Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukushima, Yoshiaki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Tamura, Kenji*; Shibata, Kaoru
Applied Clay Science, 155, p.15 - 19, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:20.48(Chemistry, Physical)Dynamics of a fluoromica (ME100) cation exchanged for dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium ion (DODA )/ polypropylene composite was analyzed by quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS), besides XRD and DSC. The QENS spectra for the DODA-ME100 at low Q=2.75 nm
)/ polypropylene composite was analyzed by quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS), besides XRD and DSC. The QENS spectra for the DODA-ME100 at low Q=2.75 nm were not changed even at temperature higher than 445 K, the melting point of DODA
were not changed even at temperature higher than 445 K, the melting point of DODA . The results suggested the long range (
. The results suggested the long range ( 2 nm) molecular motions in interlayer space are restricted due to the rigid silicate layers and the strong electrostatic interaction between DODA
2 nm) molecular motions in interlayer space are restricted due to the rigid silicate layers and the strong electrostatic interaction between DODA and the ME100. Elastic intensity scan results suggested that a little amount of motion of the polymer chains in the composite was also restricted in the molten state at 445 K. The QENS is expected to be one of the useful tools for studying the composite materials.
and the ME100. Elastic intensity scan results suggested that a little amount of motion of the polymer chains in the composite was also restricted in the molten state at 445 K. The QENS is expected to be one of the useful tools for studying the composite materials.
Shibata, Akira; Kato, Yoshiaki; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Maekawa, Katsuhiro*
Nuclear Technology, 196(1), p.89 - 99, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Cladding material Zircaloy-4 is gradually replaced by M5 (Zr-Nb alloy) and other new Nb added Zirconium alloys which are expected to have long operating life. Corrosion tests on Zircaloy-4 and M5 were performed in various hydrogen concentrations in water to research corrosion properties of those alloys. Specimens were exposed under PWR conditions. Increase of oxide layer was analysed by weight gain and observation. Electro chemical impedance spectroscopy was performed to compare corrosion properties. And effect of dissolved hydrogen concentration on increase of oxide layer of M5 is smaller than that of Zircaloy-4. M5 is less affected by local uniformity of dissolved hydrogen concentration and is more suitable as PWR fuel cladding. Results of Electro chemical spectroscopy shows that structural significant difference existed in oxidizing reaction of Zircaloy-4 and M5.
 pellets for Mo-99 production, 3
pellets for Mo-99 production, 3Ishida, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Nishikata, Kaori; Yonekawa, Minoru; Kato, Yoshiaki; Shibata, Akira; Kimura, Akihiro; Matsui, Yoshinori; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; et al.
KURRI Progress Report 2015, P. 64, 2016/08
no abstracts in English
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc solution, 1
Tc solution, 1Suzuki, Yumi*; Nakano, Hiroko; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Ishida, Takuya; Shibata, Akira; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kawamata, Kazuo; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Technology 2015-031, 58 Pages, 2015/11
Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most commonly used radioisotopes in the field of nuclear medicine. In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research and development (R&D) have been carried out for production of molybdenum-99 (
Tc) is one of the most commonly used radioisotopes in the field of nuclear medicine. In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research and development (R&D) have been carried out for production of molybdenum-99 ( Mo) by (n,
Mo) by (n,  ) method, a parent nuclide of
) method, a parent nuclide of  Tc, with the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). On the other hand, the new project as "Domestic Production of Medical Radioisotope (Technetium preparation) in Japan" was adopted in the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone on October, 2013 and the demonstration tests will be planned for the domestic production of
Tc, with the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). On the other hand, the new project as "Domestic Production of Medical Radioisotope (Technetium preparation) in Japan" was adopted in the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone on October, 2013 and the demonstration tests will be planned for the domestic production of  Mo/
Mo/ Tc with the JMTR. Thus, new facilities and analysis devices were equipped in the JMTR Hot Laboratory in 2014 as the part of this project. As the part of the analytical device equipment, the
Tc with the JMTR. Thus, new facilities and analysis devices were equipped in the JMTR Hot Laboratory in 2014 as the part of this project. As the part of the analytical device equipment, the  -TLC analyzer and the radiation detector connected with the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) were installed for quality inspection of the
-TLC analyzer and the radiation detector connected with the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) were installed for quality inspection of the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc solution and the extracted
Tc solution and the extracted  Tc solution in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. The performance tests of these devices such as detection sensitivity, resolution, linearity and selectivity of energy range were carried out with
Tc solution in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. The performance tests of these devices such as detection sensitivity, resolution, linearity and selectivity of energy range were carried out with  Cs and
Cs and  Eu as alternative radionuclides of
Eu as alternative radionuclides of  Mo and
Mo and  Tc, respectively. In the results, bright prospects were obtained concerning the quality inspection of the
Tc, respectively. In the results, bright prospects were obtained concerning the quality inspection of the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc and
Tc and  Tc solutions using these devices. This report describes the results of those performance tests.
