Investigation and research on depth distribution in soil of radionuclides released by the TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故に伴い放出された放射性物質の土壌中深度方向の分布状況に関する調査研究
佐藤 治夫; 新里 忠史 
 ; 天野 健治
; 天野 健治 
 ; 田中 真悟; 青木 和弘
; 田中 真悟; 青木 和弘 
Sato, Haruo; Niizato, Tadafumi; Amano, Kenji; Tanaka, Shingo; Aoki, Kazuhiro
平成23年3月11日に発生した東北太平洋沖地震によって東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故が発生した。4月初旬までに Csで1.2-1.5
Csで1.2-1.5 10
10 Bq、I-131で1.5-1.6
Bq、I-131で1.5-1.6 10
10 Bq放出されたと推定されており、それらは福島県を中心に土壌表面や森林などに沈着した。本調査は文部科学省が進める放射線量率や放射性物質によって汚染された土壌の分布マップを作成するための調査の1つとして実施したもので、事故から3か月後の深度方向の分布状況についてジオスライサー調査を実施した。調査は、二本松,川俣町,浪江町の11地点で行った。
Bq放出されたと推定されており、それらは福島県を中心に土壌表面や森林などに沈着した。本調査は文部科学省が進める放射線量率や放射性物質によって汚染された土壌の分布マップを作成するための調査の1つとして実施したもので、事故から3か月後の深度方向の分布状況についてジオスライサー調査を実施した。調査は、二本松,川俣町,浪江町の11地点で行った。 Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs, 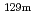 Te,
Te, 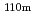 Agが検出され、
Agが検出され、 Csと
Csと Csはすべての調査地点で、
Csはすべての調査地点で、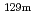 Teと
Teと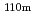 Agは空間線量率が高いエリアで検出された。地表面土壌については多くの地点で沈着量の99%以上は表層10cm以内に存在した。一方、元農地と推定される土壌は地表面土壌よりも深い位置まで検出される傾向であるものの、沈着量の99%以上は表層14cm以内であった。表層付近の濃度分布から求めた見掛けの拡散係数D
Agは空間線量率が高いエリアで検出された。地表面土壌については多くの地点で沈着量の99%以上は表層10cm以内に存在した。一方、元農地と推定される土壌は地表面土壌よりも深い位置まで検出される傾向であるものの、沈着量の99%以上は表層14cm以内であった。表層付近の濃度分布から求めた見掛けの拡散係数D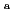 は、すべての核種について元農地と推定される土壌(D
は、すべての核種について元農地と推定される土壌(D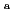 =0.1-1.5
=0.1-1.5 10
10 m
m /s)の方が地表面土壌(D
/s)の方が地表面土壌(D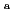 =0.65-4.4
=0.65-4.4 10
10 m
m /s)よりも大きく、多くの拡散係数はD
/s)よりも大きく、多くの拡散係数はD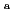 =10
=10 (m
(m /s)付近であった。バッチ法によりCsとIに対する分配係数Kdも取得しており、K
/s)付近であった。バッチ法によりCsとIに対する分配係数Kdも取得しており、K とD
とD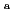 との関係を総合すると、濃度分布の形成は雨が降った際の移流による分散の効果が支配的であったと考えられる。
との関係を総合すると、濃度分布の形成は雨が降った際の移流による分散の効果が支配的であったと考えられる。
The accident of the TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant occurred by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on 11 March, 2011. It is estimated that 1.2-1.5 10
10 Bq for
Bq for  Cs and 1.5-1.6
Cs and 1.5-1.6 10
10 Bq for I-131 were released until the beginning of April and those radionuclides (RN) were deposited on soil surface and forest etc. widely around Fukushima Pref. This work was carried out as one of the investigations for making the distribution maps of radiation dose rate and soil contaminated by RNs which the MEXT promotes. The Geoslicer investigation on the depth distribution of RNs in soil was carried out after 3 months from the accident. The investigation was conducted at 11 locations in Nihonmatsu City, Kawamata Town and Namie Town, and soil samples of depth 50 cm to 1 m were taken. Both of
Bq for I-131 were released until the beginning of April and those radionuclides (RN) were deposited on soil surface and forest etc. widely around Fukushima Pref. This work was carried out as one of the investigations for making the distribution maps of radiation dose rate and soil contaminated by RNs which the MEXT promotes. The Geoslicer investigation on the depth distribution of RNs in soil was carried out after 3 months from the accident. The investigation was conducted at 11 locations in Nihonmatsu City, Kawamata Town and Namie Town, and soil samples of depth 50 cm to 1 m were taken. Both of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were detected in all investigated locations, and
Cs were detected in all investigated locations, and 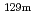 Te and
Te and 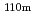 Ag were detected only in areas where radiation dose rates are high. At many locations investigated, radiocaesium more than 99% distributed within a depth of 10 cm in soil in the surface layer. On the other hand, RNs tended to distribute to deeper part in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer, and radiocaesium more than 99% in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland also distributed within a depth of around 14 cm. The apparent diffusion coefficients of RNs derived from penetration profiles near the surface layer showed a tendency to be higher in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer. The distribution coefficients by a batch method were also obtained for Cs and I, and the relationship between D
Ag were detected only in areas where radiation dose rates are high. At many locations investigated, radiocaesium more than 99% distributed within a depth of 10 cm in soil in the surface layer. On the other hand, RNs tended to distribute to deeper part in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer, and radiocaesium more than 99% in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland also distributed within a depth of around 14 cm. The apparent diffusion coefficients of RNs derived from penetration profiles near the surface layer showed a tendency to be higher in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer. The distribution coefficients by a batch method were also obtained for Cs and I, and the relationship between D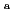 and K
and K was discussed.
was discussed.