Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
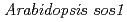 mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance
mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance有賀 裕剛*; 香取 拓*; 吉原 亮平*; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成; 井内 聖*; 小林 正智*; 手塚 健二*; 坂田 洋一*; et al.
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 8(7), p.e24779_1 - e24779_5, 2013/07
シロイヌナズナの354系統の中には、NaCl濃度を0mMから225mmに急激に変化させる試験において、対照となるCol-0系統に比べて高い耐塩性を示す系統がある。また、Zu-Oを含む数系統では、中程度の塩ストレスに暴露された後に高い耐塩性が誘導される。したがって、シロイヌナズナは塩ショックに対する耐性と塩馴化による耐性の少なくとも2種類の耐性機構を有すると思われる。シロイヌナズナの耐塩性系統の耐性メカニズムを明らかにするため、われわれはイオンビームで変異処理したZu-0の実生から塩感受性の変異体を単離した。この変異体は、SOS1遺伝子の1塩基欠失によって塩ショックストレス下で著しい生育抑制を示し、Col-0よりも塩に感受性である。しかし、この変異体はZu-0と同様に、100mMのNaClに7日間暴露した後に750mMのソルビトールに20日間暴露した後も生育することができるが、Col-0は同条件において明らかな白化を示した。したがって、塩馴化に必要な遺伝子は塩ショック耐性に必要な遺伝子とは異なり、塩や浸透圧耐性の獲得に重要な役割を果たしていると考えられる。
 -rays and carbon ion beams in
-rays and carbon ion beams in  seedlings
seedlings吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
Journal of Radiation Research, 54(6), p.1050 - 1056, 2013/05
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:69.45(Biology)To assess the mutational effects of radiations in vigorously proliferating plant tissue, mutation spectrum was analyzed with  seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing
seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing 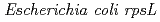 gene were irradiated with
gene were irradiated with  -rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV
-rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV  C
C ), and mutations in the
), and mutations in the 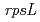 gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by
gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by  -rays, but not by 320 MeV
-rays, but not by 320 MeV  C
C . Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only
. Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only  -rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV
-rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV  C
C than by
than by  -rays in
-rays in  seedlings.
seedlings.  -rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV
-rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV  C
C slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,
slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,  -rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in
-rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in  cells.
cells.
 YgjD and YeaZ are involved in the repair of DNA cross-links
YgjD and YeaZ are involved in the repair of DNA cross-links小野寺 威文; 佐藤 勝也; 太田 敏博*; 鳴海 一成
Extremophiles, 17(1), p.171 - 179, 2013/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:25.06(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Orthologs of 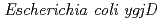 and
and 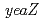 genes are highly conserved in various organisms. The genome of the radioresistant bacterium
genes are highly conserved in various organisms. The genome of the radioresistant bacterium  possesses single orthologs of
possesses single orthologs of 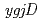 (DR_0382) and
(DR_0382) and 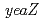 (DR_0756). Complete loss of either one or both genes did not result in any significant changes in cell growth efficiency, indicating that both genes are not essential for cell viability in
(DR_0756). Complete loss of either one or both genes did not result in any significant changes in cell growth efficiency, indicating that both genes are not essential for cell viability in  , unlike the case with other species such as
, unlike the case with other species such as  ,
, 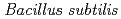 and
and  . Survival rates following DNA damage induced by hydrogen peroxide,
. Survival rates following DNA damage induced by hydrogen peroxide,  -methyl-
-methyl-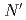 -nitro-
-nitro- -nitrosoguanidine, ultra violet radiation,
-nitrosoguanidine, ultra violet radiation,  -rays, cisplatin and mitomycin C (MMC) were compared among the wild-type strain and
-rays, cisplatin and mitomycin C (MMC) were compared among the wild-type strain and 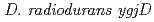 /
/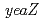 null mutants. Interestingly, the null mutants exhibited high sensitivity to MMC, which mainly causes interstrand DNA cross-links. The sensitivity of the null mutants to MMC was restored to that of the wild-type by transformation with plasmids expressing these genes. These results suggest that
null mutants. Interestingly, the null mutants exhibited high sensitivity to MMC, which mainly causes interstrand DNA cross-links. The sensitivity of the null mutants to MMC was restored to that of the wild-type by transformation with plasmids expressing these genes. These results suggest that 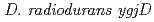 and
and 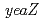 genes are involved in DNA repair and play a role in the repair of DNA cross-links in
genes are involved in DNA repair and play a role in the repair of DNA cross-links in  .
