Pore distribution of compacted Ca-montmorillonite using NMR relaxometry and cryoporometry; Comparison with Na-montmorillonite
NMR緩和時間測定法及び凍結間隙測定法による圧縮Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布評価; Na型モンモリロナイトとの比較
大窪 貴洋*; 山崎 秋雄*; 深津 勇太 
 ; 舘 幸男
; 舘 幸男 

Okubo, Takahiro*; Yamazaki, Akio*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Tachi, Yukio
Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布が、乾燥密度(0.8-1.6g/cm ),間隙水塩濃度(脱イオン水、0.1及び1M CaCl
),間隙水塩濃度(脱イオン水、0.1及び1M CaCl ),温度(233-303K)の条件下で、
),温度(233-303K)の条件下で、 H NMR測定によって調査された。圧縮Ca型モンモリロナイト中の2層及び3層水和を含む層間間隙と層間外間隙の体積割合が、緩和時間
H NMR測定によって調査された。圧縮Ca型モンモリロナイト中の2層及び3層水和を含む層間間隙と層間外間隙の体積割合が、緩和時間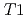 及び
及び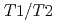 分布の分析に基づくNMR緩和時間測定法によって定量評価され、さらに、NMR凍結間隙測定法及びX線回折法による結果と比較された。これらの分析によって、Na型モンモリロナイトと比較可能な、Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布の状態を把握することができた。圧縮Ca型及びNa型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布に影響を及ぼす主要な因子は圧縮密度であり、間隙水塩濃度の影響は相対的に小さい結果となった。CaとNaの層間陽イオンの影響は高密度条件では小さいが、低密度ではその影響は顕著であった。
分布の分析に基づくNMR緩和時間測定法によって定量評価され、さらに、NMR凍結間隙測定法及びX線回折法による結果と比較された。これらの分析によって、Na型モンモリロナイトと比較可能な、Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布の状態を把握することができた。圧縮Ca型及びNa型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布に影響を及ぼす主要な因子は圧縮密度であり、間隙水塩濃度の影響は相対的に小さい結果となった。CaとNaの層間陽イオンの影響は高密度条件では小さいが、低密度ではその影響は顕著であった。
Pore distributions in water-saturated Ca-montmorillonite were investigated using  H NMR measurements under various dry densities (0.8 - 1.6 g/cm
H NMR measurements under various dry densities (0.8 - 1.6 g/cm ) and porewater salinity conditions (deionized water, 0.1 and 1 M CaCl
) and porewater salinity conditions (deionized water, 0.1 and 1 M CaCl ), at the temperature range of 233 - 303 K. The volume fractions of the interlayer pore including two and three hydrated layers and the non-interlayer pore in compacted Ca-montmorillonite were quantified by NMR relaxometry including
), at the temperature range of 233 - 303 K. The volume fractions of the interlayer pore including two and three hydrated layers and the non-interlayer pore in compacted Ca-montmorillonite were quantified by NMR relaxometry including 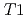 and
and 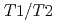 distribution analysis, and were compared with NMR cryoporometry and X-ray diffractometry. These analysis provided consistent pictures on the pore distributions in compacted Ca-montmorillonite, in contrast to Na-montmorillonite. The main factor affecting the pore distribution in compacted Ca- and Na-montmorillonite is the density, whereas the effect of porewater salinity is relatively smaller. The effect of interlayer cations is also relatively smaller at higher density, although the differences in the pore structures are significant at low density.
distribution analysis, and were compared with NMR cryoporometry and X-ray diffractometry. These analysis provided consistent pictures on the pore distributions in compacted Ca-montmorillonite, in contrast to Na-montmorillonite. The main factor affecting the pore distribution in compacted Ca- and Na-montmorillonite is the density, whereas the effect of porewater salinity is relatively smaller. The effect of interlayer cations is also relatively smaller at higher density, although the differences in the pore structures are significant at low density.