Accumulation of iodine into phytoplankton in the coastal region in the North Pacific
北太平洋沿岸域における植物プランクトン中へのヨウ素蓄積に関する研究
佐藤 雄飛; 乙坂 重嘉 
 ; 鈴木 崇史
; 鈴木 崇史 

Sato, Yuhi; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi
植物プランクトン有機物へのヨウ素蓄積は海洋におけるヨウ素動態を制御する重要な過程であるが、研究例の少なさに起因して、その過程はよく理解されていない。植物プランクトンのヨウ素蓄積効率を評価するために、培養株(珪藻,シアノバクテリア,クリプト藻,ハプト藻)および沿岸海水より採取した自然群集を用いた培養実験を行った。自然群集は北太平洋の日本沿岸域から採取した。ヨウ素の蓄積効率は植物プランクトンの種類によって幅があったが、特に珪藻において炭素量あたりの顕著なヨウ素蓄積が確認された。これは、珪藻が植物プランクトン群集へのヨウ素蓄積を制御している重要種であることを示唆する。珪藻によって生産される懸濁態有機ヨウ素(POI)のヨウ素/炭素比を求めると、約4 10
10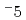 (mol/mol、平均値)であった。この比と珪藻の生産量を掛け合わせることで、現場環境で植物プランクトンにより生産されるPOI量を概算することが可能と考えられる。
(mol/mol、平均値)であった。この比と珪藻の生産量を掛け合わせることで、現場環境で植物プランクトンにより生産されるPOI量を概算することが可能と考えられる。
Accumulation of iodine into phytoplanktonic organic matter is important process regulating the iodine dynamics in the ocean but it has been poorly understood due to a small number of study examples. To evaluate an accumulation efficiency of iodine by phytoplankton, incubation experiments using cultivated cultures and natural populations obtained from coastal seawater were conducted. The accumulation efficiency of iodine was various in phytoplanktonic species; especially, diatom accumulated iodine significantly per organic carbon. This result suggests that diatom is the key specie regulating the accumulation into phytoplanktonic organic matter in the environment. An iodine/carbon ratio of particulate organic iodine (POI) produced by diatom was estimated, resulting in ca. 4 10
10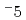 . Multiplying this ratio with net productivity of diatom, an amount of POI produced by phytoplankton in the environment may be roughly estimated.
. Multiplying this ratio with net productivity of diatom, an amount of POI produced by phytoplankton in the environment may be roughly estimated.