.

佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平*; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 103, 2013/01
 exhibits extraordinary resistance to the lethal effects of ionizing radiations. This resistance has been attributed to its highly proficient DNA repair capacity. In this study, we investigated antibiotics-resistant mutant frequencies for different LET radiations in
exhibits extraordinary resistance to the lethal effects of ionizing radiations. This resistance has been attributed to its highly proficient DNA repair capacity. In this study, we investigated antibiotics-resistant mutant frequencies for different LET radiations in  . Rifampicin is one of the antibiotics that inhibit RNA synthesis by directly interacting with the RNA polymerase beta subunit protein encoded by
. Rifampicin is one of the antibiotics that inhibit RNA synthesis by directly interacting with the RNA polymerase beta subunit protein encoded by 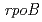 gene. By genetically altering the
gene. By genetically altering the 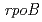 gene in genome, Rif
gene in genome, Rif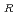 mutant can be generated. The Rif
mutant can be generated. The Rif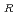 mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. The highest Rif
mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. The highest Rif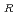 mutant frequencies were observed at a dose range that give 10
mutant frequencies were observed at a dose range that give 10 to 10
to 10 of surviving fraction. There is the possibility that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purposes.
of surviving fraction. There is the possibility that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purposes.
長谷 純宏; 吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 98, 2013/01
The accelerated heavy ions deposit most of their energy close to the end of their range. Little is known about the mutational effects of ion beams near the range end, especially in plants. We analyzed the mutations occurred in the Arabidopsis 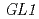 gene with the emphasis on large deletions. Arabidopsis seeds obtained by crossing the wild type with
gene with the emphasis on large deletions. Arabidopsis seeds obtained by crossing the wild type with 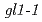 mutant were used as a material. The DNA markers that can distinguish the wild type and
mutant were used as a material. The DNA markers that can distinguish the wild type and 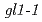 sequence were used to detect deletions. The carbon ions near the range end induced deletions (
sequence were used to detect deletions. The carbon ions near the range end induced deletions ( 6.7 kb) more frequently by 6 times than 208 MeV carbon ions.
6.7 kb) more frequently by 6 times than 208 MeV carbon ions.
宇山 嘉秀*; 大屋 寛高*; 天野 良紀*; 樫本 晃一*; 羽田野 昌二*; 野澤 樹; 吉原 亮平*; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 102, 2013/01
In order to obtain horticulturally useful mutants of 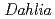 spp., tissue-cultured shoots were irradiated with ion beams at TIARA. The shoots were irradiated with carbon ions in the range of doses from 1 to 5 Gy. Irradiated shoots were transplanted to culture vessel for rooting. 247 plants were acclimated and then settle planted in the field. After blooming, we investigated mutants by focusing mainly on flower shape and color. As a result, several flower shape and flower color mutants are obtained even from 1-Gy irradiated shoots. We are planning to obtain more mutants by increasing study population. Thereafter, we will propagate horticulturally useful mutants and investigate the stability of their characteristics.
spp., tissue-cultured shoots were irradiated with ion beams at TIARA. The shoots were irradiated with carbon ions in the range of doses from 1 to 5 Gy. Irradiated shoots were transplanted to culture vessel for rooting. 247 plants were acclimated and then settle planted in the field. After blooming, we investigated mutants by focusing mainly on flower shape and color. As a result, several flower shape and flower color mutants are obtained even from 1-Gy irradiated shoots. We are planning to obtain more mutants by increasing study population. Thereafter, we will propagate horticulturally useful mutants and investigate the stability of their characteristics.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 手島 光平*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 107, 2013/01
We have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43
USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43 C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30
C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30 C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
西東 力*; 篠原 忍*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 109, 2013/01
Entomopathogenic fungi, 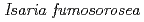 and
and  , are important agents to control insect pests, but the fungi are highly susceptible to conventional fungicides for plant diseases such as powdery mildew. The purpose of this study is to generate mutants tolerant to benomyl, a major fungicide, using carbon ion beams. We have obtained some benomyl-tolerant mutants that were selected on medium supplemented with the fungicide (1,000 ppm). In this study, IC
, are important agents to control insect pests, but the fungi are highly susceptible to conventional fungicides for plant diseases such as powdery mildew. The purpose of this study is to generate mutants tolerant to benomyl, a major fungicide, using carbon ion beams. We have obtained some benomyl-tolerant mutants that were selected on medium supplemented with the fungicide (1,000 ppm). In this study, IC (half maximal inhibitory concentration) of benomyl was determined for the mutants obtained. It is suggested that the fungicide-tolerant mutants maintained a high virulence serve as highly potential biological control agents in integrated pest management programs.
