Aggregation behavior of polyisoprene chain ends during living anionic polymerization as investigated by time-resolved small-angle neutron scatting
中性子小角散乱によるリビングアニオン重合の研究
宮元 展義; 山内 一浩*; 長谷川 博一*; 橋本 竹治; 小泉 智
Miyamoto, Nobuyoshi; Yamauchi, Kazuhiro*; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
イソプレン及びスチレンのリビングアニオン重合過程を時間分解中性子小角散乱(SANS)及びゲル浸透クロマトグラフィー(GPC)により測定し、イオン性のリビング末端が形成する会合体について以下のことを明らかにした。反応の溶媒には重水素化ベンゼン、開始剤にはsec-BuLiを用いた。イソプレンの系(最終分子量5300g/mol)では時間とともに散乱強度が増加する様子が観察された。GPCにより測定した分子量の時間変化に関するデータを用いることで、時間分解SANSにより得られる散乱曲線を定量的に解析し、会合数の時間変化を明らかにした。一方、リビング重合を停止させるとSANSプロファイルは大きく変化し、散乱強度は大きく減少した。この結果は、重合停止に伴う末端会合の解消を示唆している。
The living anionic polymerization processes of isoprene and styrene in benzene-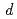
 initiated by
initiated by 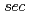 -butyl lithium were studied by in-situ small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and time-resolved molecular weight (
-butyl lithium were studied by in-situ small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and time-resolved molecular weight (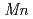 ) measurement by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). In the course of the polymerization of isoprene (
) measurement by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). In the course of the polymerization of isoprene (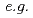
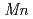 = 5300 g mol
= 5300 g mol ), the small angle scattering increased with the reaction time
), the small angle scattering increased with the reaction time 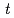 . The molecular weight and its time-change, determined by GPC, is crucial to quantitatively analyze time-resolved SANS measurements; we were able to determine association number
. The molecular weight and its time-change, determined by GPC, is crucial to quantitatively analyze time-resolved SANS measurements; we were able to determine association number 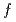 uniquely as a function of
uniquely as a function of 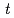 . Upon termination of the living polymerization, SANS profile greatly changed: the scattering intensity in the intermediate
. Upon termination of the living polymerization, SANS profile greatly changed: the scattering intensity in the intermediate 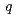 -region (0.2
-region (0.2 
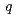
 1.0 nm
1.0 nm ) remarkably decreased, indicating disaggregation of the living ends upon the termination. Also, strong upturn in the low-q region appeared (q
) remarkably decreased, indicating disaggregation of the living ends upon the termination. Also, strong upturn in the low-q region appeared (q  0.1 nm
0.1 nm ) due to the generation of colloidal LiOH or LiO(C
) due to the generation of colloidal LiOH or LiO(C H
H ), which are insoluble in benzene. Detailed data and analyses of isoprene and styrene systems will be given in the presentation.
), which are insoluble in benzene. Detailed data and analyses of isoprene and styrene systems will be given in the presentation.