Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
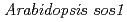 mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance
mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance有賀 裕剛*; 香取 拓*; 吉原 亮平*; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成; 井内 聖*; 小林 正智*; 手塚 健二*; 坂田 洋一*; et al.
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 8(7), p.e24779_1 - e24779_5, 2013/07
シロイヌナズナの354系統の中には、NaCl濃度を0mMから225mmに急激に変化させる試験において、対照となるCol-0系統に比べて高い耐塩性を示す系統がある。また、Zu-Oを含む数系統では、中程度の塩ストレスに暴露された後に高い耐塩性が誘導される。したがって、シロイヌナズナは塩ショックに対する耐性と塩馴化による耐性の少なくとも2種類の耐性機構を有すると思われる。シロイヌナズナの耐塩性系統の耐性メカニズムを明らかにするため、われわれはイオンビームで変異処理したZu-0の実生から塩感受性の変異体を単離した。この変異体は、SOS1遺伝子の1塩基欠失によって塩ショックストレス下で著しい生育抑制を示し、Col-0よりも塩に感受性である。しかし、この変異体はZu-0と同様に、100mMのNaClに7日間暴露した後に750mMのソルビトールに20日間暴露した後も生育することができるが、Col-0は同条件において明らかな白化を示した。したがって、塩馴化に必要な遺伝子は塩ショック耐性に必要な遺伝子とは異なり、塩や浸透圧耐性の獲得に重要な役割を果たしていると考えられる。
 -rays and carbon ion beams in
-rays and carbon ion beams in  seedlings
seedlings吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
Journal of Radiation Research, 54(6), p.1050 - 1056, 2013/05
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:69.64(Biology)To assess the mutational effects of radiations in vigorously proliferating plant tissue, mutation spectrum was analyzed with  seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing
seedlings via plasmid rescue method. Transgenic plants containing 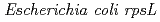 gene were irradiated with
gene were irradiated with  -rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV
-rays and carbon ion beams (320 MeV  C
C ), and mutations in the
), and mutations in the 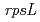 gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by
gene were analyzed. Mutant frequency was significantly increased by  -rays, but not by 320 MeV
-rays, but not by 320 MeV  C
C . Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only
. Mutation spectrum showed that both radiations increased the frequency of frameshifts and other mutations including deletion/insertion but that only  -rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV
-rays increased the frequency of total base substitutions. These results suggest that the type of DNA lesions which cause base substitutions were less induced by 320 MeV  C
C than by
than by  -rays in
-rays in  seedlings.
seedlings.  -rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV
-rays never increased the frequencies of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversions, which are caused by oxidized guanine, though 320 MeV  C
C slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,
slightly increase the both transversions. Instead,  -rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in
-rays significantly increased the frequency of G:C to A:T transition. These results suggest that 8-oxoguanine has little effect on mutagenesis in  cells.
cells.
長谷 純宏; 吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 98, 2013/01
The accelerated heavy ions deposit most of their energy close to the end of their range. Little is known about the mutational effects of ion beams near the range end, especially in plants. We analyzed the mutations occurred in the Arabidopsis 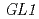 gene with the emphasis on large deletions. Arabidopsis seeds obtained by crossing the wild type with
gene with the emphasis on large deletions. Arabidopsis seeds obtained by crossing the wild type with 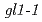 mutant were used as a material. The DNA markers that can distinguish the wild type and
mutant were used as a material. The DNA markers that can distinguish the wild type and 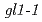 sequence were used to detect deletions. The carbon ions near the range end induced deletions (
sequence were used to detect deletions. The carbon ions near the range end induced deletions ( 6.7 kb) more frequently by 6 times than 208 MeV carbon ions.
6.7 kb) more frequently by 6 times than 208 MeV carbon ions.