(half maximal inhibitory concentration) of benomyl was determined for the mutants obtained. It is suggested that the fungicide-tolerant mutants maintained a high virulence serve as highly potential biological control agents in integrated pest management programs.
相野 公孝*; 松浦 克成*; 長澤 尚胤; 吉井 文男; 田口 光正; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 106, 2013/01
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed  -(1-4)-linked D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. By
-(1-4)-linked D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. By  -irradiation of chitosan in diluted solutions, low molecular weight chitosan (oligo-chitosan) can be obtained. Oligo-chitosan has potential use in agriculture. In this study, the possibility of oligo-chitosan as a plant growth promoter in tomato was investigated. The combination of oligo-chitosan and bio-pesticide was totally ineffective when tomato was treated at same time. On the other hand, the suppression effect against the pathogen significantly increased when tomato was treated with oligo-chitosan one day before transplant to soil contaminated by the pathogen. This result strongly suggests that oligo-chitosan enhances pathogen resistance in tomato seedling treated with bio-pesticide.
-irradiation of chitosan in diluted solutions, low molecular weight chitosan (oligo-chitosan) can be obtained. Oligo-chitosan has potential use in agriculture. In this study, the possibility of oligo-chitosan as a plant growth promoter in tomato was investigated. The combination of oligo-chitosan and bio-pesticide was totally ineffective when tomato was treated at same time. On the other hand, the suppression effect against the pathogen significantly increased when tomato was treated with oligo-chitosan one day before transplant to soil contaminated by the pathogen. This result strongly suggests that oligo-chitosan enhances pathogen resistance in tomato seedling treated with bio-pesticide.
松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 105, 2013/01
We have been studying ion beam-induced mutations in budding yeast S288c (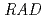
 ) as a model of eukaryote cell. We report a new method to evaluate DNA lesions caused by high-LET radiation using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR is one of the most reliable methods for detecting DNA damage as the amplification stops at the site of the damage. In this study, the 804-bp region of
) as a model of eukaryote cell. We report a new method to evaluate DNA lesions caused by high-LET radiation using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR is one of the most reliable methods for detecting DNA damage as the amplification stops at the site of the damage. In this study, the 804-bp region of 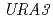 gene was amplified by PCR reaction using a specific oligonucleotide primer set. The PCR device adopted was an Eco Real-Time PCR System (Illumina). The percentage of undamaged template DNA was tended to decrease with an increase in absorbed dose of radiation. The higher LET radiations resulted in the higher rate of decrease in undamaged template DNA. This result suggests that different types of lesions are produced on DNA depending on the LET value of radiations.
gene was amplified by PCR reaction using a specific oligonucleotide primer set. The PCR device adopted was an Eco Real-Time PCR System (Illumina). The percentage of undamaged template DNA was tended to decrease with an increase in absorbed dose of radiation. The higher LET radiations resulted in the higher rate of decrease in undamaged template DNA. This result suggests that different types of lesions are produced on DNA depending on the LET value of radiations.
田中 淳; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 石川 秀高*; 小池 亜紀*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 96, 2013/01
From 2009, ion beams have been utilized for the Sub-Project on Composition or Quality in Rice (FY 2007-2012) under the Mutation Breeding Project of the Forum for Nuclear Cooperation in Asia (FNCA). This sub-project contributes to increase food production and to improve food quality in Asia, by developing new rice mutant varieties that are more resistant to disease, insects, and drought, or give higher yields and offer higher quality. Eight participant countries, i.e., Bangladesh, China, Indonesia, Korea, Malaysia, The Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam joined this project and irradiated seeds of their own rice varieties with ion beams. In FY2011, most of participant countries finished to decide the best doses for mutation induction and have started to harvest descendant plants and mutant screening.
