Elastic and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high pressure in the frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO
弾性および非弾性中性子散乱実験によるフラストレート反強磁性体CuFeO の磁気相互作用に対する高圧効果の研究
の磁気相互作用に対する高圧効果の研究
寺田 典樹*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; 浅井 晋一郎*; 益田 隆嗣*; 齋藤 開*; 中島 多朗*; 長壁 豊隆 

Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
フラストレート反強磁性体CuFeO は、圧力により、コメンシュレートなコリニアー相(CM1)からいくつかのインコメンシュレートでノンコリニアーな相への複雑な磁気相転移を示す。圧力が磁気相互作用に及ぼす影響を調べるために、高圧下で中性子回折および非弾性中性子散乱実験を行った。圧力が増すと、CM1基底状態は臨界圧力(
は、圧力により、コメンシュレートなコリニアー相(CM1)からいくつかのインコメンシュレートでノンコリニアーな相への複雑な磁気相転移を示す。圧力が磁気相互作用に及ぼす影響を調べるために、高圧下で中性子回折および非弾性中性子散乱実験を行った。圧力が増すと、CM1基底状態は臨界圧力(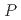
 3GPa)以下でも磁場の印加に対して不安定になる。これは、2.1GPaで臨界磁場
3GPa)以下でも磁場の印加に対して不安定になる。これは、2.1GPaで臨界磁場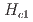 が7.5Tから4.5Tに大幅に減少したことで確かめられた。さらに、スピン波分散関係のエネルギーギャップは、
が7.5Tから4.5Tに大幅に減少したことで確かめられた。さらに、スピン波分散関係のエネルギーギャップは、 =2.1GPaの圧力印加によって1.0meVから0.88meVに減少する。実験結果をスピン波計算と比較すると、スピン波励起の変化は、一軸異方性項または最近接交換相互作用の分離度のいずれかの減少によって説明できることがわかった。
=2.1GPaの圧力印加によって1.0meVから0.88meVに減少する。実験結果をスピン波計算と比較すると、スピン波励起の変化は、一軸異方性項または最近接交換相互作用の分離度のいずれかの減少によって説明できることがわかった。
The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (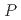
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 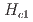 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 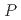 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.