 atomic X-ray spectroscopy using a counter-emulsion hybrid method
atomic X-ray spectroscopy using a counter-emulsion hybrid method
Counter-emulsion hybrid法を用いた 原子X線分光
原子X線分光
藤田 真奈美; 長谷川 勝一 

 ; 細見 健二
; 細見 健二 
 ; 市川 真也; 市川 裕大
; 市川 真也; 市川 裕大 

 ; Kim, S.; 七村 拓野; 佐甲 博之
; Kim, S.; 七村 拓野; 佐甲 博之 

 ; 田村 裕和; 山本 剛史
; 田村 裕和; 山本 剛史 
 ; 他32名*
; 他32名*
Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Kim, S.; Nanamura, Takuya; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; Yamamoto, Takeshi; 32 of others*
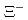 atomic X-ray spectroscopy is one of the most useful methods for investigation of the
atomic X-ray spectroscopy is one of the most useful methods for investigation of the  -nucleus strong interaction. Since the X-ray energy is shifted and/or broadened due to the
-nucleus strong interaction. Since the X-ray energy is shifted and/or broadened due to the  -nucleus strong interaction compared to those calculated from electromagnetic interaction alone, the measurement of the energy shift,
-nucleus strong interaction compared to those calculated from electromagnetic interaction alone, the measurement of the energy shift,  E, and the width,
E, and the width,  , give us information on the
, give us information on the  -nucleus potential. A serious problem in the measurement is the significant background derived from in-flight
-nucleus potential. A serious problem in the measurement is the significant background derived from in-flight 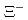 decay. A novel method of identifying stopped
decay. A novel method of identifying stopped 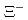 events using the nuclear emulsion was developed to realize the first
events using the nuclear emulsion was developed to realize the first 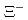 atomic X-ray spectroscopy experiment as the J-PARC E07 experiment, which also aimed at searching for
atomic X-ray spectroscopy experiment as the J-PARC E07 experiment, which also aimed at searching for 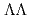 and
and 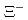 hypernuclei in the emulsion. The X-rays emitted from
hypernuclei in the emulsion. The X-rays emitted from 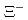 Br and
Br and 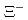 Ag atoms were measured using germanium detectors. No clear peaks were observed in the obtained spectra. However, we succeeded in reducing the background to 1/170 by this method employing coincidence measurements using nuclear emulsion and X-ray detectors.
Ag atoms were measured using germanium detectors. No clear peaks were observed in the obtained spectra. However, we succeeded in reducing the background to 1/170 by this method employing coincidence measurements using nuclear emulsion and X-ray detectors.