Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小山 真一; 池内 宏知; 三次 岳志; 前田 宏治; 佐々木 新治; 大西 貴士; Tsai, T.-H.; 高野 公秀; 深谷 洋行; 中村 聡志; et al.
廃炉・汚染水・処理水対策事業事務局ホームページ(インターネット), 216 Pages, 2023/11
令和3年度及び4年度に原子力機構が補助事業者となって実施した令和3年度開始「廃炉・汚染水対策事業費補助金に係る補助事業(燃料デブリの性状把握のための分析・推定技術の開発(燃料デブリの分析精度向上、熱挙動の推定及び簡易分析のための技術開発))」の成果概要を最終報告として取りまとめた。本報告資料は、廃炉・汚染水・処理水対策事業事務局ウェブサイトにて公開される。
Balestrazzi, A.*; Achary V Mohan Murali*; Macovei, A.*; 愿山 郁*; 坂本 綾子
Frontiers in Plant Science (Internet), 7, p.64_1 - 64_2, 2016/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:61.23(Plant Sciences)植物は固着生活を行うため、環境に存在するDNA損傷物質の影響を受け続ける運命にある。ゲノム保持の基本メカニズムは動物界と植物界で保存されているが、それに加えて植物はDNA損傷に対処する独自のシステムを発達させてきた。実際、過去数十年の研究により、植物が巧妙なゲノム保持システムを持つことが明らかにされて来ている。例えば、DNA損傷物質に曝されると植物は直ちに反応し、DNA損傷の修復や細胞分裂の制御、代謝経路の変更などにとりかかる。この電子書籍は、植物のゲノム健全性維持にかかわるさまざまな機構、特にDNA損傷の感知、シグナリング、修復ならびにDNA複製機構に焦点をあてた12報の優れた論文をとりあげている。特に、ゲノム保持に関わる複雑な分子ネットワークに注目し、植物の多様なDNA損傷応答についての現在進行中の研究を総括している。植物におけるDNA損傷の蓄積・感知・シグナリング・修復に関わる知識の蓄積は、古典的な育種法や遺伝子導入技術を用いた農作物の改良をより加速させることが期待できる。
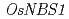 gene in rice via targeted mutagenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
gene in rice via targeted mutagenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 system雑賀 啓明*; 三上 雅史*; 遠藤 真咲*; 坂本 綾子; 土岐 精一*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 97, 2016/02
Arabidopsis thaliana cells, in which DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) have occurred, select either DNA repair, cell death or endocycle. Avoidance of entry into endocycle even under genotoxic conditions, rice (Oryza sativa L.) is more suitable than Arabidopsis for the study of DSBs repair in plants. Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (NBS1) protein consists of the Mre11/Rad50/NBS1 (MRN) complex plays an important role in response to DNA damage in mammal. Although rice has a homologue of NBS1, OsNBS1, its function remains unclear. Here, we attempted to knockout the OsNBS1 gene using the recently developed clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system. Rice (cv. Nipponbare) cells were transformed via Agrobacterium and obtained 72 lines of cali. Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) analysis detected mutations in 58 lines. Biallelic mutations in theOsNBS1 gene were induced in 24 lines. Sequence analyses of PCR products in #2 and #4 detected not only small mutations but also large modifications at the expected cleavage site. The large insertions involved one or two fragments that seem to be copied from sequences around the cleavage site. These mutations are thought to be repaired by a synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA)-like system as proposed in a previous report in barley.