Zaiton, A.*; Affrida, A. H.*; Shakinah, S.*; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 97, 2013/01
Chrysanthemum is one of the leading cut flowers in Malaysia's cut flower industry. Due to the increasing demand of chrysanthemum cut flower, there is a need for new variety of chrysanthemum in order to compete to the ever-competitive cut flower market. Induced mutation breeding using ionizing radiation is one of the effective methods in plant breeding that resulted in generation of new mutated alleles and most unique feature. Attempt was carried out to apply mutation breeding technique using ion beam radiation to produce new variety of chrysanthemum. A pink variety of  was used in this experiment. The experiment will be repeated to determine the accurate optimum irradiation dose for this variety. Meanwhile all shoots regenerated after irradiation are being sub-cultured and will be planted in the nursery.
was used in this experiment. The experiment will be repeated to determine the accurate optimum irradiation dose for this variety. Meanwhile all shoots regenerated after irradiation are being sub-cultured and will be planted in the nursery.
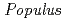 sp.
sp.Biswas, K.; 毛利 武*; 古川原 聡*; 鳴海 一成; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 100, 2013/01
Poplars are economically important trees that are favored for plantation forestry due to their capacity for rapid juvenile growth, which allows us to harvest them in a short span of time. However the rapid growth of poplar is dependent on access to plantation sites with sufficient water and this is problematic, particularly in less rainfall area. The patterns of episodic drought over the last decade suggest that the development of drought tolerant mutant plants could be a promising approach to increase sustained vegetation biomass and forest productivity. In this study, a forward genetics approach has been taken for developing drought/salt tolerant mutants by means of ion beams and in vitro regeneration system in 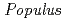 .
.
 線照射効果
線照射効果北野 沙也佳*; 宮城 敦子*; 大野 豊; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 内宮 博文*; 川合 真紀*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 101, 2013/01
 , a member of Polygonaceae, highly accumulates oxalate in leaves. Animals should restrict their intake because high level of oxalate causes of the poisoning. Therefore,
, a member of Polygonaceae, highly accumulates oxalate in leaves. Animals should restrict their intake because high level of oxalate causes of the poisoning. Therefore,  well growing in the meadow is a target of weeding. In this study, we aim to develop a low oxalate
well growing in the meadow is a target of weeding. In this study, we aim to develop a low oxalate  plant that can be used as a pasture by radiation breeding. Plant seeds irradiated with several doses of
plant that can be used as a pasture by radiation breeding. Plant seeds irradiated with several doses of  rays were used to determine the germination rate and the lethal dose. As a result, the germination rate was not affected at doses up to 2000 Gy. However, the growth abnormality was shown in the lower dose. In the doses above 700 Gy, almost plants died after 1st leaf expansion. In conclusion, the 50% lethal dose (LD50) of
rays were used to determine the germination rate and the lethal dose. As a result, the germination rate was not affected at doses up to 2000 Gy. However, the growth abnormality was shown in the lower dose. In the doses above 700 Gy, almost plants died after 1st leaf expansion. In conclusion, the 50% lethal dose (LD50) of  rays was estimated to be 213 Gy for
rays was estimated to be 213 Gy for  .
.
長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 岡田 智行*; 浅見 逸夫*; 長谷 健*; 松尾 洋一*; 金澤 章*; 本多 和茂*; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 95, 2013/01
This study is aimed to develop ion beam breeding technology and useful plant resources. In particular, our current research is focused on the step-wise improvement of traits in flower and ornamental plants. We also focus on improvement of trees and functional ingredients in crops because little knowledge has been accumulated in this area. Here, we describe recent progress made in these studies.
仁宮 一章*; 野村 知世*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 清水 宣明*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 108, 2013/01
By using immunocytochemistry and fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS), yeast population highly expressing cellulase on the cell surface was enriched from the mutant population prepared by irradiation with carbon ion beams (220 MeV  C
C , 100 Gy). Enzymatic activity of the enriched clones was quantified in vitro by a conventional biochemical method. Repeated FACS after irradiation with carbon ion beams was effective for selecting yeast population of interest.
, 100 Gy). Enzymatic activity of the enriched clones was quantified in vitro by a conventional biochemical method. Repeated FACS after irradiation with carbon ion beams was effective for selecting yeast population of interest.
