マイクロチャンネル流水試験法を用いたガラス固化体初期溶解速度のpH/温度依存性評価
Evaluation of HLW glass dissolution/alteration kinetics by using micro-channel flow-through test method; Initial glass dissolution rate as a function of pH and temperature
稲垣 八穂広*; 酒谷 圭一*; 山村 由貴*; 三ツ井 誠一郎 
 ; 野下 健司*; 三浦 吉幸*; 兼平 憲男*; 越智 英治*; 椋木 敦*; 千葉 保*
; 野下 健司*; 三浦 吉幸*; 兼平 憲男*; 越智 英治*; 椋木 敦*; 千葉 保*
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Sakatani, Keiichi*; Yamamura, Yuki*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Noshita, Kenji*; Miura, Yoshiyuki*; Kanehira, Norio*; Ochi, Eiji*; Mukunoki, Atsushi*; Chiba, Tamotsu*
これまでの静的溶解試験では、ガラス溶解に伴い反応溶液の液性が変化するため、任意の液性一定条件での測定評価が困難であった。本研究では、我が国の模擬ガラス固化体であるJAEA-P0798ガラス及びJNFL-KMOCガラスについて、新たに考案したマイクロチャンネル流水試験法を用いた任意の液性一定条件での溶解試験を行い、ガラスの本質的特性の一つである初期溶解速度(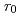 : 反応溶液中シリカ濃度がゼロの条件でのガラス溶解速度)を精密に測定し、その温度依存性,pH依存性を体系的に評価した。その結果、いずれのガラス試料についても
: 反応溶液中シリカ濃度がゼロの条件でのガラス溶解速度)を精密に測定し、その温度依存性,pH依存性を体系的に評価した。その結果、いずれのガラス試料についても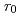 は温度とともに増大し、各温度においてpHに関してV字型の依存性を示すことがわかった。
は温度とともに増大し、各温度においてpHに関してV字型の依存性を示すことがわかった。
Conventional static test methods are not appropriate to evaluate glass dissolution behavior at an arbitrarily-fixed condition due to compositional change of the solution with glass dissolution. In this study, we applied a newly-devised micro-channel flow-through test method to measurement of the initial dissolution rates of Japanese simulated waste glasses, JAEA-P0798 and JNFL-KMOC, at arbitrarily-fixed conditions and we evaluated temperature and pH dependence of glass dissolution. The results showed that the initial dissolution rate increased with temperature and had "V-shaped" pH dependence at each temperature.