Mutational effects of  -rays and carbon ion beams in
-rays and carbon ion beams in  seedlings
seedlings
シロイヌナズナ幼植物体における 線及びイオンビームの突然変異誘発効果
線及びイオンビームの突然変異誘発効果
吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Hidema, Jun*; Sakamoto, Ayako
To assess the mutational effects of radiations in vigorously proliferating plant tissue, mutation spectrum was analyzed with  seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing
seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing 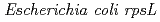 gene were irradiated with
gene were irradiated with  -rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV
-rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV  C
C ), and mutations in the
), and mutations in the 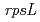 gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by
gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by  -rays, but not by 320 MeV
-rays, but not by 320 MeV  C
C . Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only
. Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only  -rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV
-rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV  C
C than by
than by  -rays in
-rays in  seedlings.
seedlings.  -rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV
-rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV  C
C slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,
slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,  -rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in
-rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in  cells.
cells.