松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 104, 2016/02
本研究では出芽酵母S288cを材料として定量的ポリメラーゼ連鎖反応(qPCR)を用いてDNA損傷量の評価を試みた。0.1から10Gyの炭素イオンを照射したゲノムDNAを用い、PCRよってURA3遺伝子領域を増幅した。線量の増加に伴ってPCRによるDNA増幅は抑制された。以前の研究からURA3遺伝子領域内で変異が起こりやすいことが示唆された領域とそれ以外の領域の損傷量において、今回の試験では有意な差はなかったことから、抽出したDNAに対する照射では、損傷量は異ならないことが確認された。
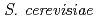
松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 119, 2015/03
高LETのイオンビームによる突然変異誘発の分子機構を明らかにするために、出芽酵母( )を材料として研究を行ってきた。これまでに、LETの増加に伴って致死率および
)を材料として研究を行ってきた。これまでに、LETの増加に伴って致死率および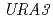 遺伝子の突然変異率が上昇する傾向があること、ならびに突然変異の分布としてヌクレオソーム構造のリンカーDNAにおいて局所的に突然変異が誘発されることを示唆する結果を報告した。ここでは、突然変異が誘発される部位がヌクレオソーム構造に関係があるという仮説を検証するために、野生株と異なるヌクレオソーム構造の
遺伝子の突然変異率が上昇する傾向があること、ならびに突然変異の分布としてヌクレオソーム構造のリンカーDNAにおいて局所的に突然変異が誘発されることを示唆する結果を報告した。ここでは、突然変異が誘発される部位がヌクレオソーム構造に関係があるという仮説を検証するために、野生株と異なるヌクレオソーム構造の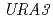 遺伝子を持つ組換え株を作成し、突然変異誘発スペクトルを分析した。野生株での突然変異の位置と、ヌクレオソーム構造が異なる株での
遺伝子を持つ組換え株を作成し、突然変異誘発スペクトルを分析した。野生株での突然変異の位置と、ヌクレオソーム構造が異なる株での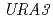 遺伝子の突然変異位置には相違があり、突然変異が生じる位置がヌクレオソーム構造に依存することが示唆された。
遺伝子の突然変異位置には相違があり、突然変異が生じる位置がヌクレオソーム構造に依存することが示唆された。
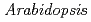
寺西 美佳*; 山口 弘子*; 坂本 綾子; 日出間 純*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 115, 2015/03
Ion beams induce DNA damage, such as strand breaks, possibly resulting in an increased mutation frequency. To elucidate the mechanism of mutation induction in plants, it is important to know about which DNA damage converted into a mutation. In this study, we examined the method for determining the number of DNA strand breaks induced by carbon ion beams in Arabidopsis seedlings. Seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana (wild-type Colombia) were aseptically sown on Murashige and Skoog agar plates. The seedlings were irradiated with carbon ion beams from an AVF cyclotron. After irradiation, whole plants were harvested immediately in order to detect the induced DNA strand breaks. The number of DNA strand breaks increased with increasing dose of carbon ion beams. Irradiation of seedlings with 960 Gy of carbon ion beams resulted in up to 2.3 strand breaks per megabase (Mb). In this study, only DNA double strand breaks can be detected using the non-denatured agarose gel electrophoresis. To elucidate the mechanism of mutation induction in plants, measurement of the extent of DNA damage other than DNA strand breaks should be needed. Further analysis is in progress.
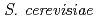
松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成*; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 112, 2014/03
To investigate the nature of mutations induced by accelerated ions in eukaryotic cells, the effects of carbon-ion irradiation were compared with those of  -ray irradiation in the budding yeast
-ray irradiation in the budding yeast  . Previous studies suggested that the mutation sites induced by carbon ions were localized near the linker regions of nucleosomes, whereas mutations induced by
. Previous studies suggested that the mutation sites induced by carbon ions were localized near the linker regions of nucleosomes, whereas mutations induced by  rays were located uniformly throughout the gene. We hypothesized that the locus of mutations might be related to the nucleosome structure. To confirm this hypothesis, we examined the mutation spectrum in the
rays were located uniformly throughout the gene. We hypothesized that the locus of mutations might be related to the nucleosome structure. To confirm this hypothesis, we examined the mutation spectrum in the 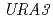 gene with the altered nucleosome structure. It is likely that sites of mutations occurred in the
gene with the altered nucleosome structure. It is likely that sites of mutations occurred in the 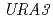 with altered nucleosome structure is inconsistent with those in the wild type. We will further accumulate the data to examine the above hypothesis.
with altered nucleosome structure is inconsistent with those in the wild type. We will further accumulate the data to examine the above hypothesis.
