Characterization of 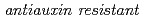 mutants; A Small acidic protein 1 (SMAP1) that mediates responses of the arabidopsis root to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
mutants; A Small acidic protein 1 (SMAP1) that mediates responses of the arabidopsis root to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
アンチオーキシン抵抗性変異体の解析; 合成オーキシンに対するシロイヌナズナ根の反応を仲介するsmall acidic protein 1 (SMAP1)
大野 豊; Rahman, A.*; Biswas, K. K.*; Chhun, T.*; 鶴見 誠二*; 鳴海 一成
Ono, Yutaka; Rahman, A.*; Biswas, K. K.*; Chhun, T.*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Narumi, Issei
植物ホルモンオーキシンの作用メカニズムは幾つかのオーキシン変異体の同定によって明らかになりつつあるが、情報伝達系の詳細な制御機構や既知のオーキシン受容体であるTIR1/AFBsですべてのオーキシン反応が説明できるかどうかは不明である。オーキシン情報伝達にかかわる未知因子を明らかにするため、われわれはアンチオーキシンPCIBの存在下でも根が長く伸びる変異体のスクリーニングを行った。変異体は既知の遺伝子座である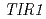 や
や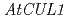 を含め五つのグループに分類された。さらにその中の新規変異体である
を含め五つのグループに分類された。さらにその中の新規変異体である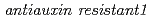 (
(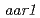 )の生理学的/分子生物学的解析を行い、small acidic protein 1が2,4-Dで誘導されるオーキシン反応を仲介する制御因子であること、また2,4-Dの作用機構が同じオーキシンであるIAAとは部分的に異なることを明らかにした。
)の生理学的/分子生物学的解析を行い、small acidic protein 1が2,4-Dで誘導されるオーキシン反応を仲介する制御因子であること、また2,4-Dの作用機構が同じオーキシンであるIAAとは部分的に異なることを明らかにした。
The mechanism of plant hormoneauxin action has been revealed by identification of several auxin-related mutants. However, the detailed regulatory system of signaling pathway and whether known auxin receptors TIR1/AFBs accounts for all auxin response largely remains unclear. It is may be possible that other uncharacterized proteins are involved in TIR1/AFBs dependent or independent auxin signaling pathway. To investigate novel factors involved in auxin signaling, we screened new mutants that exhibits a long primary root in presence of antiauxin PCIB. The mutants were classified at least 5 independent loci including two known auxin-related loci 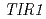 and
and 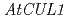 . Furthermore, physiological and molecular characterization of a novel auxin-related mutants,
. Furthermore, physiological and molecular characterization of a novel auxin-related mutants, 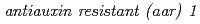 suggested that small acidic protein 1 is a regulatory component that mediates 2,4-D-induced auxin response and mode of action of 2,4-D is distinct from that of IAA at least in part.
suggested that small acidic protein 1 is a regulatory component that mediates 2,4-D-induced auxin response and mode of action of 2,4-D is distinct from that of IAA at least in part.