Genetic changes in progeny of bystander human fibroblasts after microbeam irradiation with X-rays, protons or carbon ions; The Relevance to cancer risk
マイクロビーム照射でバイスタンダー効果を誘導した細胞の子孫における遺伝的変化の解析
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Plante, I.*; Liu, C.*; 小西 輝昭*; 宇佐美 徳子*; 舟山 知夫; Azzam, E.*; 村上 健*; 鈴木 雅雄*
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Plante, I.*; Liu, C.*; Konishi, Teruaki*; Usami, Noriko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Azzam, E.*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Suzuki, Masao*
放射線がん治療の実施にあたり、放射線誘発バイスタンダー効果が治療域周辺の正常細胞に健康影響リスクを及ぼすかどうかは重要な問題である。そこで、本研究では、バイスタンダー効果が誘導された細胞の子孫細胞における有害影響の伝播に、照射した放射線の線質と、ギャップジャンクションを介した細胞間情報伝達機構が果たす役割について解析を行った。実験では、コンフルエントに培養したヒト正常線維芽細胞試料に対し、LETの異なるマイクロビームで、その全体の0.036 0.4%の細胞のみに照射を行い、バイスタンダー効果を誘導した。この細胞を照射後20世代にわたって培養し回収した後に、微小核形成、
0.4%の細胞のみに照射を行い、バイスタンダー効果を誘導した。この細胞を照射後20世代にわたって培養し回収した後に、微小核形成、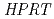 遺伝子への変異誘発、及びタンパク質酸化を指標に解析を行った。その結果、バイスタンダー細胞の子孫細胞における有害影響の伝播は、照射した放射線のLETによって違いがあることが明らかになった。
遺伝子への変異誘発、及びタンパク質酸化を指標に解析を行った。その結果、バイスタンダー細胞の子孫細胞における有害影響の伝播は、照射した放射線のLETによって違いがあることが明らかになった。
Radiation-induced bystander effects have important implications in radiotherapy. Their persistence in normal cells may contribute to risk of health hazards, including cancer. This study investigates the role of radiation quality and gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) in the propagation of harmful effects in progeny of bystander cells. Confluent human skin fibroblasts were exposed to microbeam radiations with different linear energy transfer (LET) by which 0.036 0.4% of the cells were directly targeted by radiation. Following 20 population doublings, the cells were harvested and assayed for micronucleus formation, gene mutation and protein oxidation. The results showed that expression of stressful effects in the progeny of bystander cells is dependent on LET.
0.4% of the cells were directly targeted by radiation. Following 20 population doublings, the cells were harvested and assayed for micronucleus formation, gene mutation and protein oxidation. The results showed that expression of stressful effects in the progeny of bystander cells is dependent on LET.