宇山 嘉秀*; 大屋 寛高*; 天野 良紀*; 樫本 晃一*; 羽田野 昌二*; 野澤 樹; 吉原 亮平*; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 102, 2013/01
In order to obtain horticulturally useful mutants of 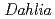 spp., tissue-cultured shoots were irradiated with ion beams at TIARA. The shoots were irradiated with carbon ions in the range of doses from 1 to 5 Gy. Irradiated shoots were transplanted to culture vessel for rooting. 247 plants were acclimated and then settle planted in the field. After blooming, we investigated mutants by focusing mainly on flower shape and color. As a result, several flower shape and flower color mutants are obtained even from 1-Gy irradiated shoots. We are planning to obtain more mutants by increasing study population. Thereafter, we will propagate horticulturally useful mutants and investigate the stability of their characteristics.
spp., tissue-cultured shoots were irradiated with ion beams at TIARA. The shoots were irradiated with carbon ions in the range of doses from 1 to 5 Gy. Irradiated shoots were transplanted to culture vessel for rooting. 247 plants were acclimated and then settle planted in the field. After blooming, we investigated mutants by focusing mainly on flower shape and color. As a result, several flower shape and flower color mutants are obtained even from 1-Gy irradiated shoots. We are planning to obtain more mutants by increasing study population. Thereafter, we will propagate horticulturally useful mutants and investigate the stability of their characteristics.
雑賀 啓明*; 吉原 亮平*; 坂本 綾子; 土岐 精一*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 99, 2013/01
To date, many commercial varieties of various kinds of plants have been developed by ion beam breeding. However, to further improve the ion beam breeding system, it is important to gather more basic information on the mutagenic effects of ion beams in plants. To this end, we try to establish a novel mutation detection system using a conditional negative selection marker to stop cell growth. Cultured cell such as callus that can clonally propagate efficiently and easily are well-suited to this system. In this study, we checked the sensitivity of callus of the model plants Arabidopsis and rice to carbon ion beams.
長谷 純宏; 吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 731(1-2), p.41 - 47, 2012/03
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:69.59(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)植物におけるイオンビームの変異誘発効果に関する知見を深めるため、飛程末端に近い炭素イオン(平均LET 425keV/ m)と種子を透過する炭素イオン(平均LET 113keV/
m)と種子を透過する炭素イオン(平均LET 113keV/ m)の変異効果を比較した。照射した植物体からの大腸菌由来
m)の変異効果を比較した。照射した植物体からの大腸菌由来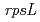 遺伝子のプラスミドレスキュー法では、113keV/
遺伝子のプラスミドレスキュー法では、113keV/ m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が2.7倍上昇したのに対して、425keV/
m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が2.7倍上昇したのに対して、425keV/ m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が上昇しなかったことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンで誘発される突然変異は、プラスミドレスキューでは検出できないことが示唆された。非相同末端結合修復能を欠損するシロイヌナズナのDNA ligase IV遺伝子の変異体は、両者の炭素イオンに対して野生型よりも高い感受性を示したが、野生型と変異体の感受性の差は425keV/
m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が上昇しなかったことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンで誘発される突然変異は、プラスミドレスキューでは検出できないことが示唆された。非相同末端結合修復能を欠損するシロイヌナズナのDNA ligase IV遺伝子の変異体は、両者の炭素イオンに対して野生型よりも高い感受性を示したが、野生型と変異体の感受性の差は425keV/ m炭素イオンでは113keV/
m炭素イオンでは113keV/ m炭素イオンに比べて極めて小さいことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンは修復困難なDNA損傷を誘発することが示唆された。シロイヌナズナの
m炭素イオンに比べて極めて小さいことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンは修復困難なDNA損傷を誘発することが示唆された。シロイヌナズナの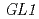 遺伝子を利用した変異解析では、無毛変異の形成頻度は両者の炭素イオンで差がなかったが、大規模な欠失変異(
遺伝子を利用した変異解析では、無毛変異の形成頻度は両者の炭素イオンで差がなかったが、大規模な欠失変異(
 30kb)の頻度は425keV/
30kb)の頻度は425keV/ m炭素イオンが6倍高かったことから、LETが高まるに従って大規模な欠失変異の割合が高まることが示唆された。
m炭素イオンが6倍高かったことから、LETが高まるに従って大規模な欠失変異の割合が高まることが示唆された。
長谷 純宏; 吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 103, 2012/01
The accelerated heavy ions deposit most of their energy close to the end of their range. Little is known about the mutational effects of ion beams near range end, especially in plants. Here, we carried out several experiments to characterize mutational effects of carbon ions near range end in plants. Out results suggested the possibility that large structural alterations, which cannot be detected by plasmid rescue, were frequently induced by the carbon ions near range end. It was also suggested that the carbon ions near range end induce much irreparable DNA lesions. Analysis using 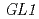 locus suggested that ion beams with very high LET frequently induce large deletions in Arabidopsis genome.
locus suggested that ion beams with very high LET frequently induce large deletions in Arabidopsis genome.