増淵 隆*; 高島 智里*; 上山 修*; 池永 裕*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 110, 2013/01
In the previous study, we have obtained high ethyl caproate producing Sake yeasts No.227 and No.1333 by carbon-ion irradiation. In this study, to identify the mutation sites of the mutant strains, the specific region (226 bp; nucleotide positions 3,642-3,867) in the fatty acid synthase gene 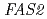 that might be involved in the higher production of ethyl caproate was sequenced and compared with the corresponding sequence in the parental strain Kyokai-901. Consequently, strains No.227 and No.1333 carried G/A and A/C mutations, respectively, at nucleotide position 3,748 as a heterozygous state. This result strongly suggested that the higher production of ethyl caproate in strains No.227 and No.1333 is attributed to a dominant mutation in
that might be involved in the higher production of ethyl caproate was sequenced and compared with the corresponding sequence in the parental strain Kyokai-901. Consequently, strains No.227 and No.1333 carried G/A and A/C mutations, respectively, at nucleotide position 3,748 as a heterozygous state. This result strongly suggested that the higher production of ethyl caproate in strains No.227 and No.1333 is attributed to a dominant mutation in 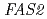 gene.
gene.
布柴 達男*; 平澤 佑啓*; 山内 理子*; 佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平*; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 111, 2013/01
The LOH (loss of heterozygosity) induction by various ion beam radiations was investigated in diploid  . The ion beams
. The ion beams  C
C ,
,  C
C ,
,  He
He and
and  Ar
Ar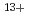 at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30-50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly (
at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30-50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly ( 90%) resulted from gene conversion or crossover through homologous recombination, and followed by chromosome loss through chromosome mis-segregation. Induction of LOH by
90%) resulted from gene conversion or crossover through homologous recombination, and followed by chromosome loss through chromosome mis-segregation. Induction of LOH by  C
C was also examined in
was also examined in 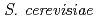 deficient in AP endonuclease (Apn1), translesion DNA polymerases Pol
deficient in AP endonuclease (Apn1), translesion DNA polymerases Pol encoded by Rad30 and Pol
encoded by Rad30 and Pol encoded by Rev3 and Rev7. Pol
encoded by Rev3 and Rev7. Pol may be involved in the induction of LOH, because a slight induction of LOH by
may be involved in the induction of LOH, because a slight induction of LOH by  C
C was observed in the Rev3-deficient strain.
was observed in the Rev3-deficient strain.
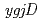 and
and 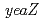 orthologs, in DNA repair of
orthologs, in DNA repair of 
小野寺 威文; 佐藤 勝也; 太田 敏博*; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 104, 2013/01
The 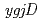 and
and 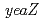 orthologs are highly conserved in eubacteria, and the former is also widely found in the genomes of archaea and eukaryotes.
orthologs are highly conserved in eubacteria, and the former is also widely found in the genomes of archaea and eukaryotes.  , well known as a radioresistant bacterium, possesses the both orthologs, hereafter
, well known as a radioresistant bacterium, possesses the both orthologs, hereafter 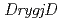 and
and  . In this study, we successfully constructed
. In this study, we successfully constructed 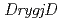 disruptant,
disruptant,  disruptant and
disruptant and 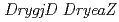 double-disruptant strains. This result clearly indicated that neither
double-disruptant strains. This result clearly indicated that neither 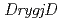 nor
nor  genes is essential for cell viability in
genes is essential for cell viability in  . These gene disruptant strains exhibited extreme sensitivity to mitomycin-C compare to the wild-type strain. The deficiency of
. These gene disruptant strains exhibited extreme sensitivity to mitomycin-C compare to the wild-type strain. The deficiency of 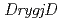 and
and  genes was complemented to restore the wild-type phenotype by introducing plasmids that express these genes.
genes was complemented to restore the wild-type phenotype by introducing plasmids that express these genes.
 -sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival
-sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival手島 光平*; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 112, 2013/01
Biofertilizer is a substance that holds beneficial microorganisms for plant growth in the carrier such as peat, perlite, charcoal and soil. To use biofertilizer more efficiently, it is necessary to keep the amount of viable inoculants in the biofertilizer for a definite period of time.  -irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of  -sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria
-sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria 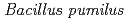 strain TUAT1 and
strain TUAT1 and 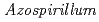 sp. strain MAFF210364.
sp. strain MAFF210364.