Tc solutions using these devices. This report describes the results of those performance tests.
Shibata, Akira; Kato, Yoshiaki; Oishi, Makoto; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Ito, Masayasu; Yonekawa, Minoru; Kawamata, Kazuo
KAERI/GP-418/2015, p.151 - 165, 2015/05
The JMTR stopped its operation in 2006 for refurbishment. The reactor facilities have been refurbished from 2007. After refurbishment, JMTR Hot laboratory is expected to perform various post irradiation examinations. In this report, installations of experimental apparatuses and recent experimental method are introduced. (1) A nano-indenter with radius spherical indenter. Inverse analysis using FEM could presume material constants from load-depth curve of indentation. Mechanical properties of oxide layer of zirconium alloy and irradiated stainless steel will be analyzed. (2) Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM). TEM is capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes or normal SEM. JAEA installed a TEM apparatus (JEOL JEM-2800) in JMTR Hot laboratory. The maximum magnification is 150,000,000 times. It can be operated from a remote location using a computer network. This contributes to the convenience of remote researchers and reducing the amount of exposure.
Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Kino, Koichi*; Furusaka, Michihiro*; Hiraga, Fujio*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Kato, Kiyoshi*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Oshima, Masumi; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1781 - 1784, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.11(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The project of the comprehensive nuclear data research for the development of the advanced reactor systems had been executed successfully by eight organizations from 2005 to 2009. In this project, we constructed the pulsed neutron beamline that was aimed to obtain neutron capture cross-sections of long-lived fission products and minor actinides accurately. The energy spectra, spatial distributions, and pulses of the beam were studied by measurements and simulation calculations, and they were found to be consistent with those of the beamline design. In this paper, we present the overview of the project and the properties of the neutron beam provided by this beam line.
Yonekawa, Minoru; Sozawa, Shizuo; Kato, Yoshiaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2010-049, 18 Pages, 2010/11
The hot laboratory (JMTR-HL) was founded to examine the objects mainly irradiated in the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor), and has been operated since 1971. The JMTR has been stopped from FY2006 for the refurbishment and will be re-started from FY2011. The post irradiation examination for high burn up fuels and large specimen will be carried out in the restarted JMTR. The JMTR-HL plans to put a three dimensional X-ray Computerized Tomography (CT) inspection system in place until the restart of JMTR in order to satisfy the requirement of valuable irradiation data for safety and plant life time management of nuclear power plants in the future. The three dimensional X-ray CT inspection system is able to observe a defect geometry closely and visually compared with a two dimensional system. In this paper, system design, production, installation and performance tests of an X-ray CT inspection system in a hot cell are reported. The X-ray CT inspection system consists of a computed tomography scanner, an X-ray source, a movable sample positioned, an X-ray detector, a collimator, and so on. After installation of apparatus, performance tests using irradiated fuel rods and radioisotopes were carried out to confirm the influence of  rays and transmission X-ray property. By this development of the X-ray CT inspection system, it became possible to provide data with high technical value for post irradiation examination of high burn-up fuels and large type specimens.
rays and transmission X-ray property. By this development of the X-ray CT inspection system, it became possible to provide data with high technical value for post irradiation examination of high burn-up fuels and large type specimens.