Affrida, A. H.*; Zaiton, A.*; Salahbiah, A. M.*; Shakinah, S.*; 吉原 亮平; 鳴海 一成; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 62, 2011/01
Chrysanthemum is one of the leading temperate flowers in Malaysia, and contributes 23% of the total value of cut flower production. The objectives of this study are to develop an effective method for mutation induction of local chrysanthemum varieties using ion beams and to determine the optimum dose for callus formation using petals. After 4 weeks, the percentage of survived petals of  cv. Reagan Red decreased drastically at doses above 10 Gy. After 8 weeks, more cultures developed shoots or shoot buds. Irradiation dose of 15 Gy and higher was found to adversely affect the capability of the petal cultures to form shoots as the percentage of shoot regeneration were less than 5%.
cv. Reagan Red decreased drastically at doses above 10 Gy. After 8 weeks, more cultures developed shoots or shoot buds. Irradiation dose of 15 Gy and higher was found to adversely affect the capability of the petal cultures to form shoots as the percentage of shoot regeneration were less than 5%.
 -rays and carbon ion beams on
-rays and carbon ion beams on  seedlings
seedlings吉原 亮平; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 坂本 綾子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 59, 2011/01
To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis by ion beams in higher plant seedlings, mutational effects of ion beams an  -rays were investigated. Mutant frequency was increased by the irradiation of both radiations. Deletion/insertion and G to A transition were major mutations induced by both radiations. However, base change mutations induced by oxidized guanine (G to T and A to C) were not increased in
-rays were investigated. Mutant frequency was increased by the irradiation of both radiations. Deletion/insertion and G to A transition were major mutations induced by both radiations. However, base change mutations induced by oxidized guanine (G to T and A to C) were not increased in  seedlings as in dry seeds, suggesting that the effects of oxidized guanine induced by ionizing radiation may be lower in plant than in other organisms irrespective of LET.
seedlings as in dry seeds, suggesting that the effects of oxidized guanine induced by ionizing radiation may be lower in plant than in other organisms irrespective of LET.
冨川 優*; 前田 智雄*; 本多 和茂*; 嵯峨 紘一*; 石川 隆二*; 秋田 祐介; 吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 73, 2011/01
Red pepper "Hirosaki zairai" is a local variety grown around Hirosaki city in Aomori Prefecture. It has been promoted as one of the valuable local brands. In this study, we tried to create additional values on this variety via mutation breeding using ion beam. As a result, some extremely small fruits and atypical double fruits (a small fruit was formed in a fruit) were observed at 40-Gy irradiated samples. This result suggested that ion-beam irradiation affected fruit formation in red peppers.
松尾 洋一*; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 吉原 亮平; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 66, 2011/01
本研究では、柑橘類に320MeV炭素イオンビームを照射し、放射線感受性の程度を調査した。温州ミカンのカルスに照射した場合の再分化率は品種によってばらつきが見られた。再分化率の結果から、川田早生については2から4Gy、今村温州については4Gyが適正線量であると考えられた。カラタチ種子に照射した場合の発芽率は、12Gyで70%以上、16Gyでは50%以下となった。急激に発芽率が低下する直前が適正線量と考えられるため、次回試験では12Gyから16Gyの間で照射試験を実施する予定である。
岡田 智行*; 池田 洋*; 大野 豊; 吉原 亮平; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 63, 2011/01
群馬県農業技術センターが開発したコギク品種「小夏の風」の葉片培養体にイオンビームを照射することで、エネルギー及び線量が植物体再生に及ぼす影響を調査し、変異誘導に適した照射条件を検討した。その結果、220MeV  C
C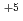 では、0.5Gy以上で植物体再生率が下がり始め、2Gyでは植物体の再生率が3.3%であった。一方、320MeV
では、0.5Gy以上で植物体再生率が下がり始め、2Gyでは植物体の再生率が3.3%であった。一方、320MeV  C