高野 成央*; 高橋 祐子*; 山本 充*; 寺西 美佳*; 山口 弘子*; 坂本 綾子; 長谷 純宏; 藤澤 弘子*; Wu, J.*; 松本 隆*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 54(4), p.637 - 648, 2013/07
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:51.97(Biology)UVB radiation suppresses photosynthesis and protein biosynthesis in plants, which in turn decreases growth and productivity. Here, an ultraviolet-B (UVB)-tolerant rice mutant, 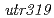 (
(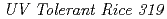 ), was isolated from a mutagenized population derived from 2,500 M1 seeds that were exposed to carbon ions. The
), was isolated from a mutagenized population derived from 2,500 M1 seeds that were exposed to carbon ions. The 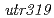 mutant was more tolerant to UVB than the wild type. Neither the levels of UVB-induced CPDs, nor the repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers or (6-4) pyrimidine-pyrimidone photodimers was altered in the
mutant was more tolerant to UVB than the wild type. Neither the levels of UVB-induced CPDs, nor the repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers or (6-4) pyrimidine-pyrimidone photodimers was altered in the 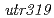 mutant. Thus, the
mutant. Thus, the 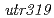 mutant may be impaired in the production of a previously unidentified factor that confers UVB tolerance. To identify the mutated region in the
mutant may be impaired in the production of a previously unidentified factor that confers UVB tolerance. To identify the mutated region in the 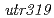 mutant, microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis was performed. Two adjacent genes on chromosome 7were predicted to represent the mutant allele. Sequence analysis of the chromosome region in
mutant, microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis was performed. Two adjacent genes on chromosome 7were predicted to represent the mutant allele. Sequence analysis of the chromosome region in 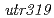 revealed a deletion of 45,419 bp. Database analysis indicated that the Os07g0265100 gene,
revealed a deletion of 45,419 bp. Database analysis indicated that the Os07g0265100 gene, 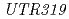 , encodes a putative protein with unknown characteristics or function. In addition, the homologs of UTR319 are conserved only among land plants. Therefore,
, encodes a putative protein with unknown characteristics or function. In addition, the homologs of UTR319 are conserved only among land plants. Therefore, 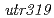 is a novel UVB-tolerant rice mutant and UTR319 may be crucial for the determination of UVB sensitivity in rice, although the function of UTR319 has not yet been determined.
is a novel UVB-tolerant rice mutant and UTR319 may be crucial for the determination of UVB sensitivity in rice, although the function of UTR319 has not yet been determined.
 -rays and carbon ion beams in
-rays and carbon ion beams in  seedlings
seedlings吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
Journal of Radiation Research, 54(6), p.1050 - 1056, 2013/05
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:69.45(Biology)To assess the mutational effects of radiations in vigorously proliferating plant tissue, mutation spectrum was analyzed with  seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing
seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing 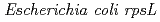 gene were irradiated with
gene were irradiated with  -rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV
-rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV  C
C ), and mutations in the
), and mutations in the 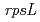 gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by
gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by  -rays, but not by 320 MeV
-rays, but not by 320 MeV  C
C . Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only
. Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only  -rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV
-rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV  C
C than by
than by  -rays in
-rays in  seedlings.
seedlings.  -rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV
-rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV  C
C slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,
slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,  -rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in
-rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in  cells.
cells.
雑賀 啓明*; 吉原 亮平*; 坂本 綾子; 土岐 精一*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 99, 2013/01
To date, many commercial varieties of various kinds of plants have been developed by ion beam breeding. However, to further improve the ion beam breeding system, it is important to gather more basic information on the mutagenic effects of ion beams in plants. To this end, we try to establish a novel mutation detection system using a conditional negative selection marker to stop cell growth. Cultured cell such as callus that can clonally propagate efficiently and easily are well-suited to this system. In this study, we checked the sensitivity of callus of the model plants Arabidopsis and rice to carbon ion beams.
松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 105, 2013/01
We have been studying ion beam-induced mutations in budding yeast S288c (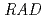
 ) as a model of eukaryote cell. We report a new method to evaluate DNA lesions caused by high-LET radiation using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR is one of the most reliable methods for detecting DNA damage as the amplification stops at the site of the damage. In this study, the 804-bp region of
) as a model of eukaryote cell. We report a new method to evaluate DNA lesions caused by high-LET radiation using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR is one of the most reliable methods for detecting DNA damage as the amplification stops at the site of the damage. In this study, the 804-bp region of 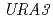 gene was amplified by PCR reaction using a specific oligonucleotide primer set. The PCR device adopted was an Eco Real-Time PCR System (Illumina). The percentage of undamaged template DNA was tended to decrease with an increase in absorbed dose of radiation. The higher LET radiations resulted in the higher rate of decrease in undamaged template DNA. This result suggests that different types of lesions are produced on DNA depending on the LET value of radiations.
gene was amplified by PCR reaction using a specific oligonucleotide primer set. The PCR device adopted was an Eco Real-Time PCR System (Illumina). The percentage of undamaged template DNA was tended to decrease with an increase in absorbed dose of radiation. The higher LET radiations resulted in the higher rate of decrease in undamaged template DNA. This result suggests that different types of lesions are produced on DNA depending on the LET value of radiations.
