中性子局所ドーピングに向けた Si同位体濃縮薄膜の作製
Si同位体濃縮薄膜の作製
Fabrication of  Si-enriched thin film for local neutron transmutation doping
Si-enriched thin film for local neutron transmutation doping
山田 洋一; 山本 博之; 大場 弘則 
 ; 笹瀬 雅人*; 江坂 文孝
; 笹瀬 雅人*; 江坂 文孝 
 ; 山口 憲司; 鵜殿 治彦*; 社本 真一
; 山口 憲司; 鵜殿 治彦*; 社本 真一 
 ; 横山 淳; 北條 喜一
; 横山 淳; 北條 喜一
Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Oba, Hironori; Sasase, Masato*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Udono, Haruhiko*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hojo, Kiichi
中性子ドーピングは、熱中性子によるSi同位体の核変換( Si
Si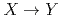
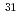 P)を利用し、均一かつ欠陥の少ない不純物注入を可能とする。本手法は、不純物や欠陥濃度の揺らぎが物性に大きく影響するナノレベルでの半導体材料創製において特に有効と期待される。このとき、
P)を利用し、均一かつ欠陥の少ない不純物注入を可能とする。本手法は、不純物や欠陥濃度の揺らぎが物性に大きく影響するナノレベルでの半導体材料創製において特に有効と期待される。このとき、 Si同位体濃縮原料により作製したナノ構造に中性子ドーピングを施せば、ナノスケールの半導体デバイス創製が可能となる。今回、プラズマCVD法により、
Si同位体濃縮原料により作製したナノ構造に中性子ドーピングを施せば、ナノスケールの半導体デバイス創製が可能となる。今回、プラズマCVD法により、 Si同位体濃縮薄膜を作製した。Si
Si同位体濃縮薄膜を作製した。Si F
F の赤外多光子解離により
の赤外多光子解離により Siを濃縮したSiF
Siを濃縮したSiF 気体(
気体( Si: 6.8%)とH
Si: 6.8%)とH の混合気体を用い、高周波電力13MHz, 300Wの条件で、Si(100)基板上(550
の混合気体を用い、高周波電力13MHz, 300Wの条件で、Si(100)基板上(550 C)に、膜厚約100nmの薄膜を作製した。作製された同位体濃縮薄膜の光電子分光測定により、薄膜中の主な不純物であるFは0.6at.%以下であることを確認した。また、二次イオン質量分析測定の結果、薄膜中の
C)に、膜厚約100nmの薄膜を作製した。作製された同位体濃縮薄膜の光電子分光測定により、薄膜中の主な不純物であるFは0.6at.%以下であることを確認した。また、二次イオン質量分析測定の結果、薄膜中の Si同位体濃度は7.1%(天然存在比3.1%)であり、原料ガスとほぼ同じ同位体組成比の薄膜が得られた。講演では作製した同位体濃縮薄膜の構造と、本薄膜に中性子ドーピングを施した際の電気特性の変化についても述べる。
Si同位体濃度は7.1%(天然存在比3.1%)であり、原料ガスとほぼ同じ同位体組成比の薄膜が得られた。講演では作製した同位体濃縮薄膜の構造と、本薄膜に中性子ドーピングを施した際の電気特性の変化についても述べる。
 Si in natural Si has been widely used for a doping source, since
Si in natural Si has been widely used for a doping source, since  Si can be transmuted into
Si can be transmuted into  P by thermal neutron (Neutron Transmutation Doping, NTD). NTD of nanostructure fabricated from
P by thermal neutron (Neutron Transmutation Doping, NTD). NTD of nanostructure fabricated from  Si-enriched materials can serve as a controlled local doping method with tunable dopant concentration, which cannot be realized by conventional doping methods such as ion implantation. In the present study,
Si-enriched materials can serve as a controlled local doping method with tunable dopant concentration, which cannot be realized by conventional doping methods such as ion implantation. In the present study,  Si-enriched thin film has been fabricated in order to demonstrate the local NTD. The
Si-enriched thin film has been fabricated in order to demonstrate the local NTD. The  Si-enriched film with thickness of 100 nm was deposited on the Si(100) substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition using
Si-enriched film with thickness of 100 nm was deposited on the Si(100) substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition using  Si-enriched SiF
Si-enriched SiF as the source gases. The film contains 7.1 % of
as the source gases. The film contains 7.1 % of  Si, which is twice higher than that of natural Si. Possible contaminant, fluorine, is lower than 0.6 at.% determined from X-ray photoelectron spectra. Nanostructure of films and changes of electronic properties by the neutron irradiation will also be discussed.
Si, which is twice higher than that of natural Si. Possible contaminant, fluorine, is lower than 0.6 at.% determined from X-ray photoelectron spectra. Nanostructure of films and changes of electronic properties by the neutron irradiation will also be discussed.