照射食品に誘導されるラジカルの減衰挙動
Initial decay process of radicals induced in irradiated food
貝森 良彦; 坂本 侑輝*; 菊地 正博; 亀谷 宏美*; 中村 秀夫*; 下山 雄平; 小林 泰彦; 鵜飼 光子*
Kaimori, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yuki*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kameya, Hiromi*; Nakamura, Hideo*; Shimoyama, Yuhei; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ukai, Mitsuko*
In order to determine radical decay behaviors of  -irradiated food, we analyzed radicals in the food using ESR. We detected the ESR signal of specimens just several minutes after irradiation. The singlet signal intensity at
-irradiated food, we analyzed radicals in the food using ESR. We detected the ESR signal of specimens just several minutes after irradiation. The singlet signal intensity at 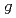 = 2.0, originated from organic free radicals was increased as followed by the increasing radiation dose. Singlet signal intensity that increased by
= 2.0, originated from organic free radicals was increased as followed by the increasing radiation dose. Singlet signal intensity that increased by  -irradiation was decreased with time. The phenomena of decay of the ESR singlet signal showed two phase that are rapid decay and slow decay. It was suggested that those two phase decay is due to at least the two radical species. Also we concluded that after three hours of radiation treatment long life radical as ESR signal intensity was detected in irradiated specimens; black pepper, green coffee bean and ginseng, showed the same decay phenomena. But the signal intensity of irradiated black pepper was three times larger than that of irradiated green coffee bean and irradiated ginseng.
-irradiation was decreased with time. The phenomena of decay of the ESR singlet signal showed two phase that are rapid decay and slow decay. It was suggested that those two phase decay is due to at least the two radical species. Also we concluded that after three hours of radiation treatment long life radical as ESR signal intensity was detected in irradiated specimens; black pepper, green coffee bean and ginseng, showed the same decay phenomena. But the signal intensity of irradiated black pepper was three times larger than that of irradiated green coffee bean and irradiated ginseng.