高野 成央*; 高橋 祐子*; 山本 充*; 寺西 美佳*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 田中 淳; 日出間 純*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 104, 2012/01
UVB radiation can affect the plant growth and development. The aim of this study is identify new factor(s) related to UVB tolerance in plants by bioengineering or breeding programs. To produce UVB tolerant or sensitive mutants, dry seeds of Japanese rice cultivar Sasanishiki were exposed with carbon ion beams, and two UVB tolerant and three UVB sensitive mutants were isolated from the offspring of irradiated plants. By analysis of comparative genomic hybridization and sequencing of bacterial artificial chromosome library, we identified the mutated regions in a UVB tolerant mutant 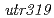 and a UVB sensitive mutant
and a UVB sensitive mutant 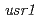 .
.

松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 108, 2012/01
We have been studying ion-beam induced mutations in the budding yeast as a model of eukaryote cell. Yeast cells were irradiated with 220 MeV carbon ions with 107 keV/ m LET. The survival rates following irradiation were determined on the basis of colony-forming ability.
m LET. The survival rates following irradiation were determined on the basis of colony-forming ability. 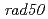 and
and 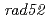 strains showed hyper sensitivity, while the
strains showed hyper sensitivity, while the 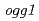 and
and 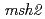 strains showed relatively lower sensitivity to the carbon ion irradiation. The expression of
strains showed relatively lower sensitivity to the carbon ion irradiation. The expression of 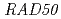 gene was up-regulated following carbon ion irradiation but not
gene was up-regulated following carbon ion irradiation but not  rays. This difference may result from the repair pathway that operates in mutant strains.
rays. This difference may result from the repair pathway that operates in mutant strains.
 , AtRev1 and AtPol
, AtRev1 and AtPol in
in  -ray-induced mutagenesis
-ray-induced mutagenesis中川 繭*; 高橋 真哉*; 鳴海 一成; 坂本 綾子
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 6(5), p.728 - 731, 2011/05
Ionizing radiations have been applied to plants as useful mutagens, but its molecular mechanism(s) for mutagenesis is less understood. The AtPol , AtRev1 and AtPol
, AtRev1 and AtPol are Arabidopsis translesion synthesis (TLS)-type polymerases involved in the UV-induced mutagenesis. To investigate a role(s) of TLS-type DNA polymerases in radiation-induced mutagenesis, we analyzed the mutation frequency in AtPol
are Arabidopsis translesion synthesis (TLS)-type polymerases involved in the UV-induced mutagenesis. To investigate a role(s) of TLS-type DNA polymerases in radiation-induced mutagenesis, we analyzed the mutation frequency in AtPol -, AtRev1- or AtPol
-, AtRev1- or AtPol -knockout plants,
-knockout plants, 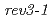 ,
, 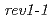 and
and 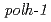 , respectively. The mutation frequency in
, respectively. The mutation frequency in 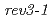 was little changed, whereas the frequency in
was little changed, whereas the frequency in 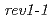 greatly decreased and in
greatly decreased and in 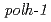 slightly increased compared to that of wild type. Abasic (apurinic/apyrimidinic; AP) site, induced by radiations or generated during DNA repair process, leads to incorporation of any kinds of nucleotides at the opposite strand. The 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG), induced by radiation through the formation of reactive oxygen species, makes pairs with cytosine and adenines. Therefore, AtRev1 possibly inserts dC opposite AP-site or 8-oxo-dG, which results in G to T transversions.
slightly increased compared to that of wild type. Abasic (apurinic/apyrimidinic; AP) site, induced by radiations or generated during DNA repair process, leads to incorporation of any kinds of nucleotides at the opposite strand. The 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG), induced by radiation through the formation of reactive oxygen species, makes pairs with cytosine and adenines. Therefore, AtRev1 possibly inserts dC opposite AP-site or 8-oxo-dG, which results in G to T transversions.

吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 雑賀 啓明*; 寺西 美佳*; 土岐 精一*; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 74, 2011/01
This study aimed to elucidate the effects of ion beams on  . We focus on (1) what kinds of damage are produced by ion beams, and (2) what kinds of cellular processes are involved in turn the damage into mutations. Our results suggest that 220 MeV carbon ions may induce more numbers of DNA lesions or more severe types of DNA lesions than
. We focus on (1) what kinds of damage are produced by ion beams, and (2) what kinds of cellular processes are involved in turn the damage into mutations. Our results suggest that 220 MeV carbon ions may induce more numbers of DNA lesions or more severe types of DNA lesions than  -rays and 50 MeV helium ions. Our results also suggest that the considerable amount of DNA lesions induced by
-rays and 50 MeV helium ions. Our results also suggest that the considerable amount of DNA lesions induced by  -rays and 50 MeV helium ions are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair mechanism, but the majority of DNA lesions induced by 220 MeV carbon ions are not repaired by NHEJ.
-rays and 50 MeV helium ions are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair mechanism, but the majority of DNA lesions induced by 220 MeV carbon ions are not repaired by NHEJ.
 -rays and carbon ion beams on
-rays and carbon ion beams on  seedlings
seedlings吉原 亮平; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 坂本 綾子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 59, 2011/01
To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis by ion beams in higher plant seedlings, mutational effects of ion beams an  -rays were investigated. Mutant frequency was increased by the irradiation of both radiations. Deletion/insertion and G to A transition were major mutations induced by both radiations. However, base change mutations induced by oxidized guanine (G to T and A to C) were not increased in
-rays were investigated. Mutant frequency was increased by the irradiation of both radiations. Deletion/insertion and G to A transition were major mutations induced by both radiations. However, base change mutations induced by oxidized guanine (G to T and A to C) were not increased in  seedlings as in dry seeds, suggesting that the effects of oxidized guanine induced by ionizing radiation may be lower in plant than in other organisms irrespective of LET.
seedlings as in dry seeds, suggesting that the effects of oxidized guanine induced by ionizing radiation may be lower in plant than in other organisms irrespective of LET.
 cells
cells清水 喜久雄*; 松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 坂本 綾子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 79, 2011/01
To elucidate the molecular mechanism of mutagenesis caused by ion beam irradiation in yeast, two mutant strains 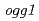 and
and 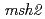 which are deficient in mismatch repair mechanisms were used to measure mutation spectra. Several hot spots were found in the
which are deficient in mismatch repair mechanisms were used to measure mutation spectra. Several hot spots were found in the 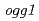 mutant, while mutations in the
mutant, while mutations in the 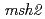 mutant were distributed evenly for base substitution except one hot spot at position 345. These results suggest that the incorporation of damaged nucleotides was not uniform in yeast cells.
mutant were distributed evenly for base substitution except one hot spot at position 345. These results suggest that the incorporation of damaged nucleotides was not uniform in yeast cells.