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Shigetome, Yoshiaki
JNC TN8200 2001-006, 19 Pages, 2001/12
Global2001 (International Conference: "Back-End of the Fuel Cycle: From Research to Solutions ") was held for six days from September 9 to September 14 in Paris in France. In this year, there were about 420 participants from each country and about 70 people participated from Japan. This conference consisted of the reactor and fuel cycle field, the reprocessing field, the disposal field, and the non-proliferation field, etc. The main topics of this conference were the back end of the nuclear fuel cycle, the management of long-lived nuclide, the advanced concept of reactor and fuels. Advanced fuel recycle technology division reported about the feasibility study on commercialized FR cycle systems, the nuclear fuel and the reprocessing process in the oral session and poster session. Each report was audited and information was collected. It is possible to refer to information on Global2001 by the following homepages. http://www.cea.fr/conferences/global2001 /index.him*
Koyama, Tomozo; ; Omori, Eiichi; ; ; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Shigetome, Yoshiaki
JNC TN8410 99-027, 423 Pages, 1999/12
The bituminization demonstration facility of Tokai Reprocessig Plant had a fire and explosion incident. The cause of the incident was investigated. Also, the facility condition and release of radioactive materials were evaluated. The cause of the fire and subsequent explosion was determined in a two year investigation. The main cause of the fire was that the temperature of the bituminized product rose to an unusually high temperature by a physical heating phenomena inside the extruder, which was caused by the lowering the feed rate of liquid waste. A moderate chemical reaction in the bituminized product continued and consequently the bituminized product overheated and ignited. The cause of the explosion was the accumulation of flammable gases generated from insufficiently extinguished bituminized product in the filling room in which the ventilation system had been shut down. The flammable gas was ignited by another bituminized product that overheated to the flash point temperature. This report details the condition of the facility before and after the incident, cause of the incident, and an evaluated amount of released radioactive materials.
Hayashi, Kimio; Ishihara, Masahiro; Shibata, Taiju; Ishino, Shiori*; Terai, Takayuki*; Ito, Hisayoshi; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Yamawaki, Michio*; Shikama, Tatsuo*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st Information Exchange Meeting on Basic Studies on High-Temperature Engineering, p.41 - 58,268, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
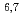 Li(n,d)
Li(n,d)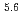 He and
He and 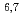 Li(n,t)
Li(n,t)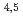 He at 14.1 MeV
He at 14.1 MeVShirato, Shoji*; Shibuya, Shinji*; Hata, Kazuhiro*; Ando, Yoshiaki*; Shibata, Keiichi
JAERI-M 89-107, 27 Pages, 1989/08
no abstracts in English
Yamakawa, Tadashi*; Shibata, Yoshiaki*
JNC TJ7420 2004-002, 63 Pages, 1988/01
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshiaki*; Nagamine, Takashi*
JNC TJ7420 2004-001, 75 Pages, 1988/01
no abstracts in English
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Shibata, Akira; Kato, Yoshiaki; Arai, Kensaku*; Nakata, Kiyotomo*
no journal, ,
In order to investigate the effect of dose rate on SCC growth behavior, the SCC growth tests were carried out under simulated boiling water reactor (BWR) water conditions using irradiated materials at different dose rate. It was confirmed that the effect of dose rate on SCC growth rate was considered to be small.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Shibata, Akira; Kato, Yoshiaki; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Nakano, Junichi; Tsukada, Takashi; Takakura, Kenichi*; Nakata, Kiyotomo*
no journal, ,
SCC growth tests have been carried out using type 304 stainless steel that had been pre-irradiated 0.62 to 9.2dpa under BWR simulated high temperature water condition at 288 C in the JMTR. This paper describes the investigated results of crack growth rate characteristics from the point of view of microstructure, radiation hardening and radiation induced segregation.