C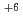 では、0.1Gyで再生率が23.7%と大きく下がり、2Gyでは1.7%まで下がった。
では、0.1Gyで再生率が23.7%と大きく下がり、2Gyでは1.7%まで下がった。 C
C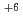 では植物体再生に及ぼす影響が極めて強いことから、「小夏の風」へのイオンビーム照射には
では植物体再生に及ぼす影響が極めて強いことから、「小夏の風」へのイオンビーム照射には C
C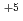 の方が適していると考えられた。
の方が適していると考えられた。
浅見 逸夫*; 辻 孝子*; 長谷川 徹*; 福田 至朗*; 黒柳 悟*; 長谷 純宏; 吉原 亮平; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 68, 2011/01
鹿児島県と原子力機構が共同で育成した白一輪ギク「新神2」は、無側枝性並びに低温開花性を有し、イオンビーム照射が労働及び光熱コストを低減できる品種の育成に有効であることが示されている。本研究では、この実績を、愛知県育成白一輪ギク品種「白粋」に応用し、生産額全国第1位の愛知県のキク生産農家が望む新品種を育成することを目的とする。現在までに、無側枝性については3候補を、また、低温開花性については12候補を選抜した。今後は、得られた有望個体を維持し、次年度にそれぞれの特性の再評価・二次選抜を行う予定である。

吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 雑賀 啓明*; 寺西 美佳*; 土岐 精一*; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 74, 2011/01
This study aimed to elucidate the effects of ion beams on  . We focus on (1) what kinds of damage are produced by ion beams, and (2) what kinds of cellular processes are involved in turn the damage into mutations. Our results suggest that 220 MeV carbon ions may induce more numbers of DNA lesions or more severe types of DNA lesions than
. We focus on (1) what kinds of damage are produced by ion beams, and (2) what kinds of cellular processes are involved in turn the damage into mutations. Our results suggest that 220 MeV carbon ions may induce more numbers of DNA lesions or more severe types of DNA lesions than  -rays and 50 MeV helium ions. Our results also suggest that the considerable amount of DNA lesions induced by
-rays and 50 MeV helium ions. Our results also suggest that the considerable amount of DNA lesions induced by  -rays and 50 MeV helium ions are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair mechanism, but the majority of DNA lesions induced by 220 MeV carbon ions are not repaired by NHEJ.
-rays and 50 MeV helium ions are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair mechanism, but the majority of DNA lesions induced by 220 MeV carbon ions are not repaired by NHEJ.
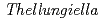 のイオンビーム照射効果の評価
のイオンビーム照射効果の評価太治 輝昭*; 堀口 茜*; 池田 彬郎*; 中島 千尋*; 坂田 洋一*; 吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 72, 2011/01
本研究では、自然界で高い塩耐性を示す植物の耐性メカニズムを遺伝学的に明らかにするため、耐塩性 Zu-0及び
Zu-0及び に近縁の塩生植物
に近縁の塩生植物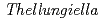 の種子にさまざまな線量のイオンビームを照射し、本葉の展開率と稔性を指標に変異誘導に最適な線量を検討した。その結果、
の種子にさまざまな線量のイオンビームを照射し、本葉の展開率と稔性を指標に変異誘導に最適な線量を検討した。その結果、 Zu-0については50Gy、
Zu-0については50Gy、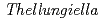 については25Gyが変異誘導に最適な線量であることが明らかとなった。
については25Gyが変異誘導に最適な線量であることが明らかとなった。
世取山 守*; 高野 純一*; 生井 潔*; 吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 71, 2011/01
栃木県が育成したイチゴ品種「とちおとめ」は、作付面積が全国一であり、優れた果実品質を有するが、最重要病害の萎黄病に罹患性であるため、生産者から耐病性品種の育成が強く望まれている。本研究では、イオンビームを用いて「とちおとめ」の萎黄病耐病性個体を作出することを目的とした。現在までに、萎黄病耐病性検定まで終了した供試葉片は1828葉片であった。選抜の結果、対照の多芽体由来「とちおとめ」に比較して発病程度の軽かった1Gy照射区の2個体、2.5Gy照射区の1個体の計3個体を選抜した。
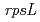 transgenic
transgenic 
吉原 亮平; 長谷 純宏; 佐藤 良平*; 滝本 晃一*; 鳴海 一成
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 86(2), p.125 - 131, 2010/02
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:79.85(Biology)LETの異なる放射線により高等植物内で誘発される突然変異の特徴を解析するために、シロイヌナズナ内における炭素イオンビーム及び 線による変異誘発効果を調査した。変異検出は、
線による変異誘発効果を調査した。変異検出は、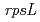 遺伝子導入シロイヌナズナを用いた突然変異検出システムを用い、遺伝子内変異の解析を行うこととした。われわれは、208-MeV炭素イオンビームと
遺伝子導入シロイヌナズナを用いた突然変異検出システムを用い、遺伝子内変異の解析を行うこととした。われわれは、208-MeV炭素イオンビームと 線を
線を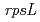 遺伝子導入シロイヌナズナに照射し、変異頻度及び変異スペクトルの解析を行った。その結果、208-MeV炭素イオンビームと
遺伝子導入シロイヌナズナに照射し、変異頻度及び変異スペクトルの解析を行った。その結果、208-MeV炭素イオンビームと 線は、シロイヌナズナ種子内で異なる変異誘発効果を示すことが示唆された。
