PET imaging of norepinephrine transporter-expressing tumors using  Br-
Br-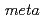 -bromobenzylguanidine
-bromobenzylguanidine
 Br-
Br-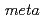 -bromobenzylguanidineを用いたノルエピネフリントランスポーター発現腫瘍のPETイメージング
-bromobenzylguanidineを用いたノルエピネフリントランスポーター発現腫瘍のPETイメージング
渡邉 茂樹; 花岡 宏史*; Liang, J. X.; 飯田 靖彦*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 石岡 典子
Watanabe, Shigeki; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Liang, J. X.; Iida, Yasuhiko*; Endo, Keigo*; Ishioka, Noriko
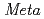 -iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) labeled has been widely used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of norepinephrine transporter (NET)-expressing tumors. This study demonstrated that a positron emitter
-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) labeled has been widely used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of norepinephrine transporter (NET)-expressing tumors. This study demonstrated that a positron emitter  Br labeled
Br labeled 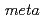 -bromobenzylguanidine (
-bromobenzylguanidine ( Br-MBBG) was prepared and evaluated as a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing tumors.
Br-MBBG) was prepared and evaluated as a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing tumors.  Br-MBBG was stable in vitro, but some time-dependent dehalogenation was observed after administration in normal mice. MBBG showed high uptake in PC-12 tumor cells, and this uptake was significantly decreased by the addition of NET inhibitors. In biodistribution, MBBG showed high tumor accumulation (32.0
Br-MBBG was stable in vitro, but some time-dependent dehalogenation was observed after administration in normal mice. MBBG showed high uptake in PC-12 tumor cells, and this uptake was significantly decreased by the addition of NET inhibitors. In biodistribution, MBBG showed high tumor accumulation (32.0  18.6% ID/g at 3 h p.i.) and the tumor-to-blood ratio reached as high as 54.4
18.6% ID/g at 3 h p.i.) and the tumor-to-blood ratio reached as high as 54.4  31.9. Tumor uptake of MBBG correlated very well with that of
31.9. Tumor uptake of MBBG correlated very well with that of  I-MIBG (r = 0.997), but not with
I-MIBG (r = 0.997), but not with  F-FDG. MBBG-PET showed a very clear image of the transplanted tumor with high sensitivity, and the visualized lesion was different from that by FDG-PET. These results indicated that
F-FDG. MBBG-PET showed a very clear image of the transplanted tumor with high sensitivity, and the visualized lesion was different from that by FDG-PET. These results indicated that  Br-MBBG would be a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing neuroendocrine tumors, and could provide useful information for determining the indications for
Br-MBBG would be a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing neuroendocrine tumors, and could provide useful information for determining the indications for  I-MIBG therapy.
I-MIBG therapy.