C in the JMTR. This paper describes the investigated results of crack growth rate characteristics from the point of view of microstructure, radiation hardening and radiation induced segregation.
Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Kurihara, Toshikazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Noriyuki*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Matsumura, Akira*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Hiraga, Fujio*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru*; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Fukushima, Yoshiaki*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kambara, Wataru; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Akira; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Aoyagi, Tatsuhiko; Ito, Masayasu; Kato, Yoshiaki; Yonekawa, Minoru; Kawamata, Kazuo
no journal, ,
 Tc from irradiated High-density MoO
Tc from irradiated High-density MoO Pellets Solution
Pellets SolutionShibata, Akira; Ishida, Takuya; Shiina, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Masaaki*; Tanase, Masakazu*; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kimura, Akihiro; Ota, Akio*; Yamamoto, Asaki*; Morikawa, Yasumasa*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Tc, a daughter nuclide of
Tc, a daughter nuclide of  Mo, is commonly used as a radiopharmaceutical. In case of Japan, all of
Mo, is commonly used as a radiopharmaceutical. In case of Japan, all of  Mo are imported from foreign countries. R&D for domestic production of
Mo are imported from foreign countries. R&D for domestic production of  Mo by the (n,
Mo by the (n,  ) method has been being performed in JMTR from viewpoints of nuclear proliferation resistance and waste management. In this study, experiments of
) method has been being performed in JMTR from viewpoints of nuclear proliferation resistance and waste management. In this study, experiments of  Mo/
Mo/ Tc production were performed to enhance recovery yields of
Tc production were performed to enhance recovery yields of  Tc. High-density MoO
Tc. High-density MoO pellets were irradiated in the Kyoto University Reactor (KUR). Solvent extraction method with MEK was used to extract
pellets were irradiated in the Kyoto University Reactor (KUR). Solvent extraction method with MEK was used to extract  Tc from
Tc from  Mo/
Mo/ Tc solution and the maximum recovery yields as high as 80% was achieved. Quality tests were performed, and impurities in
Tc solution and the maximum recovery yields as high as 80% was achieved. Quality tests were performed, and impurities in  Tc solution were evaluated and were efficiently low. It is concluded that
Tc solution were evaluated and were efficiently low. It is concluded that  Tc solution produced by this method is suitable for a raw material of radiopharmaceutical.
Tc solution produced by this method is suitable for a raw material of radiopharmaceutical.
 ray emitting nuclides at CPF
ray emitting nuclides at CPFMotoyama, Risa; Hinai, Hiroshi; Ichige, Yoshiaki; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori
no journal, ,
Various properties of radioactive wastes generated at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station have been analyzed at Chemical Processing Facility (CPF) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to contribute to their future treatment and disposal studies. The radioactive concentration of  ray emitting nuclides is one of the essential information as well as those of
ray emitting nuclides is one of the essential information as well as those of  ray and
ray and  ray emitting nuclides. It needs to develop separation and purification methods for each
ray emitting nuclides. It needs to develop separation and purification methods for each  -emitter from unfamiliar mediums to the nuclear fuel cycle field. Due to the restrictions of the facility, these methods should avoid using halogen reagents. The steady analysis procedures of H-3, Sr-90 and I-129 have been already developed and in practice. Among them, the analysis method of I-129 will be presented and the determination method for Se-79 will be reported as issue currently under consideration.
-emitter from unfamiliar mediums to the nuclear fuel cycle field. Due to the restrictions of the facility, these methods should avoid using halogen reagents. The steady analysis procedures of H-3, Sr-90 and I-129 have been already developed and in practice. Among them, the analysis method of I-129 will be presented and the determination method for Se-79 will be reported as issue currently under consideration.