Structural and functional characterization of the  copper nitrite reductase; Involvement of the unique N-terminal region in the interprotein electron transfer with its redox partner
copper nitrite reductase; Involvement of the unique N-terminal region in the interprotein electron transfer with its redox partner
海洋性好熱菌由来銅型亜硝酸還元酵素の構造と機能; 特異なN末端領域のタンパク質間電子伝達への関与
福田 庸太*; 小手石 泰康*; 米田 涼平*; 玉田 太郎; 高見 英人*; 井上 豪*; 野尻 正樹
Fukuda, Yota*; Koteishi, Hiroyasu*; Yoneda, Ryohei*; Tamada, Taro; Takami, Hideto*; Inoue, Tsuyoshi*; Nojiri, Masaki
海洋性好熱菌 HTA426由来銅型亜硝酸還元酵素(CuNIR)の全長体およびN末端領域(68アミノ酸)欠損変異体の結晶構造を各々1.3
HTA426由来銅型亜硝酸還元酵素(CuNIR)の全長体およびN末端領域(68アミノ酸)欠損変異体の結晶構造を各々1.3 、および1.8
、および1.8 分解能で決定した。全体構造は既知のCuNIRと同様に2つのグリークキー
分解能で決定した。全体構造は既知のCuNIRと同様に2つのグリークキー バレルドメインから構成されていたが、N末端側に
バレルドメインから構成されていたが、N末端側に ストランドと
ストランドと へリックスからなる本酵素に特異的な領域が存在していた。この領域はタイプ1銅結合部位の方に伸びており、他の脱窒系におけるCuNIRと酸化還元パートナーである電子供与体(チトクロム
へリックスからなる本酵素に特異的な領域が存在していた。この領域はタイプ1銅結合部位の方に伸びており、他の脱窒系におけるCuNIRと酸化還元パートナーである電子供与体(チトクロム )との電子伝達複合体構造との重ね合わせから、この領域が
)との電子伝達複合体構造との重ね合わせから、この領域が 脱窒系の電子伝達反応における電子供与体との一時的な結合に寄与していることが推察された。さらに、N末端領域欠損変異体と
脱窒系の電子伝達反応における電子供与体との一時的な結合に寄与していることが推察された。さらに、N末端領域欠損変異体と を由来チトクロム
を由来チトクロム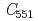 を用いた電子伝達反応の速度論的解析結果を組み合わせた結果、この領域が電子供与体の認識に直接関与していることが示された。
を用いた電子伝達反応の速度論的解析結果を組み合わせた結果、この領域が電子供与体の認識に直接関与していることが示された。
The crystal structures of copper-containing nitrite reductase (CuNiR) from the thermophilic Gram-positive bacterium  HTA426 and the amino (N)-terminal 68 residue-deleted mutant were determined at resolutions of 1.3
HTA426 and the amino (N)-terminal 68 residue-deleted mutant were determined at resolutions of 1.3 and 1.8
and 1.8 , respectively. Both structures show a striking resemblance with the overall structure of the well-known CuNiRs composed of two Greek key
, respectively. Both structures show a striking resemblance with the overall structure of the well-known CuNiRs composed of two Greek key  -barrel domains; however, a remarkable structural difference was found in the N-terminal region. The unique region has one
-barrel domains; however, a remarkable structural difference was found in the N-terminal region. The unique region has one  -strand and one
-strand and one  -helix extended to the northern surface of the type-1 copper site. The superposition of the
-helix extended to the northern surface of the type-1 copper site. The superposition of the  CuNiR model on the electron-transfer complex structure of CuNiR with the redox partner cytochrome
CuNiR model on the electron-transfer complex structure of CuNiR with the redox partner cytochrome 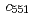 in other denitrifier system led us to infer that this region contributes to the transient binding with the partner protein during the interprotein electron transfer reaction in the
in other denitrifier system led us to infer that this region contributes to the transient binding with the partner protein during the interprotein electron transfer reaction in the 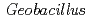 system. Furthermore, electron-transfer kinetics experiments using N-terminal residue-deleted mutant and the redox partner,
system. Furthermore, electron-transfer kinetics experiments using N-terminal residue-deleted mutant and the redox partner, 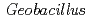 cytochrome
cytochrome 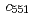 , were carried out. These structural and kinetics studies demonstrate that that region is directly involved in the specific partner recognition.
, were carried out. These structural and kinetics studies demonstrate that that region is directly involved in the specific partner recognition.