 , AtRev1 and AtPol
, AtRev1 and AtPol in UV light-induced mutagenesis in Arabidopsis
in UV light-induced mutagenesis in Arabidopsis![$$^{1[W]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWMK1K3OX0JA.gif)
中川 繭*; 高橋 真哉*; 田中 淳; 鳴海 一成; 坂本 綾子
Plant Physiology, 155(1), p.414 - 420, 2011/01
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:41.13(Plant Sciences)損傷乗り越え複製(TLS)は、特殊なDNAポリメラーゼによって損傷DNAをバイパスすることによって複製障害を回避する機構である。われわれは高等植物における損傷乗り越え複製機構の役割を調べるため、TLS型DNAポリメラーゼを欠失させたシロイヌナズナの変異株における紫外線誘発突然変異頻度を解析した。AtPol 及びAtRev1を欠失させた植物では突然変異頻度は低下したことから、これらのポリメラーゼは突然変異を起こしやすいことがわかった。これに対し、AtPol
及びAtRev1を欠失させた植物では突然変異頻度は低下したことから、これらのポリメラーゼは突然変異を起こしやすいことがわかった。これに対し、AtPol を欠失した植物では突然変異頻度が上昇したことから、AtPol
を欠失した植物では突然変異頻度が上昇したことから、AtPol は突然変異を起こしにくいことがわかった。AtPol
は突然変異を起こしにくいことがわかった。AtPol とAtRev1の2重変異ではAtRev1の単独変異とほぼ同等の変異頻度であったのに対し、AtPol
とAtRev1の2重変異ではAtRev1の単独変異とほぼ同等の変異頻度であったのに対し、AtPol とAtPol
とAtPol の2重変異では、AtPol
の2重変異では、AtPol で見られた高い変異頻度がほぼ失われた。このことから、AtPol
で見られた高い変異頻度がほぼ失われた。このことから、AtPol and AtRev1は同一の経路で働くのに対し、AtPol
and AtRev1は同一の経路で働くのに対し、AtPol はこれらとは別の経路で働くことが示唆された。
はこれらとは別の経路で働くことが示唆された。
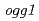 and
and 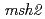 mutants
mutants松尾 陽一郎*; 西嶋 茂宏*; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 坂本 綾子; 鳴海 一成; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 75, 2009/12
本研究では、真核生物の一種である出芽酵母の野生株、塩基除去修復が不活性であるogg1株及びミスマッチ修復が不活性であるmsh2株を用いて、炭素イオンビーム照射で誘発される突然変異について、URA3遺伝子の突然変異を検出する5-FOAによる選択系で、変異スペクトルの解析を行った。その結果、野生株及びogg1株ともに塩基置換の頻度が高く、特にogg1株では変異のすべてが塩基置換であった。また、msh2株では、一塩基欠失が全体の突然変異の大部分を占め、その中でもGC to TAのトランスバージョン変異が多く誘発されることが確認された。これらの結果から、8-oxoGの生成がイオンビームに起因する突然変異をおもに誘導し、OGG1及びMSH2遺伝子が遺伝子の安定性に強く貢献していることが示唆された。
 is defective in the DNA damage response
is defective in the DNA damage response坂本 綾子; Lan, V. T. T.*; Puripunyavanich, V.*; 長谷 純宏; 横田 裕一郎; 鹿園 直哉; 中川 繭*; 鳴海 一成; 田中 淳
Plant Journal, 60(3), p.509 - 517, 2009/07
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:49.93(Plant Sciences)細胞分裂周期の進行は、内的又は外的なさまざまな要因によって常にストレスを受けており、それによってDNA複製の中断や染色体の分配異常などが引き起こされることが知られている。細胞周期チェックポイントとは、こうした異常事態の際に細胞周期の進行を停止し、適切な処理が行われるまで次のステップに移行しないようにするための機構である。われわれは、シロイヌナズナの紫外線感受性変異株のスクリーニングの過程で、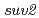 (sensitive to UV 2)変異株を単離した。
(sensitive to UV 2)変異株を単離した。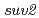 変異株は、さまざまなDNA変異原やヒドロキシウレアに対して感受性を示し、その表現系は損傷チェックポイントにかかわるAtATRの欠損株に非常によく似ていた。さらに、SUV2蛋白質はGCN4型のコイルドコイルドメインを持つ蛋白質をコードしており、N末側にはPI3K様プロテインキナーゼのターゲット配列が2か所存在していた。そこで、SUV2蛋白質同士どうしの相互作用を酵母two-hybridの系で解析したところ、
変異株は、さまざまなDNA変異原やヒドロキシウレアに対して感受性を示し、その表現系は損傷チェックポイントにかかわるAtATRの欠損株に非常によく似ていた。さらに、SUV2蛋白質はGCN4型のコイルドコイルドメインを持つ蛋白質をコードしており、N末側にはPI3K様プロテインキナーゼのターゲット配列が2か所存在していた。そこで、SUV2蛋白質同士どうしの相互作用を酵母two-hybridの系で解析したところ、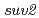 は2量体を形成することが明らかになった。以上の結果から、われわれは
は2量体を形成することが明らかになった。以上の結果から、われわれは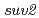 がATRの活性を制御するATRIPのシロイヌナズナにおけるホモログであると結論づけ、AtATRIPと命名した。
がATRの活性を制御するATRIPのシロイヌナズナにおけるホモログであると結論づけ、AtATRIPと命名した。