Development of a land surface model including cloud water deposition on vegetation
植生への霧水捕集過程を考慮した陸面モデルの開発
堅田 元喜; 永井 晴康 
 ; Wrzesinsky, T.*; Klemm, O.*; Eugster, W.*; Burkard, R.*
; Wrzesinsky, T.*; Klemm, O.*; Eugster, W.*; Burkard, R.*
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Wrzesinsky, T.*; Klemm, O.*; Eugster, W.*; Burkard, R.*
陸面と大気の間の熱・水交換を詳細に予測するために、植生への霧水捕集過程を考慮した陸面モデルを開発した。植生への霧水沈着量を計算するための新しいスキームを陸面モデルに考慮した。森林上の熱及び霧水フラックスの計算値と測定値を比較によってモデルの性能を確認した。また、このモデルは広く用いられている霧水沈着モデルに比べて霧水の乱流及び重力フラックスをより高精度に予測した。加えて、観測値と計算値との両方において、森林上の水平風速と沈着速度の間に線形関係を見いだした。葉の種類(針葉樹及び広葉樹)と森林構造(葉面積指数(LAI)及び樹高)が沈着速度へ及ぼす影響を調べるために、数値実験を実施した。LAI及び樹高が同じ場合、葉の大きさが小さい広葉樹は針葉樹よりも大きな霧水を捕集しうる。ある葉面積密度(LAD)における霧水に対する大気及び森林のコンダクタンスの関係は、沈着速度に強く影響を与えた。この結果から、LAD 0.1m
0.1m m
m の樹木が霧水を最も効率的に捕集することが見いだされた。実験から得られた霧水沈着量のLADに対する勾配の簡易予測式は、広域における全霧水沈着量を予測するうえで有用である。
の樹木が霧水を最も効率的に捕集することが見いだされた。実験から得られた霧水沈着量のLADに対する勾配の簡易予測式は、広域における全霧水沈着量を予測するうえで有用である。
A land surface model including cloud water deposition to vegetation was developed to better predict water exchanges between biosphere and atmosphere. High performance of our new model was confirmed and it provided a better prediction of measured cloud water flux than the commonly used model. Simple linear relationships between wind speed and deposition velocity (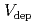 ) were found. Numerical experiments were performed to study the influences of leaf shapes (needle and broad leaves) and canopy structure (Leaf area index (LAI) and canopy height) on
) were found. Numerical experiments were performed to study the influences of leaf shapes (needle and broad leaves) and canopy structure (Leaf area index (LAI) and canopy height) on 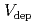 . Broad leaves with small sized leaves can capture larger amounts of cloud water than needle leaves. From the analyses of conductances at given Leaf Area Density (LAD), we found that trees whose LAD
. Broad leaves with small sized leaves can capture larger amounts of cloud water than needle leaves. From the analyses of conductances at given Leaf Area Density (LAD), we found that trees whose LAD  0.1 m
0.1 m m
m are the most efficient structures for cloud water deposition. A simple expression for the slope of
are the most efficient structures for cloud water deposition. A simple expression for the slope of 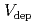 against LAD obtained from the experiments can be useful to predict cloud water deposition.
against LAD obtained from the experiments can be useful to predict cloud water deposition.