A Small acidic protein 1 (SMAP1) mediates responses of the arabidopsis root to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
シロイヌナズナ根の合成オーキシン2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acidに対する応答を制御する低分子酸性タンパク質1(SMAP1)
Rahman, A.*; 中曽根 光*; Chhun, T.*; 大浦 千春*; Biswas, K. K.*; 内宮 博文*; 鶴見 誠二*; Baskin, T. I.*; 田中 淳; 大野 豊
Rahman, A.*; Nakasone, Akari*; Chhun, T.*; Oura, Chiharu*; Biswas, K. K.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Baskin, T. I.*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ono, Yutaka
2,4-Dは、IAAの化学的アナログで、オーキシンとして投与し植物の生長を制御する際に広く使用されており、IAAと共通した応答経路で作用すると考えられている。本論文では、2,4-Dに対して感受性が低下しているがIAAに対しては野生型と同様の感受性を示す変異体であるアンチオーキシン耐性変異体(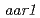 )について報告する。
)について報告する。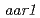 の2,4-D応答変化の特異性は、
の2,4-D応答変化の特異性は、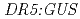 ,
, 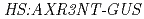 などのマーカー遺伝子の発現や
などのマーカー遺伝子の発現や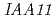 遺伝子のリアルタイムPCR法などにより確認された。2系統の
遺伝子のリアルタイムPCR法などにより確認された。2系統の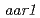 変異遺伝子座を調べたところ、両者とも複数の遺伝子にまたがるゲノムDNAの欠失が起こっていた。そこで、相補試験、及びRNAi形質転換体の解析を行い、欠失領域に存在する単一の遺伝子が2,4-D応答変化に関与していることを証明した。この遺伝子は、機能未知のタンパク質をコードする遺伝子(
変異遺伝子座を調べたところ、両者とも複数の遺伝子にまたがるゲノムDNAの欠失が起こっていた。そこで、相補試験、及びRNAi形質転換体の解析を行い、欠失領域に存在する単一の遺伝子が2,4-D応答変化に関与していることを証明した。この遺伝子は、機能未知のタンパク質をコードする遺伝子(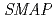 :
: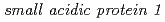 )で動植物には存在するが、菌類や原核生物には報告がないものであった。本研究により、SMAP1は2,4-D応答の調節因子であること、2,4-DとIAAに対する応答反応は部分的に異なる経路で引き起こされることが示唆された。
)で動植物には存在するが、菌類や原核生物には報告がないものであった。本研究により、SMAP1は2,4-D応答の調節因子であること、2,4-DとIAAに対する応答反応は部分的に異なる経路で引き起こされることが示唆された。
2,4-D, a chemical analogue of IAA, is widely used as a growth regulator and exogenous source of auxin. It is believed that they share a common response pathway. Here, we show that a mutant, 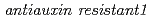 (
(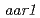 ) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the
) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the 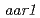 mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the
mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the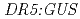 and
and 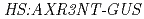 backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of
backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of 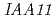 expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a
expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a 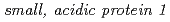 with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.
with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.