity obtained in different experimental cases. It was found that increasing the amount of concrete in the samples and changing the neutron moderation conditions in the experimental core configurations produced similar changes in the shape of the sensitivity energy profile. This result shows the possibility of reproducing the characteristics of MCCI products through practical critical experiments using concrete materials that do not contain fissile materials.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-050, 178 Pages, 2024/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long- term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2021 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Fernex, F.*; Leclaire, N.*; Bardelay, A.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
Institut de radioprotection et de s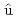 ret
ret nucl
nucl aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Arakaki, Yu; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called STACY from a solution system to a light-water moderated heterogeneous system to validate computation results of criticality characteristics of fuel debris generated in the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. To experimentally simulate the composition and characteristics of fuel debris, we will prepare several grid plates which make particular neutron moderation conditions and a number of rod-shaped concrete and stainless-steel materials. Experiments to evaluate fuel debris's criticality characteristics are scheduled using these devices and materials. This series of STACY experiments are planned to measure the reactivity of fuel debris-simulated samples, measure the critical mass of core configurations containing structural materials such as concrete and stainless steels, and the change in critical mass when their arrangement becomes non-uniform. Furthermore, two divided cores experiments are scheduled that statically simulate fuel debris falling, and also scheduled that subcriticality measurement experiments with partially different neutron moderation conditions. The experimental plans have been considered taking into account some experimental constraints. This paper shows the schedule of these experiments, as well as the computation results of the optimized core configurations and expected results for each experiment.
Sono, Hiroki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Yoritsune, Tsutomu; Suyama, Kenya; Tonoike, Kotaro
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has constructed and operated nine critical assemblies. Of these nine facilities as of 2023, four have already been dismantled, four are under decommissioning, and only STACY is active but under temporally shutdown. STACY is scheduled to restart in 2024 after core modification from a "critical assembly using uranium nitrate solution fuel" to a "general-purpose critical assembly using uranium fuel rods and light-water moderator." The immediate objective of new STACY is to acquire criticality data for fuel debris removal from the damaged reactors in Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. After the critical experiment program regarding fuel debris, the new STACY is expected to be used for various R&D on next-generation power reactors and others. In addition, the new STACY will serve as an educational and training reactor. These activities are useful not only for Japan but also for international collaborative research and joint use.
Gunji, Satoshi; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
Since the compositions and properties of the fuel debris are uncertain, critical experiments are required to validate calculation codes and nuclear data used for the safety evaluation. For this purpose, JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called "STACY". The first criticality of the new STACY is scheduled for spring 2024. This paper reports the consideration results of the core configurations of the new STACY at the first criticality. We prepared two sets of gird plates with different neutron moderation conditions (their intervals are 1.50 cm and 1.27 cm). However, there is a limitation on the number of available UO fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
 variations by nonuniform core configurations
variations by nonuniform core configurationsGunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Suyama, Kenya
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 197(8), p.2017 - 2029, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The fuel debris generated by the accident at the Tokyo Electric Power Company's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is expected to have not only heterogeneous but also nonuniform compositions. Similarly, damaged fuel assemblies remaining in the reactor vessels also have nonuniform configurations due to some missing fuel rods. This non-uniformity may cause changing neutron multiplication factors. The effect of non-uniformity on the neutron multiplication factor is clarified by computations, and the possibility of experimentally validating the computations used for criticality management is being investigated. For this purpose, in this study the criticality effects of several core configurations of a new critical assembly, STACY, of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency with nonuniform arrangements of uranium oxide fuel rods, concrete rods, and stainless-steel rods were studied to confirm benchmarking potential. The difference in these arrangements changed the neutron multiplication factor by more than 1 $. We confirmed that changes in local neutron moderation conditions and the clustering of specific components caused this effect. In addition, the feasibility of benchmark experimental cores with nonuniform arrangements is evaluated. If benchmarking of such experiments could be realized, it would help to validate calculation codes and to develop criticality management methods by machine learning.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-009, 165 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2020 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-006, 153 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, are transferred to NSRI newly. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2019 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has tackled the experimental approach for determining the criticality of pseudo-fuel debris plausibly simulating actual fuel debris since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. To elucidate the characteristics of the pseudo-fuel debris, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency modified the STACY (STAtic experiment Critical facilitY) to conduct critical experiments simulating fuel debris. Thus, we proposed three types of modified STACY core configurations. In critical experiments in the modified STACY core, it is important to judge whether the proposed modified STACY core configurations are representative of molten core-concrete interaction debris or not. In this study, we built pseudo-fuel debris models considering a volume ratio of pseudo-fuel debris to moderation (V /V
/V ) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C
) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C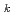 ) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V
) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V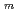 /V
/V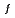 values. The main contributions to C
values. The main contributions to C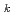 values were
values were  U
U 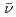 ,
,  U
U  , and
, and  Fe (n,
Fe (n, ), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Suyama, Kenya; Izawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors 2022 (PHYSOR 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/05
The fuel debris is expected to have not only heterogeneous but also non-uniform compositions. Therefore, the calculation method used in their criticality management is required to be validated experimentally. In this study, several core configurations of a new critical assembly "STACY" of JAEA with non-uniform arrangements of uranium oxide fuel rods, concrete rods and stainless steel rods, which are components of the fuel debris, were studied. In each case, the median value of 100 sample patterns was larger than the mean effective multiplication factor. It was also confirmed that there are differences in the effective multiplication factor of more than one dollar by the pattern changing, and that the neutron spectra can change significantly by changing the local neutron moderation conditions. In particular, the effective multiplication factor became smaller when over-moderated regions with large water-to-fuel ratios were formed in the core configurations due to increases in thermal neutron absorption. Such criticality experiments with non-uniform arrangements of multiple compositions will be useful to evaluate the validity of the calculation code.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2021-072, 141 Pages, 2022/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2018 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center and Materials Science Research Center, and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2021-067, 135 Pages, 2022/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Fukushima Technology Development and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each departments manage facilities and develop related technologies to achieve the "Middle-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2017 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by the Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Materials Sciences Research Center, and development activities of Nuclear Human Resources Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.