Advanced control scenario of high-performance steady-state operation for JT-60 superconducting tokamak
JT-60SCにおける高性能定常運転のための先進制御シナリオ
玉井 広史  ; 栗田 源一; 松川 誠; 浦田 一宏*; 櫻井 真治; 土屋 勝彦; 森岡 篤彦; 三浦 友史; 木津 要; 鎌田 裕; 逆井 章; 石田 真一
; 栗田 源一; 松川 誠; 浦田 一宏*; 櫻井 真治; 土屋 勝彦; 森岡 篤彦; 三浦 友史; 木津 要; 鎌田 裕; 逆井 章; 石田 真一
Tamai, Hiroshi; Kurita, Genichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Sakurai, Shinji; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Kamada, Yutaka; Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi
JT-60SCの高性能定常運転シナリオをTOPICSを用いて検討・評価し、

 5で自発電流割合
5で自発電流割合 86%の定常状態をI
86%の定常状態をI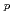 =1.5MA, B
=1.5MA, B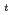 =2T, NBパワー11MWで維持できることを示した。またERATO-Jを用いた解析を行い、導体壁半径とプラズマ小半径との平均比約1.2では、トロイダルモード数1、または2の外部キンクモードに対する壁安定効果により、
=2T, NBパワー11MWで維持できることを示した。またERATO-Jを用いた解析を行い、導体壁半径とプラズマ小半径との平均比約1.2では、トロイダルモード数1、または2の外部キンクモードに対する壁安定効果により、

 5.5まで達成可能であることを示した。さらに 、プラズマを壁に近付けることによって発生する抵抗性壁モードは、容器内コイルを用いた能動制御により抑制されると予測している。一方、
5.5まで達成可能であることを示した。さらに 、プラズマを壁に近付けることによって発生する抵抗性壁モードは、容器内コイルを用いた能動制御により抑制されると予測している。一方、
 のさらなる向上のためにTOSCAによるプラズマ形状の解析を行い、S=(I
のさらなる向上のためにTOSCAによるプラズマ形状の解析を行い、S=(I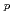 /aB
/aB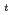 )q
)q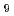
 で定義されるプラズマ形状係数(非円形度と三角形度に強く依存)を
で定義されるプラズマ形状係数(非円形度と三角形度に強く依存)を 4から
4から 6まで変えられることを示した。これは高性能プラズマ運転を実現するうえで重要な電流分布と圧力分布の制御性の拡張を示唆している。
6まで変えられることを示した。これは高性能プラズマ運転を実現するうえで重要な電流分布と圧力分布の制御性の拡張を示唆している。
High performance steady-state operation for JT-60SC are evaluated by the TOPICS analysis. 

 5 and bootstrap current fraction
5 and bootstrap current fraction  86% is kept steady at I
86% is kept steady at I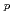 =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B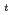 =2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at
=2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at 

 5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
 accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I
accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I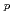 /aB
/aB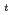 )q
)q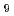
 and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from
and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from  4 to
4 to  6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.