Neutron scattering of iron-based superconductors
鉄系超伝導体の中性子散乱
社本 真一 
 ; 脇本 秀一
; 脇本 秀一 
 ; 樹神 克明
; 樹神 克明 

 ; 石角 元志; Christianson, A. D.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; 梶本 亮一
; 石角 元志; Christianson, A. D.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; 梶本 亮一 
 ; 中村 充孝
; 中村 充孝 

 ; 稲村 泰弘; 新井 正敏; 加倉井 和久; 江坂 文孝
; 稲村 泰弘; 新井 正敏; 加倉井 和久; 江坂 文孝 
 ; 伊豫 彰*; 鬼頭 聖*; 永崎 洋*
; 伊豫 彰*; 鬼頭 聖*; 永崎 洋*
Shamoto, Shinichi; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kodama, Katsuaki; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Christianson, A. D.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Arai, Masatoshi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Esaka, Fumitaka; Iyo, Akira*; Kito, Hijiri*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*
LaFeAsO 粉末試料における低エネルギーのスピン励起について、中性子散乱を用いて調べた。超伝導体試料の動的スピン磁化率
粉末試料における低エネルギーのスピン励起について、中性子散乱を用いて調べた。超伝導体試料の動的スピン磁化率 ''(
''( )は、磁気的に秩序化した母相試料の磁化率と同程度であることがわかった。一方、
)は、磁気的に秩序化した母相試料の磁化率と同程度であることがわかった。一方、 ''(
''( )は、x=0.158で消滅する。このとき、超伝導移送温度
)は、x=0.158で消滅する。このとき、超伝導移送温度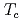 は7Kまで抑圧される。このことは、低エネルギーでのスピン励起が高温
は7Kまで抑圧される。このことは、低エネルギーでのスピン励起が高温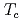 での超伝導現象と密接に関連していることを示唆している。低エネルギーでのスピン励起の消滅は、x=0.15におけるBaFe
での超伝導現象と密接に関連していることを示唆している。低エネルギーでのスピン励起の消滅は、x=0.15におけるBaFe Co
Co As
As の光電子分光測定結果のように、ホールフェルミ面の消滅と一致する可能性が高い。スピン励起とフェルミ面の関係について、他の鉄系超伝導体との比較の観点から議論する。
の光電子分光測定結果のように、ホールフェルミ面の消滅と一致する可能性が高い。スピン励起とフェルミ面の関係について、他の鉄系超伝導体との比較の観点から議論する。
We have studied low-energy spin excitations on polycrystalline LaFeAsO F
F samples by inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamical spin susceptibility
samples by inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamical spin susceptibility  ''(
''( ) of the superconducting samples is found to be comparable to that of the magnetically ordered parent sample. On the other hand,
) of the superconducting samples is found to be comparable to that of the magnetically ordered parent sample. On the other hand,  ''(
''( ) almost vanishes at x=0.158, where the superconducting transition temperature T
) almost vanishes at x=0.158, where the superconducting transition temperature T is suppressed to 7 K. This suggests that the low energy spin excitations are closely connected with high-T
is suppressed to 7 K. This suggests that the low energy spin excitations are closely connected with high-T superconductivity. The disappearance of the spin excitations at low energy would correspond to the disappearance of the hole Fermi surface as the electron concentration increases with doping, as observed in ARPES measurements of BaFe
superconductivity. The disappearance of the spin excitations at low energy would correspond to the disappearance of the hole Fermi surface as the electron concentration increases with doping, as observed in ARPES measurements of BaFe Co
Co As
As at x=0.15. The relationship between the spin excitation and the Fermi surface will be discussed in comparison with other iron-based superconductors.
at x=0.15. The relationship between the spin excitation and the Fermi surface will be discussed in comparison with other iron-based superconductors.