低温適応性セルラーゼの結晶構造解析
Crystal structure of a cold-adapted cellulase
玉田 太郎; 有森 貴夫*; 福原 宏章*; 伊藤 彰紘*; 上田 光宏*
Tamada, Taro; Arimori, Takao*; Fukuhara, Hiroaki*; Ito, Akihiro*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*
セルロースを含む木質バイオマスからのバイオエタノール生産における糖化プロセスにおいて、低温適応性セルラーゼを用いることができれば、加熱するためのエネルギーを節約できるだけではなく、並行複発酵による高濃度アルコール生産が可能となる。GHファミリー9に属するシマミミズ由来1,4- -エンドグルカナーゼ(EF-EG2)は313Kにおいて最大活性を示すが、283Kにおいても比較的高い活性を保持する。酵母を用いた組換え型EF-EG2の発現系を構築し、引き続き試料精製および結晶化を実施したところ、太さ0.02mm程度の針状結晶を得ることに成功した。この結晶を用いて1.50
-エンドグルカナーゼ(EF-EG2)は313Kにおいて最大活性を示すが、283Kにおいても比較的高い活性を保持する。酵母を用いた組換え型EF-EG2の発現系を構築し、引き続き試料精製および結晶化を実施したところ、太さ0.02mm程度の針状結晶を得ることに成功した。この結晶を用いて1.50 分解能の回折データを収集し、結晶学的
分解能の回折データを収集し、結晶学的 値が14.7%(free-
値が14.7%(free- 値が16.8%)まで精密化を完了した。さらに、触媒残基と想定されるGlu431をGlnに置換した変異体(E431Q)と基質(セロトリオース)複合体結晶を作製し、1.55
値が16.8%)まで精密化を完了した。さらに、触媒残基と想定されるGlu431をGlnに置換した変異体(E431Q)と基質(セロトリオース)複合体結晶を作製し、1.55 分解能の回折データを収集した。現在、精密化中であるが、サブサイト-2
分解能の回折データを収集した。現在、精密化中であるが、サブサイト-2 -4にセロトリオース由来の明瞭な電子密度を観測することができた。また、分子表面は負電荷に富んでいたが、この特徴は構造既知の低温適応性酵素においても広く観察されており、EF-EG2の低温適応性との関連が示唆された。
-4にセロトリオース由来の明瞭な電子密度を観測することができた。また、分子表面は負電荷に富んでいたが、この特徴は構造既知の低温適応性酵素においても広く観察されており、EF-EG2の低温適応性との関連が示唆された。
The saccharification process is essential for bioethanol production from woody biomass including celluloses. Cold-adapted cellulase, which has sufficient activity at low temperature ( 293 K), is capable of reducing heating costs during the saccharification process and is suitable for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Endo-1,4-
293 K), is capable of reducing heating costs during the saccharification process and is suitable for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Endo-1,4- -glucanase from the earthworm Eisenia fetida (EF-EG2) belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 9 has been shown to have the highest activity at 313 K, and also retained a comparatively high activity at 283 K. The recombinant EF-EG2, expressed in
-glucanase from the earthworm Eisenia fetida (EF-EG2) belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 9 has been shown to have the highest activity at 313 K, and also retained a comparatively high activity at 283 K. The recombinant EF-EG2, expressed in 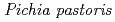 , was purified and then grew needle-shaped crystals with dimensions of 0.02
, was purified and then grew needle-shaped crystals with dimensions of 0.02  0.02
0.02  1 mm. The final model of EF-EG2, including 435 residues, two ions, seven crystallization reagents and 696 waters, was refined to a crystallographic
1 mm. The final model of EF-EG2, including 435 residues, two ions, seven crystallization reagents and 696 waters, was refined to a crystallographic  -factor of 14.7% (free
-factor of 14.7% (free  -factor of 16.8%) to 1.5
-factor of 16.8%) to 1.5  resolution. The overall structure of EF-EG2 has an(
resolution. The overall structure of EF-EG2 has an( /
/ )
) barrel fold which contains a putative active-site cleft and a negatively charged surface. Furthermore, in the structure of the E431Q mutant of EF-EG2 complexed with cellotriose (CTR), electron densities corresponding to CTR are observed well at -4 to -2 subsites. This structural information helps us understand the catalytic and cold adaptation mechanisms of EF-EG2.
barrel fold which contains a putative active-site cleft and a negatively charged surface. Furthermore, in the structure of the E431Q mutant of EF-EG2 complexed with cellotriose (CTR), electron densities corresponding to CTR are observed well at -4 to -2 subsites. This structural information helps us understand the catalytic and cold adaptation mechanisms of EF-EG2.