Development of a method of region-specific microbeam irradiation to  and analyses of effects on muscular movements
and analyses of effects on muscular movements
線虫に対するマイクロビーム局部照射法の構築と筋運動への影響の解析
鈴木 芳代; 服部 佑哉; 坂下 哲哉; 舟山 知夫; 横田 裕一郎; 小林 泰彦
Suzuki, Michiyo; Hattori, Yuya; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
We have investigated the radiation effects on muscular movements in 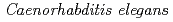 . We have so far found that whole-body irradiation significantly reduce locomotion (snake-like crawling motion) and also increase the proportion of individuals who arrest pharyngeal pumping-motion (chewing and swallowing). As the next step of the whole-body irradiation, we aimed to investigate the effects of region-specific microbeam irradiation on muscular movements immediately after irradiation, and developed a novel method for targeting a specific region of
. We have so far found that whole-body irradiation significantly reduce locomotion (snake-like crawling motion) and also increase the proportion of individuals who arrest pharyngeal pumping-motion (chewing and swallowing). As the next step of the whole-body irradiation, we aimed to investigate the effects of region-specific microbeam irradiation on muscular movements immediately after irradiation, and developed a novel method for targeting a specific region of  without anesthesia. In this method, an animal was enclosed in a ditch of a polydimethylsiloxane device with buffer solution in order to inhibit free motion during irradiation. The "head" region including the pharynx, "middle" region around the vulva and intestine, and "tail" region were targeted independently; these regions were irradiated with 12,000 carbon ions. Main findings are as follows: (1) effects of the region-specific microbeam irradiation differ depending on types of muscular movements, and (2) effects of whole-body irradiation tend to be more effective than those of the region-specific microbeam irradiation at the same dose. Further studies involving the effects of microbeam irradiation on
without anesthesia. In this method, an animal was enclosed in a ditch of a polydimethylsiloxane device with buffer solution in order to inhibit free motion during irradiation. The "head" region including the pharynx, "middle" region around the vulva and intestine, and "tail" region were targeted independently; these regions were irradiated with 12,000 carbon ions. Main findings are as follows: (1) effects of the region-specific microbeam irradiation differ depending on types of muscular movements, and (2) effects of whole-body irradiation tend to be more effective than those of the region-specific microbeam irradiation at the same dose. Further studies involving the effects of microbeam irradiation on 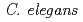 are in progress.
are in progress.