線は、シロイヌナズナ種子内で異なる変異誘発効果を示すことが示唆された。
Affrida, A. H.*; Shakinah, S.*; Zaiton, A.*; 吉原 亮平; 鳴海 一成; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 70, 2009/12
Chrysanthemum is one of the leading temperate flowers in Malaysia, and contributes 22.62% of the total value of cut flower production. The objectives of this study are to develop an effective method for mutation induction of local chrysanthemum varieties using ion beams and to determine the optimum dose for callus formation using petals. Irradiated petals that were able to produce callus and green in color were considered to have survived the irradiation, whilst those that turned brown were not. The percentage of survived petals of  cv. Reagan Red and cv. Lameet decreased drastically at doses above 20 Gy. The results reported here were from the first irradiation experiments for both varieties. The experiments will be repeated to obtain more accurate dose response curve.
cv. Reagan Red and cv. Lameet decreased drastically at doses above 20 Gy. The results reported here were from the first irradiation experiments for both varieties. The experiments will be repeated to obtain more accurate dose response curve.
 -rays and carbon ion beams in plant
-rays and carbon ion beams in plant吉原 亮平; 長谷 純宏; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 67, 2009/12
 -rays and ion beams have been used for mutagenesis in mutation breeding, however, their mutational effects in plant were little known. Mutation breeding is one of the valuable breeding techniques that can produce various new phenotypes. It is necessary to investigate which types of mutation are induced by
-rays and ion beams have been used for mutagenesis in mutation breeding, however, their mutational effects in plant were little known. Mutation breeding is one of the valuable breeding techniques that can produce various new phenotypes. It is necessary to investigate which types of mutation are induced by  -rays and ion beams for improvement of mutation breeding techniques. In this study, we analyzed mutation spectrum induced by
-rays and ion beams for improvement of mutation breeding techniques. In this study, we analyzed mutation spectrum induced by  -rays and 220 MeV carbon ions to show the mutational effects of these radiations. Both radiation induced higher incidence of G:C to A:T transition and
-rays and 220 MeV carbon ions to show the mutational effects of these radiations. Both radiation induced higher incidence of G:C to A:T transition and  2 bp deletions/insertions. The frequency of -2 and -1 frameshifts were higher in
2 bp deletions/insertions. The frequency of -2 and -1 frameshifts were higher in  -rays irradiated group. From our mutation spectrum analysis, it was shown that
-rays irradiated group. From our mutation spectrum analysis, it was shown that  -rays and carbon ions have different mutational effects. It would be effective for mutation breeding to use both
-rays and carbon ions have different mutational effects. It would be effective for mutation breeding to use both  -rays and ion beams as the situation demands to induce different types of mutation.
-rays and ion beams as the situation demands to induce different types of mutation.
 C
C イオンを照射した腋芽分裂組織及び培養細胞からの植物体再分化
イオンを照射した腋芽分裂組織及び培養細胞からの植物体再分化津呂 正人*; 稲澤 まりえ*; 野澤 樹; 吉原 亮平; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 71, 2009/12
精油成分比が親植物体と大きく異なり香調が変化したラベンダー変異体、及び香質を低下させる成分の生産が著しく低下したラベンダー変異体の作出を目指している。今回は、イオンビーム照射した培養細胞及び腋芽分裂組織からの植物体再分化法を検討した。64Gy及び128Gy照射区では、32Gy照射区に比べて、腋芽からのシュートの形成率が大きく低下したが、全体が枯死するまでには至らなかった。シュートからの発根率は、いずれの線量区でも10%以下となったが、発根した個体はいずれも容易に順化でき、温室に移植後、旺盛な成長を示した。現在、再分化個体を室外で育成中である。今後、植物体の形態調査に加え、生殖成長期に見られる出穂日や精油成分の変異等の形質を調査する予定である。