Solving the puzzles of the decay of the heaviest known proton-emitting nucleus  Bi
Bi
陽子放出する最も重い原子核 Biの崩壊パズルの解決
Biの崩壊パズルの解決
Doherty, D. T.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seweryniak, D.*; Woods, P. J.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Auranen, K.*; Ayangeakaa, A. D.*; Back, B. B.*; Bottoni, S.*; Canete, L.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Harker, J.*; Haylett, T.*; Huang, T.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Jenkins, D. G.*; Kondev, F. G.*; Lauritsen, T.*; Lederer-Woods, C.*; Li, J.*; M ller-Gatermann, C.*; Potterveld, D.*; Reviol, W.*; Savard, G.*; Stolze, S.*; Zhu, S.*
ller-Gatermann, C.*; Potterveld, D.*; Reviol, W.*; Savard, G.*; Stolze, S.*; Zhu, S.*
Doherty, D. T.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seweryniak, D.*; Woods, P. J.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Auranen, K.*; Ayangeakaa, A. D.*; Back, B. B.*; Bottoni, S.*; Canete, L.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Harker, J.*; Haylett, T.*; Huang, T.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Jenkins, D. G.*; Kondev, F. G.*; Lauritsen, T.*; Lederer-Woods, C.*; Li, J.*; M ller-Gatermann, C.*; Potterveld, D.*; Reviol, W.*; Savard, G.*; Stolze, S.*; Zhu, S.*
ller-Gatermann, C.*; Potterveld, D.*; Reviol, W.*; Savard, G.*; Stolze, S.*; Zhu, S.*
 Bi is the heaviest known proton emitting isotope. Its decay had been observed, but the assumed ground-state lifetime (
Bi is the heaviest known proton emitting isotope. Its decay had been observed, but the assumed ground-state lifetime (
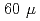 s) was incorrect, leading to unexplained hindrance. With two new experiments at Argonne National Laboratory, two states were clearly identified. One is the proton-emitting ground-state (spin 1/2
s) was incorrect, leading to unexplained hindrance. With two new experiments at Argonne National Laboratory, two states were clearly identified. One is the proton-emitting ground-state (spin 1/2 , half-life: 2.8
, half-life: 2.8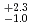
 s), the second is a 58(2)
s), the second is a 58(2)  s
s  -decaying isomer. The new data show the inversion of the ground and isomeric states compared to neighboring Bi isotopes. This is the only known example of a ground-state proton decay to a daughter nucleus (
-decaying isomer. The new data show the inversion of the ground and isomeric states compared to neighboring Bi isotopes. This is the only known example of a ground-state proton decay to a daughter nucleus (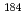 Pb) with a major shell closure.
Pb) with a major shell closure.