Systematic study of azimuthal anisotropy in Cu + Cu and Au + Au collisions at  = 62.4 and 200 GeV
= 62.4 and 200 GeV
 =62.4および200GeVでの銅-銅衝突および金-金衝突における方位角異方性のシステマティックな研究
=62.4および200GeVでの銅-銅衝突および金-金衝突における方位角異方性のシステマティックな研究
Adare, A.*; 今井 憲一; 佐藤 進 
 ; 谷田 聖
; 谷田 聖 

 ; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他420名*
; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他420名*
Adare, A.*; Imai, Kenichi; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; PHENIX Collaboration*; 420 of others*
We have studied the dependence of azimuthal anisotropy 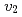 for inclusive and identified charged hadrons in Au + Au and Cu + Cu collisions on collision energy, species, and centrality. The values of
for inclusive and identified charged hadrons in Au + Au and Cu + Cu collisions on collision energy, species, and centrality. The values of 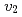 as a function of transverse momentum
as a function of transverse momentum  and centrality in Au+Au collisions at
and centrality in Au+Au collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV are the same within uncertainties. However, in Cu + Cu collisions we observe a decrease in
= 200 and 62.4 GeV are the same within uncertainties. However, in Cu + Cu collisions we observe a decrease in 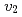 values as the collision energy is reduced from 200 to 62.4 GeV. The decrease is larger in the more peripheral collisions. By examining both Au + Au and Cu + Cu collisions we find that
values as the collision energy is reduced from 200 to 62.4 GeV. The decrease is larger in the more peripheral collisions. By examining both Au + Au and Cu + Cu collisions we find that 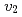 depends both on eccentricity and the number of participants,
depends both on eccentricity and the number of participants, 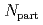 . We observe that
. We observe that 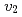 divided by eccentricity (
divided by eccentricity ( ) monotonically increases with
) monotonically increases with 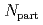 and scales as
and scales as 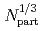 . The Cu + Cu data at 62.4 GeV falls below the other scaled
. The Cu + Cu data at 62.4 GeV falls below the other scaled 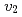 data. For identified hadrons,
data. For identified hadrons, 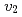 divided by the number of constituent quarks
divided by the number of constituent quarks 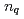 is independent of hadron species as a function of transverse kinetic energy
is independent of hadron species as a function of transverse kinetic energy 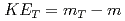 between
between 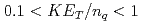 GeV. Combining all of the above scaling and normalizations, we observe a near-universal scaling, with the exception of the Cu + Cu data at 62.4 GeV, of
GeV. Combining all of the above scaling and normalizations, we observe a near-universal scaling, with the exception of the Cu + Cu data at 62.4 GeV, of 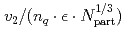 vs
vs 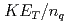 for all measured particles.
for all measured particles.